Smartkey launches RFID application driver management solution
[ad_1]
Overview
The system is based on the IC card (driver management IC card) as the mobile data carrier and basic information unit, and uses the handheld IC card POS machine as the method of automatically logging in data and information when the violation is processed. It uses the metropolitan area network (X.25/DDN/ PSTN) backbone, using modern communication methods as the means of network connection, and using the client-server model as the data structure to realize driver IC card management, which will surely greatly promote the modernization of traffic management.
Development background
With the continuous deepening of my country’s reform and opening up and the rapid development of the national economy, the number of motor vehicles is increasing at an unprecedented rate, and urban (regional) traffic management is becoming more and more important.
One of the most complicated and important aspects of traffic management is the management of drivers. However, in recent years, with the rapid expansion of the number of drivers, the complication of road traffic conditions, and the updating and development of vehicle performance and types, traditional management methods have been Can not meet the needs of management work, which requires the traffic management department to use more modern management methods.
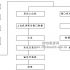
system structure
Hardware composition
computer
Pentium Pro (high-energy Pentium) or higher processor, 64M memory, 4G hard disk. The central maintenance terminal adopts the Pentium 166 model, which can be configured with 32M memory and 2G hard disk.
The internet
Adopt DDN, X.25 or public telephone network, select NOVELL’s NETWARE network operating system or WINDOWS NT AS network operating system.
Read and write equipment
Use handhelds that meet the following standards:
Using 80C32 CPU, can read and write a variety of ISO standard IC cards.
Provide a standard, hot-swappable RS232 interface. It can communicate with the host (uploading and downloading), powered by four AAA batteries, and has an external power consumption interface.
Two-line LCD display (18×2 letters), LED backlight, 16 touch keys.
32K static RAM, provide power-down protection. Replace the battery without losing its content, you can download user order and store detailed records.
Dimensions unit: 130×65×26mm.
Operating temperature: -30°C ~ +70°C.
Smart card selection
The SLE4428 chip with encryption performance has a temperature adaptation range of -30°C ~ +100°C. The capacity of the EEPROM that can be read and written by the user is up to 8KBIT, and the data communication protocol is ISO-7816 standard.
Software composition
The application system consists of the following five parts: file management system, card issuance system, punishment system, banking system, and management system.
File management system
Mainly responsible for the management of the entire system archives (update, maintenance, index, query, statistics, transfer, etc.).
Card Issuing System
Card issuance of existing drivers: The issuance of IC cards of existing drivers adopts the method of recertification, and centralized and unified card issuance.
New driver IC card issuance: the card issuance center will perform the card issuance operation. When the driver’s IC card changes, such as the driver’s basic situation changes, the driver’s location transfer, the driver’s license buckle, and the revocation of the business process are also performed by the above methods, and the card issuing subsystem rewrites the IC card , And send it to the vehicle management office and IC card management system for archiving.
Safety Management of Driver’s IC Card
Penalty system
Log in to the traffic police information: input the traffic police number and segment number to the handheld. If it is a patrol, only enter the traffic alarm number. Then, the hand-held machine automatically confirms the on-duty time.
Illegal registration: When the traffic police handles the violation, first determine whether the vehicle type to be driven is consistent with the vehicle type being driven, etc. If they do not match, the deduction and vehicle deduction will be handled immediately. If they match, insert the driver’s IC card into the handheld processor. Run the following operations:
Read the IC card information, and display and record it on the handheld. IC card information includes: driver’s name, gender, age, driver’s license number, detachment, squadron, unit phone number, driving model, violation record (time, place, vehicle license plate, reason, punishment result) and pre-delivery Fines the remaining amount.
The traffic police refer to the violation code comparison table recorded in the handheld and enter the violation code and vehicle license plate.
The handset verifies the legitimacy of the IC card. First determine whether the IC card is forged, and then check the illegal number database to confirm whether the vehicle license and driver’s license are being tracked for the vehicle and driver’s license (including whether the vehicle has not been punished due to expiration, whether the driver’s license is reported to be lost, and whether the driver’s identity is illegal. Whether to report the loss of the vehicle, whether the vehicle fails the vehicle inspection, etc.). If so, a warning signal occurs.
If the traffic police receives a warning signal, they will immediately make corresponding handling such as deduction, detention, detention, etc.
The handset writes the violation information into the IC card. Violation information includes: violation time, location, vehicle license plate number, violation code, etc.
After the above processing, the traffic police can withdraw the IC card, return it to the driver, and release it.
3 Penalties for violations
The offending driver went to the squadron to accept punishment after logging in. First, insert its IC card into the IC card reader/writer of the squadron to read the driver’s information on the IC card and the violations. Then the system automatically inquires the corresponding laws and regulations, ordinance files, and makes corresponding punishment decisions on the driver. According to the violation date and penalty date recorded on the IC card, it is determined whether the driver accepts the penalty on time, and the penalty score on the driver’s IC card, plus whether the violation score exceeds the prescribed limit, so as to make a corresponding response to the driver. Increase penalties.
If the driver accepts the penalty, he enters his personal password, and the IC card reader/writer will add the corresponding penalty points to the IC card based on the violation, and pay the fine or cash on the IC card in advance, and Corresponding punishment records are made in the squadron files. The squadron will periodically transmit these records up to the server, and then regularly settle with the bank, and transfer the amount of fines paid by the violating driver to the relevant account of the Transportation Bureau from the amount paid in advance. If the driver’s IC card pre-paid fine is not enough to pay the fine, the driver must go to the bank to renew the pre-paid fine.
If the driver refuses to be punished, the squadron will print a penalty notice, and the driver will take the penalty notice to the higher authority for reconsideration.
4 Transmission of Violation Information
After the traffic police are laid off, they connect the handheld penalty machine to the standard interface of the squadron’s microcomputer, transmit the violation records to the squadron, and update the squadron’s violation record files. At the same time, the handset confirms the time of layoff and transmits the traffic police duty status to the squadron. The squadron workstation processes the above data and stores it in the corresponding database.
Banking system
Mainly responsible for opening the driver’s pre-paid fines account and settlement between the same city traffic police detachment.
Each new driver needs to open a prepaid fine account with an IC card in a designated bank and deposit a certain amount in it. The bank writes the amount of prepaid fines into the driver’s IC card through the IC card reader and writer, and records the time and amount of each driver’s prepaid fines for inquiries. The driver can go to the bank to check whether the remaining amount of the fine paid in advance is consistent with his IC card. The bank settles with the Traffic Management Bureau once a month, and transfers the fines paid by the driver to the relevant account of the traffic police detachment.
Management system
The management system is a three-level management of “detachment-brigade-squadron”.
The municipal bureau (detachment) level management includes: business management of the municipal bureau’s order department, business management of the publicity and education division of the municipal bureau, business management of the accident division of the municipal bureau, and expert decision support capabilities.
Squadron-level management includes: penalties for violations, illegal transfers, accident transfers, and duty management.
The various business tasks of this subsystem are coordinated by the archive management subsystem through the network.
The following is a detailed description of all levels of management:
Squadron-level management
data collection. Complete the automatic log-in function of all violation records and send them to the central computer network server of the Municipal Bureau Detachment at regular intervals.
Query stats. This level of management also provides the function of statistically querying violation records and driver conditions. After completing the necessary procedures, the user can perform various types of query statistics on the violation records and the driver’s situation with the help of the file management system. For example: statistically query the traffic police to enforce the law, correct the violations, statistically query the driver’s violations, and statistically query the basic files of the driver.
Illegal transfers. The squadron regularly records the traffic violations handled by the squadron. Use the file management system to classify and index, and follow the records of the detachment, brigade, and squadron to which the driver belongs.
The violation records that are not under the jurisdiction of the detachment are sent upwards to the detachment or the headquarters order office through the network to realize the remote transfer.
Accident transfer. The specific operation process is the same as the illegal transfer.
Duty management. Perform statistical inquiries based on the traffic police on-duty status (including attendance, law enforcement, etc.) recorded by the traffic police handheld. Traffic police officers must be shut down at the time of hand-held login when they are on or off duty, and they are recorded in the service file through the connection between the hand-held machine and the squadron workstation.
This can be used as a basis for traffic police assessment.
2. Team-level management
Driver verification. Drivers regularly go to their detachments and brigade for inspection, insert the IC card into the IC card reader and writer, and each brigade workstation evaluates the driver based on the violation record and penalty points stored on the driver’s IC card. For drivers who have severely violated regulations or whose penalty points on the IC card exceed or are close to the prescribed limit, take corresponding measures such as suspension of their licenses and participation in training. Then initialize the penalty points on the IC card. Enable the driver to start from a new starting point.
Violation statistics. Each brigade regularly accepts violation records sent from their squadrons, sorts and indexes them, counts violation types, time, location, and driver conditions, and prints statistical reports to provide basis for decision-making support and various evaluations.
Accident statistics, ibid.
Duty statistics. According to the duty management files sent by each squadron, the traffic police on duty of each squadron will be statistically sorted. Provide reference for traffic police evaluation.
Traffic safety post responsibility system management. According to the violation records of the drivers in the area under the jurisdiction of each squadron. Evaluate the squadron’s job responsibility system.
3. Municipal Bureau Detachment Level Management
Order business management. Responsible for the functions of saving, querying, reporting and other data sent from each subordinate unit. Provide data, reports, etc. for the business activities of other offices and departments. Its functions mainly include the following aspects:
The overall inspection record of the driver. Obtain the general inspection records from each brigade through the Internet, sort them, and decide whether or not to run the training courses by the publicity and education sciences.
Records of violations (including time, location, circumstances of violation, number of types, punishments, etc.).
Illegal transfer of traffic safety responsibility system. The violation record data that needs to be transferred from each squadron is sent to the brigade and squadron to which the pilot belongs for storage.
After the driver was suspended for violation of the regulations, he returned to the mission department of the brigade to participate in study and duty on duty.
The records of the traffic police concerning the time of on-off and off-duty, attendance, and correction of violations by the police and the corresponding upper limit fines, etc., are used as the basis for traffic police evaluation.
The registration of invalidation of the driver’s old driver’s license is lost. After the driver’s driver’s license is lost, report the loss to the squadron to which it belongs, and the squadron will report the loss to the order office. After the order office records the loss, it will be sent to each squadron and brigade and stored in the illegal code library. When the traffic police downloads the illegal record through the interface, the illegal code library is also uploaded.
Print the report of violation records submitted to the Provincial Bureau Headquarters, etc.
Print the monthly report function required by the Legal Department, etc.
4. Business management functions of the Mission Office
Statistically summarize the violation records and accidents sent by each subordinate unit, take corresponding measures based on the statistical results, and provide a reference for the expert system.
The main functions are:
The monthly information of the offenders in the city, including name, gender, age, and type of offending, and divided by district (county) according to the location of the offender’s unit or address.
Provide information on the offenders accumulatively more than twice a month.
Calculate responsibility system control indicators for violations and accidents based on the number of drivers and employees in each unit.
According to the control index, it will automatically prompt the name, quantity and basic situation of the over-standard unit.
Provide monthly details of over-standard units in each district (county).
Provide each month the number of vehicles to be inspected, the number of drivers, the number of actual inspections, the number of missed audits across months, and the number of missed audits across years.
Provide monthly accident information (according to the scope of responsibility system work), which refers to accidents that have been assigned responsibility, including the name, gender, age, unit, type of accident, and responsibility of the accident person, and it is divided by district (county).
According to the age of the person who violated the rules, the percentage of the violation accident is provided for every five years old, and the peak value of the violation by the age group (five years old) of the person who violated the rules is also provided.
Provide whether the offender is a member.
6. Accident Department Business Management Function
The department is mainly responsible for handling traffic accidents. After accepting the accident, in addition to logging in the driver’s IC card information department, other information processing is completed by the accident department. The accident department first logs the relevant information of the accident. Then the accident punishment system will make corresponding punishment decisions based on the severity of the incident. For drivers who have been punished, or if their responsibilities are unclear, reconsideration or re-determination of responsibilities will be conducted. After handling, the accidents are classified and archived. For future inquiries and statistics. Its functions mainly include:
The registration, classification and requirements of each accident-related situation are compatible with the current traffic accident management system of the Ministry of Public Security.
Automatic transfer and statistics of responsible accidents.
Automatic penalties for drivers who cause accidents.
Management of accident files.
Accident retrieval and query.
Statistical analysis and assessment of accidents by each case-handling unit.
Statistics and appraisal of the work situation of the police handling the case.
Penalty reconsideration and changes in responsibility re-determination.
7. Functions of office business management
It analyzes the data and statistical reports sent by various departments, formulates corresponding countermeasures for problems in traffic management, and makes corresponding amendments to laws and regulations, so as to guide the law enforcement and management of lower-level departments.
For more related systems, please contact us:
Sun Dong (Northern Regional Manager)
Singapore Seamark (Beijing) Branch
Room 514, Moma Building, 199 Chaoyang North Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing
Post Code: 100026
Mobile: 13581807620 QQ: 81920843 MSN: [email protected]
Phone: 010-85982757 / 85989381/85986721
Fax: 010-85982757 / 85989381/85986721 ext. 803
Email: [email protected]
Http://www.smartkey.net
[ad_2]