Based on WiMAX technology and radio frequency module test plan
[ad_1]
1 Introduction to WiMAX
The huge demand for wireless access to the Internet and wireless multimedia data services has promoted the rapid development of wireless communication technology. Broadband communication technology, IP and mobile have become the future development trend.

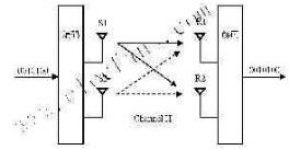
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of MIMO system
2 WiMAX RF module test
2.1 WiMAX transmitter test
Take the power amplifier as an example to illustrate the test of the WiMAX transmitter.
In order to fully measure the performance of WiMAX power amplifiers, in addition to the traditional gain, 1dB compression point and maximum output power, it is often necessary to test the following parameters:

(1) “Burst” output power.
(2) Frequency error. The frequency error can be described by the carrier frequency error relative to the center frequency of the spectrum analyzer (see Figure 2). The frequency error between the transceivers will cause each sub-carrier spectrum to move relative to the receiver FFT frequency, resulting in inter-carrier interference (ICI).
(3) Symbol clock error. Refers to the difference between the reference symbol clock relative to the system sampling clock and the actual measured symbol clock. If the symbol clock is lower than the reference clock, the OFDM signal will be longer than required, causing the sub-carrier spacing to decrease; otherwise, it will cause the sub-carrier spacing to increase. In both cases, inter-carrier interference occurs, deteriorating the EVM performance of the signal.
(4) EVM (Error Vector Magnitude). This is one of the most important test parameters to ensure that the amplifier obtains good signal quality while outputting sufficient power. The result of EVM can be for all carriers, data carriers and pilot carriers.
(5) ACPR (Adjacent Channel Power Ratio). ACPR refers to the ratio of the measured power of the adjacent channel to the power of the main channel, which reflects the interference of the amplifier distortion on the adjacent channel.
(6) Frequency spectrum flatness. Reflecting the power change of the sub-carriers of the WiMAX signal, it measures the deviation of the average power of each sub-carrier from the average power of all sub-carriers.
(7) Spectrum Difference. Measure the power difference of adjacent sub-carriers in the preamble part of the burst.
(8) Spectrum Mask. Measure the “profile” of the transmitter’s emission spectrum to ensure that there is no excessive power emission outside the main channel.
R&S provides a fast and accurate solution for WIMAX power amplifier testing. The test setup is shown in Figure 3, which mainly includes 3 parts:

●Signal source: Using R&S signal source SMU200A or SMJ100A and adding the corresponding option K49, you can easily generate 802.16-2004-OFDM, WIMAX 802.16e OFDMA and WIBRO signals. Among them, SMU200A not only has excellent radio frequency and baseband performance, but also has a powerful fading simulation function, which is more suitable for research and development.
●Spectrum analyzer: R&S FSQ series spectrum analyzer and option R&S FSQ-K92 can support 802.16-2004-OFDM signal analysis; or use R&S FSQ and option FSQ-K93, can support WiMAX 802.16e OFDMA and WIBRO signal analysis; also The R&S FSL series spectrum analyzer and the option R&S FSL-K92 can be selected to support the analysis of 802.16-2004-OFDM signals.
●Free external PC software DemoMeas_WiMAX (can be downloaded from R&S webpage www.rohde-schwarz.com): It controls R&S signal source (SMU200 or SMJ100) and spectrum analyzer (FSQ or FSL) via GPIB or LAN. As shown in Figure 4, the user only needs to select the parameters to be tested in the left column, the software can automatically complete the settings required for the test, and can generate a test report at the same time.

2.2 WiMAX receiver test
In order to test the performance of WiMAX receivers, especially 802.16e, testing in a fading environment is particularly important. SMU200A has a built-in fading simulator, which can simulate a single-channel 40-path or dual-channel 20-path fading environment, and each path can be set with corresponding parameters, such as loss, delay, moving speed, Doppler shift, etc. Currently, SUI (Stanford University Interim) models (SUI1-SUI6) and ITU (International Telecommunication Union) models (OIP-A/B and VA) can be used to perform related WiMAX fading tests. In the fading simulator of SMU200A, SUI and ITU models are predefined, and users can call them directly.
Using traditional test methods to test the performance of MIMO requires two signal sources and corresponding fading simulators. But because SMU200A (or baseband source AMU200A) can provide two completely independent baseband and radio frequency channels, only one instrument is needed to implement MIMO testing. Each signal can simulate 4 fading channels, and provides space-time coding for WiMAX. R&S’s single instrument solution not only saves space and cost, but also provides convenient settings and accurate accuracy for the synchronization and synthesis of two signals and fading channels. In addition, the intuitive operation interface greatly facilitates operation (see Figure 5).

3 WiMAX radio frequency conformance test
3.1 Introduction to WiMAX RF Conformance Certification Test
The goal of the WiMAX Forum is to transform the IEEE802.16 standard into practical applications. It is an industry association composed of manufacturers and network operators, dealing with all relevant aspects of WiMAX except for the purely technical IEEE standards. Product certification of WiMAX base stations and terminals is an important task of the forum. Its goal is to ensure the global availability and reliability of WiMAX services. A related certification work group CWG is responsible for the following related tasks: define certification and testing processes; list the required test cases; select test institutions; select conformance test systems, etc.
WiMAX products need to be tested to meet three conditions, namely, protocol conformance, radio frequency conformance, and interoperability. For the last condition, products from different manufacturers need to be tested for interoperability and performance evaluation in a test network. The first two test conditions require a special test system. WiMAX related test specifications are formulated by the Technical Working Group (TWG). One of the important radio frequency conformance test specifications RCT (Radio Conformance Test Specification) specifies the baseband and radio frequency signal test procedures and test conditions of the transceiver for testing. The degree of consistency between the radio interface and the WiMAX specification.
According to WiMAX parameters, radio frequency testing mainly evaluates and verifies the key indicators and performance of the physical layer of WiMAX technology. It is generally distinguished from the base station side and the terminal side, and the transmitter and receiver are tested on each side. Specifically, the core content of RF parameter testing usually includes receiver sensitivity, CP value and frame timing; transmitter cyclic prefix and symbol timing, modulation and coding, spectrum flatness, power control, relative constellation error, and frequency spectrum Templates and other content. It should be noted that the RF parameter test should not only refer to the requirements of the WiMAX certification RCT document, but also the specific regional indicators such as the power requirements and spurious of the transmitter, but also need to comply with the regulations of the radio management department in the region, that is, generally speaking. To pass the frequency approved test.
The test indicators for the receiver test include receiver sensitivity and dynamic range; the test indicators for the transmitter test include open-loop output power range, closed-loop power control range, maximum RF output power, minimum controlled output power, and standby output power , DRC channel output power, ACK channel output power, data channel output power, transmitter conductive spurious emissions, modulation performance, etc.; finally, it also includes terminal throughput performance testing, including uplink and downlink throughput testing.
3.2 R&S TS8970 WiMAX RF conformance certification test system
WiMAX Forum has selected R&S’s TS8970 test system as the radio frequency conformance test system for the IEEE802.16e-2005 mobile WiMAX standard (see Figure 6). At the WiMAX conference in South Korea and Vienna in May 2006, R&S launched this system for the first time. Along with the ongoing test standardization work of the WiMAX Forum, R&S is also implementing all necessary test cases on the TS8970 system.

The R&S TS8970 system is based on R&S’s high-end instruments. It uses the signal source SMU200A and its option SMx-K49 as the signal generation part, and the signal analyzer FSQ and its option FSQ-K93 as the signal analysis part. Make the connection part adopt an OEM base station and terminal emulator. At the same time, there is a fully automatic radio frequency switch matrix with a frequency of 6GHz, which can ensure the signal conversion path required by each test case between the test system and the DUT.
Like the authentication system for R&S TS895x 2G and 3G mobile communications, the R&S TS8970 system uses reliable RS-PASS control software. Because of its modular and standard-independent structure, the entire software can be quickly implemented in TS8970. Some system-specific applications, such as fully automatic RF path calibration compensation, system self-checking procedures and all management and control procedures (such as version browser, test case and test sequence editor, test parameter and result management), can all be Use directly, no need to change. In addition, some test cases specified by the original WiMAX can be developed using some basic RS-PASS procedures. Moreover, R&S TS8970 is the first test system that uses all Ethernet control.
4 WiMAX terminal wireless tester CMW270
In terms of production testing, R&S recently launched the WiMAX802.16e terminal wireless tester CMW270, which integrates non-signaling test and signaling test, which can satisfy users in non-signaling mode measurement, signaling mode measurement and functional verification, calibration, Service and quality assurance requirements in various WiMAX test areas (see Figure 7).

Figure 7 WiMAX terminal wireless tester CMW270 WiMAX products need to be tested to meet three conditions, namely protocol consistency, radio frequency consistency and interoperability. For the last condition, products from different manufacturers need to be tested for interoperability and performance evaluation in a test network. The first two test conditions require a special test system. WiMAX related test specifications are formulated by the Technical Working Group (TWG). One of the important radio frequency conformance test specifications RCT (Radio Conformance Test Specification) specifies the baseband and radio frequency signal test procedures and test conditions of the transceiver for testing. The degree of consistency between the radio interface and the WiMAX specification.
For radio frequency measurement in non-signaling mode, CMW270 can provide fast transmitter measurement, test transmitter burst power, adjacent channel power ACP, EVM and IQ unbalance and other modulation indicators, center frequency error, spectrum flatness , Spectrum performance such as spectrum spurious template. And built-in ARB signal source for receiver measurement, test the receiver sensitivity and maximum input level and other indicators under the condition of maintaining a certain PER or BER. In addition, CMW270 has a built-in general RF signal source and RF power meter, which can complete general measurement functions such as external RF cable calibration.
For RF verification in signaling mode, CMW270 can provide real-time signaling, which can be used as a base station simulator. At this time, the WiMAX terminal can operate as in an actual WiMAX network, modify some necessary transmission parameters, and simulate various complex test scenarios for testing. For example, measuring the carrier-to-interference and noise signal ratio CINR and received signal strength indicator RSSI and other indicators, as well as the verification of physical layer and MAC layer functions such as power-on search and power control.
For applications such as quality assurance and service, users can also perform manual operations through an external monitor, mouse, and keyboard to complete all the settings and measurements of the instrument.
Due to the ability of real-time signaling simulation, CMW270 can test terminals of different chip manufacturers without the need for special test mode interfaces, which greatly reduces the test time and complexity of the test system. Due to the small size of the instrument, CMW270 can be easily integrated into the production line, and can be remotely controlled via LAN, IEC/IEEE bus or USB2.0 interface.
The frequency range of CMW270 is from 100MHz to 6GHz, and it has high signal quality and accuracy, including various modulation methods such as QPSK and QAM, and various channel coding methods from 1/2, 2/3 to 3/4, which can meet the current WiMAX requirements. Various requirements of the standard.
Furthermore, CMW270 adopts a modular platform structure, which can easily adapt to the upgrade of the IEEE802.16e standard in the future. The internal measurement and signaling functions are completed by the programmable logic device FPGA and digital signal processor DSP, which can be easily upgraded through firmware upgrades to adapt to changes in standards.
CMW270 also provides the function of application testing, which tests the data throughput by sending and receiving TCP/IP data packets (data or voice) from an external PC in various test scenarios.
Due to its fast measurement capability, high accuracy and future-oriented platform design concept, R&S CMW270 provides users with a high-performance, low-cost test solution for WiMAX mobile terminals.
5 WiMAX wireless coverage test system TSMW
After completing the WiMAX network deployment, it is necessary to measure the WiMAX network coverage and test the interference existing in the network planning. Combined with WiMAX terminals, the network QoS can also be tested in the existing network. R&S uses TSMW network scanner for 802.16e to perform network coverage measurement and interference analysis. Through the control of the Romes drive test software, it is possible to analyze the coverage measurement of the cell for the ID Cell and PA Index. Output the coverage quality (CINR) and coverage level (RSSI) parameters of the Preamble. At the same time, TSMW can also measure the multipath of each ID Cell, so that the output result not only includes the combined power of all multipaths, but also provides RSSI and CINR for each multipath. Since TSMW can measure all cells in each segment, this function can be used to achieve frequency optimization after the network.
TSMW itself is set up as an independent dual-port receiver, and a single channel has a bandwidth of 20MHz. Therefore, support for MIMO was considered at the early stage of device development (see Figure 8). Its frequency range can reach 6GHz, meeting all frequency band requirements, built-in 12-channel high-sensitivity GPS receiver, can realize the perfect combination of measurement and GSS system. It is particularly outstanding in terms of radio frequency performance. The built-in preselector can improve the interference suppression of the receiving system and the dynamic range of the instrument itself. The noise figure is extremely low, which greatly improves the noise floor index of the instrument. And the direct acquisition of the provided IQ data also makes it possible to analyze some non-standard signals in the development stage.
6 Summary
In the product development stage, the powerful functions and outstanding performance of R&S WiMAX radio frequency instruments ensure that manufacturers can verify their radio frequency modules and components in a timely and accurate manner; in the product certification stage, R&S uses its leading position in the mobile communication conformance certification test, First to provide TS8970 to meet the requirements of WiMAX radio frequency conformance test; in the production test stage, R&S has a production test solution that integrates WiMAX signaling and non-signaling modes-WiMAX terminal wireless tester CMW270, thus Provides a full range of test solutions from R&D, certification to production.
[ad_2]