RFID automotive manufacturing industry system solutions
[ad_1]
1. Project background
At present, the degree of informatization in the automotive industry is uneven. Some are highly informatized, some are just in their infancy, and some even still use a completely manual method of recording. However, all enterprises hope to establish an identification system to help the management of the entire enterprise reach a certain level, the efficiency of the entire logistics link can be improved, and the error rate can be reduced. Although most companies have established their own ERP systems, each company has its own information system. The situation of information islands is serious and the degree of informatization is seriously inconsistent. The informatization status of our domestic enterprises is particularly backward. However, each enterprise’s investment in information construction is long-term, and the urgency for the establishment of the identification system is very strong.
The auto parts industry is an important part of the auto industry and the basis for ensuring the long-term stable development of the auto industry. After several years of development, the auto parts supporting market has reached 200 billion yuan, and the maintenance market has reached 60 billion yuan. Not only has a certain economic scale been formed, but the quality of automobiles has also been greatly improved. Driven by the localization of automobiles, auto parts has initially formed a relatively complete and mature parts matching system.

2. Program overview
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a rapid identification technology that has developed rapidly in recent years. It obtains information through non-contact identification of identified objects. Compared with traditional barcode technology, it has large data capacity, non-contact identification, and long storage time. , Pollution resistance, adapt to harsh environments and other characteristics, are widely used in various industries.
Compared with other industries, automakers and component suppliers face greater pressure: on the one hand, they need to continuously reduce costs; on the other hand, they must ensure that their products meet the industry’s particularly strict quality standards. In recent years, automakers have spent a lot of their IT budgets on supply chain management systems in order to achieve a transparent and flexible supply chain. The role of RFID technology in material and product tracking will have a positive impact on the automotive supply chain. By deploying the RFID system, the visualized management of the supply chain process and the distributed control of the manufacturing process can be realized.
A typical RFID automatic identification system consists of the following parts: data carrier, read/write unit and interface module. The interface module is connected to PLC, PC and other control units by bus or serial communication.
Three, system design
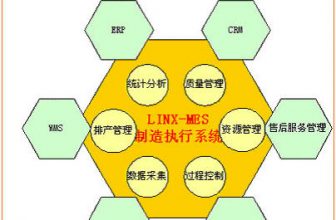
Establish a unified central database on the site of the enterprise workshop as an information platform for the circulation of goods to facilitate overall standardized management. In the industrial link, RFID technology is used to assign an identification number (ID) to each work-in-process component, which is the name of the component in the information network. Through RFID technology, the production status and inventory status are mapped to the information network and registered in the In the field center database, it is transmitted to the information system (such as ERP, MRP), etc.
Fourth, the system operation process
The application of RFID in the automotive industry system mainly includes vehicle body identification and tracking management, tracking management of parts and fixed assets, logistics management of the entire vehicle, etc.:
4.1 Car body tracking and recognition in vehicle production
The vehicle body recognition system (AVI) mainly refers to the real-time collection of production data, quality monitoring data and other information on various production lines of automobiles, and transmits them to material management, production scheduling, quality assurance and other related departments to better realize the supply of raw materials , Production scheduling, sales service, quality monitoring, and lifelong quality tracking of the entire vehicle. Before the application of RFID technology, the main storage car body information was bar codes. The advantages of using bar code recognition methods are flexible configuration and lower system cost. However, because the body information is stored in the PLC or PMC database, the speed and reliability of network communication are very high, requiring high-performance PLC, large-capacity database and high-speed PMC host.
After the RFID system is adopted, the electronic tag is generally placed on the sliding skid carrying the car body, and runs with the workpiece from beginning to end, forming a data that moves with the car body, becoming a “smart car body” that carries the database with you throughout the production process. . According to the process and production management needs, readers/writers can be installed at the entrances and exits of the paint shop, the fork of the workpiece logistics, and the entrances of important processes (such as spray booths, drying rooms, storage areas, etc.). The reading/writing station is mainly composed of a workpiece position detection switch, a label reading/writing device, a communication interface module and a man-machine interface. The basic process is: After the detection switch detects the car body in-position signal, the read/write device automatically reads the data stored in the tag installed on the skid, and sends the data to the PLC and displays it on the man-machine interface; It is uploaded to the workshop production process monitoring system PMC through PLC for further processing and calculation, so as to realize the tracking of the whole workshop workpiece logistics and production process control. The use of RFID technology on the production line does not require all the read/write devices to communicate with the main database, so the failure of communication with the main database will not cause production to stop. After the station, data can be written to the tag. Therefore, the application of RFID in the vehicle body identification system is also increasing.
4.2 Tracking management of parts and assets
Automobiles are composed of a large number of parts and components, and good parts tracking management can improve the level of logistics management and quality management. The current part tracking is mainly through two methods, one is that the label is attached to the part itself, which is called a hard link. A typical example is the use of RFID for tire tracking management. Such parts generally have the characteristics of high value, safety requirements and easy confusion between parts. The use of RFID can effectively identify and track parts. The second is to affix the label to the package or shipping rack of the part. The latter can reduce the cost of using RFID. However, it is necessary to maintain a link on the database between the tagged RFID container and the parts in the container. This method is called soft link or soft tracking.
4.3 Vehicle logistics management
The vehicle intelligent electronic tag is written in the RFID tag, which can realize the information management of vehicle logistics and help solve the problems of vehicle production, inventory management, and sales management. The vehicle identification number (VIN) is the ID card in the circulation of vehicles. This identification number can be written into the RFID tag embedded in the car to realize the management of the car’s electronic digital license plate. By reading the stored information of the vehicle’s smart electronic tags, the accuracy and work efficiency of vehicle information are greatly improved, and problems in automobile after-sales service, product tracking, and quality traceability are solved.
4.4 Application in the entire process of the automotive supply chain
RFID technology is breaking through the limitations in the factory and realizing its application in the entire process of the automotive supply chain. Toyota Motor is planning to establish such a system to track the entire process of the vehicle supply chain. In the first stage, they used reusable tags to monitor the vehicles in the assembly shop. In the second stage, they used disposable paper RFID tags to track parts and vehicles, and realized the vehicle’s monitoring in their distribution centers. Tracking management. In the third stage, Toyota is planning to use RFID in the retail sector. RFID will be permanently retained on the car and used throughout its life cycle. The information on RFID will include customer information and original production data.
In addition, RFID can also be used as an anti-counterfeiting mark for parts, such as implanting electronic tags on tires, engines, airbags, transmission shafts and other parts, using its encryption and automatic identification functions to distinguish counterfeit parts and protect consumers Legal rights. We are also trying to use RFID to manage vehicle compressed natural gas vehicle cylinders, attach RFID tags to the cylinders, and store information about the cylinder manufacturer, cylinder time, filling times, etc. on the tags, monitor the use of the cylinders, and take back the expired in time. Cylinders reduce the potential hazards in the use link.
4.5 Implementation benefits
4.5.1 Error prevention management
The application of radio frequency technology on the assembly line to produce as many customized cars as possible is based on the requirements of the user. The user can choose the color and engine of the car from tens of thousands of internal and external options. Models and tire styles are also required. In this way, the automobile assembly line has to assemble hundreds of styles of cars. Without a highly organized and complex control system, it is difficult to complete such a complex task. Equipped with an RFID system on the assembly line, using reusable radio frequency tags, the radio frequency tags can carry all the requirements required by the car in detail, and there are readers at each work point, which can ensure that the car is The assembly task can be completed without error at each assembly line position.
4.5.2 Warehouse Management
Spare parts management: establish complete supplier delivery quality records and batch information: each supplier can carry out label records for the parts that each supplier enters the enterprise according to the electronic version, and understand its model, type, batch, production date, etc., Carry out warehouse-in and out-warehouse management.
4.5.3 Real-time monitoring of the production line
RFID tracking management is carried out for the entire production process from the product entering the assembly workshop to the final inspection of the vehicle.
4.5.4 Cost control
Use modern logistics theory to improve the storage of auto parts and complete vehicles, save costs, and save the waste of production and temporary inventory in each workshop of the enterprise.
4.5.5 Product traceability
my country has formally implemented the automobile recall system, which puts forward higher requirements for product traceability. Product traceability requires detailed production site records, including all aspects of production, quality, and materials.
According to the RFID tag information, the production and manufacturing information of each key station in the assembly workshop of the car can be inquired in real time, such as production time, operator, inspector, batch, serial number, quality data, process data, test data, etc., and understand Information about the manufacturing process, such as repair and processing results.
According to the RFID tag information, you can query the quality information of the car at important stations, including defect data and measurement data, as well as various data such as the process capability of the station;
According to the RFID tag information, the quality information of the important parts and safety parts of the car, the information of the manufacturer of the main parts, the specific details of the installation and other related information can be traced;
According to product information, it can be traced back to product batches and key component batches to find out other products of the same batch; upwards can be traced to materials and components, and downwards can be traced to end users.
4.5.6 Defect management
The whole vehicle production is mainly assembled and involves a large number of parts (including in-house self-made parts and outsourced parts). Various defects will inevitably occur during the assembly process. Some of them come from parts, some are produced in this process, and there are also previous processes. produced. In order to improve the quality and reduce the repair rate, it is necessary to monitor the defects of each car in real time, record them in real time, and take timely measures.
[ad_2]