The application scheme of RFID in discrete manufacturing production control system
[ad_1]
1 Introduction
In the next few years, the scale of the RFID market in Mainland China will maintain steady growth. It is conservatively estimated that its market size will reach 4.08 billion yuan in 2010, and the hardware, software and service markets will reach 2.37 billion, 1.05 billion and 660 million yuan respectively. Among them, there will be a leapfrog development in 2008. The market size that year will reach 3.05 billion yuan, and the hardware, software and service markets will reach 1.89 billion, 740 million and 420 million yuan respectively. On June 9, 2006, 15 ministries and commissions in my country jointly issued the “China Radio Frequency Identification RFID Technology Policy White Paper”, marking that my country’s RFID development has entered a new era. According to the forecast of the Shuimu Tsinghua Research Center, the total demand for RFID tags in China will reach 5.5 billion in 2010. Large-scale events such as the 2008 Olympic Games and the 2010 World Expo will generate great market demand for RFID. In addition to the application of electronic tickets, security and anti-counterfeiting, the food for the 2008 Beijing Olympics will also be managed through electronic tags. In the manufacturing industry, quality control, batch tracking, product recall, accurate and transparent inventory management, labor and material costs. RFID has good applications in areas such as asset utilization outsourcing manufacturing management and supplier management.
2 Industry characteristics and information control characteristics of discrete manufacturing companies
2.1 Industry characteristics of discrete manufacturing
The production process of discrete manufacturing enterprise products is usually broken down into many processing tasks to complete. Each task requires only a small part of the company’s capabilities and resources. Such as machining, electronic component manufacturing, automobiles, household appliances, medical equipment, ceramic products, toy production, etc.
It has the following industry characteristics:
(1) Product structure. The product of a discrete manufacturing company consists of a fixed number of parts, and its product structure can be described by the concept of a tree. The final product must be composed of a fixed number of parts or components. These relationships are very clear and fixed.
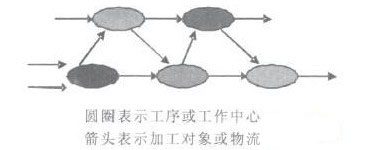
(2) Process flow. Order-oriented discrete manufacturing is characterized by multiple varieties and small batches. Therefore, the layout of production equipment is not arranged according to products but according to processes, for example. Arrange the position of the machine tool according to turning, grinding, planing, and milling. The process of each product may be different, and there are multiple machine tools that can perform the same processing technology. Therefore, the processed materials need to be dispatched, and the intermediate products need to be transported. Discrete manufacturing for mass production of stocks, such as the automobile industry, arranges production equipment according to technological processes. As shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Discrete enterprise production process
(3) Material storage. The raw materials of discrete industrial enterprises are mainly solid, and the products are also in solid shape. Therefore, storage is mostly indoor warehouses or outdoor open-air warehouses.
(4) The level of automation. Since discrete manufacturing enterprises are discrete processing, the quality and productivity of their products largely depend on the technical level of workers. Automation is mainly at the unit level, such as CNC machine tools and flexible manufacturing systems. Therefore, discrete manufacturing is also a personnel-intensive industry. , The level of automation is relatively low.
(5) Production plan management. A typical discrete manufacturing company is mainly engaged in single-piece, small-batch production, and the process of the product is often changed. Therefore, a good plan is required. Discrete industry mainly organizes production according to orders. Because it is difficult to predict when the order will arrive, the planning of the procurement and production workshop requires a good production planning system, especially the computer to participate in the work of the planning system. As long as the plan is appropriate, the benefits of the plan are quite high in discrete manufacturing.
2.2 Information control characteristics of discrete manufacturing enterprises
In terms of information control, it is reflected in the large amount of information, many types of information, complex relationships between information, and difficulty in describing transaction processing rules. Therefore, its business operation information model is the most complex, difficult and challenging in all industries, and it needs to be considered from a technical and management perspective. Mainly manifested as:
(1) Production plan: ① There are many factors that affect the plan, and the information form is complex; ② The capacity requirements are mixed and difficult to predict.
(2) Production process control: ① There are many production tasks, and it is very difficult to control the production process; ② There are many production data, and the workload of data collection, maintenance and retrieval is heavy; ③ The workflow passes through different processing workshops according to the different specific products. Because each production task has different requirements for the ability of the same workshop, the workflow often appears unbalanced; ④Due to the variety of products and many non-standard products, the equipment and workers must have sufficient flexibility to adapt; ⑤ Normally , The processing cycle of a product is long, and the queue time for each job in front of the work center is very long, which causes delays in processing time and increases in inventory of products.
3 RFIDApplication in Production Control System of Discrete Manufacturing Enterprise
3.1 Bottlenecks in the production control system of traditional discrete manufacturing enterprises
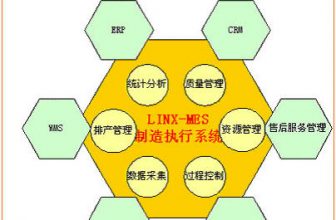
Judging from the current situation, the management information system represented by ERP strives to meet the needs of the upper management of the enterprise, while the process control technology represented by PCS is used to achieve effective on-site control. However, despite the two types of systems The promotion has achieved certain results, but it ignores the effective cooperation between the two, leading to the lack of effective real-time information support for the upper management of the enterprise, and the lack of optimized scheduling and coordination in the lower control links. This creates the phenomenon of information islands and faults. In discrete enterprises, the manufacturing execution system MES builds a bridge between the management plan management and the underlying control, filling the gap between the two. In fact, MES occupies an important position in the three-tier enterprise architecture , Mainly in:
(1) MES can refine and decompose the production management information from the ERP software, and pass the operation instructions from the planning layer to the bottom control layer;
(2) MES can collect the status data of the production process to monitor the status of the production process in real time, and then through analysis, calculation and processing, and timely feedback of the production status to the planning layer.
The question is: what technologies and methods are suitable for building this kind of bridge? For the MES connected with ERP, the data collection subsystem mainly completes the network configuration of the equipment, the communication interface (protocol) setting, the definition of the collection parameters, the collection of data, and the storage of the collected data in the database in a certain format Medium; and can be identified and processed by ERP. And these so-called data acquisition subsystems mainly rely on such as bar code technology, RFID technology and other analog-to-digital and digital-to-digital conversion technologies.
3.2 Application advantages of RFID
Due to the variety of products in the production line of discrete enterprises and the complex process flow, it also determines that it is difficult for enterprises to effectively and continuously monitor the logistics and personnel flow on the production line, and it is difficult to obtain corresponding information. With the decline of production costs and the continuous enhancement of performance, RFID as an identification technology has begun to be widely used in production lines as a means of monitoring product production. my country has listed “The Application of RFID Technology in the Production Line of Discrete Manufacturing” as one of the major projects of the 2006 863 Program “Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology and Application” in the field of advanced manufacturing technology. In general, the current application research of RFID technology is entering the core of the manufacturing process from the supply chain. Compared with other automatic identification technologies (such as barcodes, etc.), the advantage of RFID technology is that it can find, track, monitor or count items faster and more accurately. RFID tags can be affixed to almost any physical objects, such as: items (luggage, clothing, televisions, computers, pets, etc.); cargo boxes or pallets; transportation tools (such as trucks); company employees, etc. Using the writing function of the RFID radio frequency card, the product marking, processing level, quality data and technical requirements can be recorded in the radio frequency label, and necessary modifications can be made to it. In this way, data streams can be established in different positions, and the burden on the control system can be reduced accordingly. On the other hand, the use of RFID technology can correspondingly reduce manual intervention, optimize the configuration of product lines, and provide strong support for enterprise information integration and decision-making.
The current strategy adopted by the existing RFID application architecture is to gradually adopt RFID technology in the factory floor, and IT support providers can obtain information from it and pass it on to the existing, verified and industrially powerful control system infrastructure, and configure RFID Functional supply chain coordination.Domestic companies have made beneficial attempts in the application of RFID technology. For example, Qingdao Haier’s refrigerator production line uses industrial grade
The reader is used to collect product information, and the RFID reader product is also used in the production line of Tianjin Toyota Motor Corporation’s Crown car for management.
3.3 RFIDApplication in production control system
The application of RFID technology in the manufacturing process can complete the operation of automated production lines, realize the identification and tracking of raw materials, parts, semi-finished products and finished products on the entire production line, reduce manual identification costs and error rates, and improve efficiency and benefits. Especially on the assembly line that adopts the JIT (Just-in-Time) production method, the raw materials and parts must be delivered to the work station on time. After the use of RFID technology, it is possible to quickly and accurately find the raw materials and parts required by the workstation from a wide range of inventory by identifying electronic tags. RFID technology can also help managers send replenishment information in a timely manner based on the production schedule, achieve a balanced and stable production line, and also strengthen quality control and tracking.
RFID technology can be used to monitor the production process on the production lines of sanitary ware manufacturers. For example, through the material trolley, tooling pallet support, when all products are completed and put into the warehouse, the forklift, production line, packaging table/product transportation line and other locations are used for data collection. Such an approach can achieve repeated use under closed-loop conditions. However, the interface problems between different devices and application systems, how to process and utilize a large amount of complex RFID data, how to seamlessly integrate the RFID system with the existing information system, etc. are all urgently to be solved. The way to solve these problems is to build and deploy a set of RFID middleware. Connecting the RFID system with the existing back-end system through the interface provided by the middleware is the best way to solve how to integrate the RFID technology into the existing system. Middleware can solve the problems caused by the inconsistency of existing standards. Using middleware, the data received by the front-end reader can be converted into a data format that meets the requirements of the back-end equipment, which can bring great flexibility to users sex. Many RFID middleware systems have hook technology to connect to the operation monitor, and users can monitor the tags used in real time. At the same time, middleware also has the ability to connect readers and databases.
4 Application examples in the bathroom industry
4.1 Company profile
XX Company, located in Haizhu District, Guangzhou, was established in Guangzhou in 1996. After 11 years of rapid development, the company has grown from more than 100 employees at the beginning of its establishment to 2,500 employees and a production area of more than 180,000 square meters. A super-large modern enterprise integrating production and sales. It has ten major production departments, including electronics, hardware molds and stamping, plastic molds, injection molding, machining, massage bathtubs, and steam room production. The company now has a four-question factory, introducing advanced Italian production lines and production equipment, and realizing RFID configuration and product assembly information control on the product assembly line. System control process: activation of reusable RFID electronic billboard tags (accessory materials for product manufacturing process), real-time information collection on the production site (electronic probe), control information feedback (LED display, buzzer), generation of external tags, confirmation of storage, and collection and collection Sleep label. The management function of the system includes analysis of the completion of production orders; analysis of daily production plan progress; online material distribution management; daily cost analysis, etc.
4.2 System Features
(1) The application of RFID technology in the sanitary ware production industry realizes the whole-process tracking during the production and storage of sanitary appliances.
(2) RFID technology is applied in the bathroom production control process to obtain real-time, efficient and accurate product data, and real-time statistical analysis of product status information.
(3) ApplicationRFIDTechnology, real-time monitoring of the production status, production quality and the specific location of the product during the production process.
4.3 Application benefit analysis
After the application of this system, XX company can reduce procurement costs by 5%, increase direct labor productivity by 5%, reduce indirect labor costs by 20%, reduce inventory by 20%, and reduce production costs by 5%. It is expected to directly generate economic benefits of 1,000 per year. More than ten thousand yuan. See Table 1 for details.
Table 1 Estimated economic benefits of ×× company

5 Conclusion
The characteristics of the production control system of discrete manufacturing enterprises show that the use ofRFIDTechnology will fundamentally improve the management level of item flow monitoring and dynamic coordination in the production process. The RFID technology system is suitable for the production process control application of most discrete production enterprises (such as the bathroom industry). It can not only improve the production efficiency of the enterprise, but also reduce the production cost and improve the competitiveness of the enterprise. It has high practical value and has Very good market prospects.
[ad_2]