Library Management System Solution
[ad_1]
I. Introduction
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses wireless transmission to realize non-contact identification of people or objects and data information exchange. It is a brand-new automation technology that can be applied to book management and circulation.
In library applications, RFID tags can store a unique identification symbol for a book or a CD, and can use this symbol for fast and efficient circulation processing and inventory management. The RFID library system is based on RFID technology, and uses RFID middleware as the medium to realize the organic combination of advanced RFID technology and book management methods. It organically combines advanced RFID technology with the book management system, effectively improving the book management Efficiency, simplifies the process of library management, and reduces the labor intensity of library managers.
According to incomplete statistics, 2% of libraries in the United States have installed RFID technology, and 8% of libraries in the world have begun to use RFID technology. In Asia, RFID systems have been put into use in Singapore, Thailand, Taiwan, and the mainland. Globally, the number of libraries using RFID is increasing at a rate of 30% per year.
2. System function
Using RFID technology to identify, track, and protect all library materials, it can realize the functions of self-borrowing, returning, ordering, searching, and inventory of books.
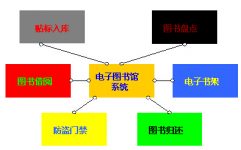
Three, system composition
The entire system includes: label initialization conversion system, self-service borrowing system, self-service book return system, counter service system, handheld device query inventory system, security access control and anti-theft system.

Figure 1: The composition of the intelligent library management system
The system is an efficient library management system based on the application of RFID technology with many automatic operation functions. it includes:
1. Related hardware, such as RFID tags, long/short-distance RFID readers, removable industrial-grade PDAs, etc.;
2. Optimize the firmware protocol to enable high-speed wireless communication between hardware devices;
3. Supporting software and database management technology to meet any specific book file management organization.
The following figure is an overall view of library management based on RFID technology applied to a large library.

Figure 2: The effect of intelligent library management
Four, management process
As long as six simple steps, the daily business of using the system library can be greatly simplified. This process is also shown in Figure 2.
1. Labeling
The label of the library management system is in full compliance with the ISO15693 standard. The following figure shows a label specially designed for library book management. A thin 45mm x 45mm label, encapsulated in a strong, tear-proof plastic, will not be damaged even if the book is dropped, handled or soaked. Using a long-distance reader, the reading and writing distance of a 45mm x 45mm tag is about 0.9m. The label is usually affixed to the back cover of the book. In addition to the above tags, RFID tags of other sizes and brands can also be used, as long as they comply with the ISO15693, ISO14443 standards or the I-Code 1 coding standard.

Figure 3: Labeling Figure 4: RFID label
For audio-visual materials such as CDs and DVDs, labels with special shapes and materials need to be designed and used.
Different tags have different data transmission efficiencies, leading to different ranges of tag read and write operations. So pay special attention to the choice of RFID tags.

Figure 5: Smart Bookshelf
2. Bookshelf management and book inventory
Figure 5 shows the smart bookshelf management system, which cleans up and locates a forgotten book. Special customized RFID antennas are installed on the sides of each layer of a bookshelf. Through the multiplexer, the antenna cable is connected to a very important LR (Long Range) RFID reader that can dispatch the book inventory task. Using time-sharing processing mechanism, and with the help of antenna multiplexer, LR-RFID reader reads the RFID information of each shelf. The data (IDs) collected in each layer are sent to the PC, and the current data information is updated and displayed.
Figure 6 shows a cost-effective bibliographic management system suitable for general library collections. The librarian is equipped with a handheld RFID reader with a shovel antenna. The shovel antenna is a specially designed antenna for reading RFID tags from the side. Scanning the shovel antenna from left to right and from top to bottom can read all book information and store it on the handheld RFID reader. When the handheld RFID reader is brought back, the data can be easily downloaded to a personal computer to generate display and tracking information. It shows high efficiency in the inventory work of books.

Figure 6: Small smart bookshelf and shovel antenna
3. Self-service borrowing
Figure 7 shows the self-service lending system. The reader places the RFID library card in the SR (short-range) card reader, and reads the borrower’s detailed information from the card. The books to be lent or returned are stacked on the MR (medium range) reader, and the MR reader obtains the IDs (numbers) of all the stacked books. Subsequently, the obtained borrower number and book number are sent to the background processing terminal for storage records.

Figure 7: Self-service lending terminal system
4. Counter service
Counter services are also equipped with RFID readers, so that readers can register at the self-service counter smoothly at the counter. Normally, counter operations should be minimized. Currently, at the National Library of Singapore, counter services have been reduced to one-person operations. In fact, most of the counter service functions are to solve readers’ needs and provide readers with high-level services, rather than helping readers complete simple registration operations.
The counter can also be used as a backup for daily station (borrowing station, book returning station) failure, it can monitor the working conditions of each station (borrowing station, book returning station, sorting station, etc.) and remotely control them through the network.

Figure 8: USb interface handheld reader for counter service
5. Anti-theft access control

Figure 9: Multi-channel access control system
Figure 9 shows a multi-channel access control system. Several doors are connected to a long-distance reader through a 1 input/16 output antenna converter. The antenna system on the door is specially designed to ensure that books with RFID tags can be successfully identified in any direction.
In addition, the access control system uses the EAS anti-theft function. Unauthorized library collections or books and materials that have forgotten to borrow and register will be taken away from the library, which will trigger an alarm. In addition to the sound and light alarms, the camera system will also be triggered, which greatly provides Access security performance.
The access control system can also be used to collect information about visitors or borrowers and record the time they pass. If the output port of the remote RFID reader is connected to a PC terminal that is properly equipped with database tools, visitor statistics, such as peak hours, book volume, and visitor or borrower frequency, can be easily generated.
If 16 gate antennas are connected to the 16 output terminals of the 1 input/16 output antenna multiplexer, then a system with a maximum of 15 entrances and exits will be designed. However, not all library management systems require so many entrances and exits. A single channel access control does not require an antenna multiplexer, and only contains a simple signal splitter and compensator to ensure that it can be identified in all directions.
6. Self-service book return
As shown in Figure 10 below, the book return equipment is usually placed outside the library, allowing books to be returned after the library is closed. The books to be returned are simply placed in the return slot, and the RFID reader antenna is installed near the return slot, so that the information of the returned book can be captured. At the same time, the RFID tag of the returned book will be reset, and the indicator light will show that the book has been returned successfully. Safe operation and correct reading rate when returning books are considered important indicators in this link. The book return system is seamlessly connected with the existing sorting system of the library, which can greatly improve work efficiency.

Figure 10 Book return self-service station
Five, functional characteristics
1. Open
Longer library opening hours (realize 7*24 hours book return service);
The open access control channel is set to ensure unobstructed flow.
2. Convenient
Book loan and return service anytime, anywhere;
Avoid long waiting in line, which is more convenient and faster.
3. Efficient
Higher and more advanced management mode
Improve the optimal allocation of human resources, from low-level services to high-level services;
Simplify manual operations, greatly saving time and cost;
Accurate and easy collection management reduces the intensity of physical labor.
4. Personalization
A more civilized and humane service environment;
More and more personalized customized services;
Give readers more choices and protect personal privacy.
6. Reference Significance to Domestic Libraries
1. Openness
With open access control channels, the core issue is whether the design of the door antenna can achieve the RF action area in the 3D direction. If this requirement is not met, the recognition rate of the access control system will be greatly reduced, and the openness will be meaningless.
In addition, the arrangement of the book return link is also very important. In Singapore, self-service book return equipment is installed outside the library, including the community, which greatly facilitates the readers to return books. However, for domestic libraries, considering the cost and other factors, it is not suitable to adopt such an approach at present.
2. Security
Although designed with the EAS function, the access control channel system can alert the books that have forgotten to go through the borrowing procedures. However, if the electronic tag attached to the book is damaged, the EAS function will lose its function. Considering the possibility of this situation, domestic libraries should adopt magnetic strips and tags at the same time to ensure the safety of books. After a period of double protection, it transitions to the use of a single label.
In addition, when the network fails, the safe operation of the system will be greatly challenged. Therefore, in addition to being equipped with an uninterruptible power supply, it is necessary to be equipped with handheld devices.
3. Connectivity with existing systems
RFID devices all provide API interfaces, including Windows-based standard DLLs and Active controls. Coupled with the continuous development of RFID application platforms, the connection with the library’s existing systems is no longer a problem.
4. Scalability
The adoption of electronic bookshelf may require years of step-by-step implementation, which requires the system to be scalable.
In addition, with the popularization of second-generation ID cards, the era when reader ID cards and ID cards are commonly used in libraries will soon come. Therefore, when considering system equipment, the application of identity documents should also be considered.
5. After-sales service
At present, many libraries mostly consider the feasibility of the equipment when selecting equipment. In fact, the localization and timeliness of product after-sales service are also very important.
7. Conclusion
In terms of large-scale library management systems, RFID technology has achieved clear and significant success. The automated library cataloging work and the application of friendly customer self-service equipment can not only reduce the labor cost of the library to a large extent, but also enable the library to gain more customers’ favor. While gaining higher prestige, the library has more time to carry out special activities and increase related income.
With the continuous development of RFID technology and the reduction of tag costs, more and more libraries will adopt RFID technology.
However, we should note that the application of RFID is limited. The attenuation of RFID signals caused by a large number of metal structures in the library may lead to an increase in RFID read/write errors. Inappropriate antenna system design and inferior RFID equipment will cause unnecessary customer complaints. Therefore, it is very important to choose carefully among the numerous RFID equipment providers.
[ad_2]



