Quan Shunhong RFID Warehouse Management (WMS) System Solution
[ad_1]
1. Project background
1.1 Background
Enterprise warehousing management is the management of the warehouse and the materials in the warehouse. It is the planning, organization, control and coordination process of the enterprise in order to make full use of its warehousing resources to provide efficient warehousing services. As a link between producers and consumers, it plays a vital role in the entire logistics and economic activities.
Different enterprise scales and product categories have different warehousing management processes and requirements, but the core part is still the warehouse operations including in and out of the warehouse, and the inventory control operations including the shift and inventory. With the changes in the entire manufacturing environment, product cycles have become shorter and shorter, and a variety of small-scale production methods have emerged. Demand from the market has put forward higher requirements for warehousing management.
The simple and static traditional warehouse management model generally has huge material inventory, difficult material tracking, low capital and material turnover efficiency, high labor cost, backward logistics management information and methods, and other shortcomings, which can no longer adapt to the new warehouse management. need. Break through the traditional warehouse management model, actively explore new information management technology, build a new warehouse management information system platform based on the original management process of the enterprise, coordinate the operation of all links, and ensure timely and accurate warehouse entry and exit operations And real-time and transparent inventory control operations, rationally allocate warehouse resources, optimize warehouse layout and improve warehouse operations, improve warehousing service quality, save labor and inventory space, and reduce operating costs, thereby enhancing corporate market competitiveness.
1.2 System requirements
FUWIT combines customer project requirements and practical application experience in the RFID warehousing WMS system, and concludes that a high-quality warehousing management system lies in the optimal configuration of warehousing resources, precise warehouse operation control, and real-time and effective warehousing data flow. Therefore, the construction of its information system platform will mainly focus on the needs of six aspects, which will be briefly explained below.
1.2.1 Visualized warehouse management
The visualized warehouse-in/out management mainly covers the warehouse-in and out-of-warehouse of goods (pallets). The system should be able to realize the visual management of warehouse real-time data in the management center. Realize the synchronization of physical logistics and data flow.
1.2.2 Electronic pallet and location management
Realizing the electronicization of pallets and storage locations is the basis for realizing visualization and intelligent warehouse management. The goods in the warehouse are circulated and stored in units of pallets. Through the realization of electronic pallets, the identification of each pallet, real-time tracking of storage and transfer locations can be realized, combined with electronic (digital) location management , Which can provide the necessary data foundation for visualized warehouse management.
By dividing the physical space of the warehouse into regions, each physical space is assigned a label, which can effectively locate the goods in the warehouse and quickly retrieve them.
1.2.3 Real-time inventory
By using a handheld (or mobile inventory machine) to scan and identify physical objects on site, generate physical information, compare with ERP data, and produce inventory information tables to ensure that the accounts and objects are consistent.
1.2.4 Cargo Search
When you need to find a certain cargo, enter the relevant cargo information in the handheld and scan the cargo within a certain range. When the cargo is scanned, the system will sound a prompt to facilitate the quick finding of the cargo.
1.2.5 Related system (MES/WCS/SAP) interface
The warehouse management system should not be an independent system. The relevant data should be able to interact with the company’s existing production management (MES), EPR (SAP), and customer systems (WCS) in a timely manner through certain interfaces. The actual management needs of the enterprise.
1.2.6 Realize the unification of information flow and physical logistics
Traditional warehousing management, due to technical constraints, inevitably faces real-time data lag, and cannot accurately reflect warehousing inventory and logistics in real time, resulting in a serious disconnect between information flow and physical logistics. Moreover, because manual identification of cargo information is not only inefficient, error-prone, and heavy workload, the ultimate goal of constructing this system is to introduce effective technical means to finally realize the unification of information flow and physical logistics in enterprise warehousing management. Real-time visualized warehouse logistics management.
2. Technical background
2.1 Introduction to RFID technology
RFID is a new type of information technology that can realize the non-contact and rapid transmission of data and information. At present, it has been widely used in manufacturing, anti-counterfeiting, traceability, logistics and supply chain management and other fields. It has brought great technological innovation to these fields, especially in the field of warehousing and logistics. Because of the characteristics of technology, it will greatly improve logistics information. The speed of collection and the efficiency of logistics operations.
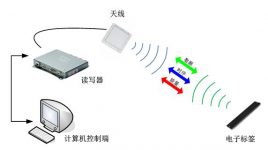
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a non-contact automatic identification technology and one of the core technologies of the Internet of Things. It automatically recognizes the target object (electronic tag) through radio frequency signals and obtains or records related data. The recognition work does not require manual intervention and can work in various harsh environments. A typical RFID system is composed of a host computer, RFID reader, antenna, and electronic tag. The electronic tag has a data storage area for storing information. The RFID reader is used to identify the electronic tag, read or write data, and is responsible for Complete data interaction with the host computer, and the host computer is the interface that controls the work of the entire system. The system structure is shown in Figure 2-1-1. Consultation hotline 400-833-1258

Figure 2-1-1: RFID system structure diagram
2.2 Technical advantages
The biggest feature of RFID technology is non-contact high-speed identification. It communicates wirelessly. The radio frequency tag can be read without exposing the electrical contacts. Therefore, even if the radio frequency tag is attached to the inside of the packaging material, it can be identified. RFID The identification system can also identify multiple radio frequency tags and high-speed moving radio frequency tags at the same time, which can realize the high efficiency of the goods circulation process. The specific advantages are as follows:
Non-contact reading and writing
As long as the reader of the RFID system can read the information directly into the database without contact, this has a great advantage over the original information entered by a dedicated documentary member, and various information about the logistics processing status can be written into the label. Reduce a lot of information collection time for the next stage of the process.
Simultaneous reading of multiple tags
Through the RFID reader, multiple RFID radio frequency tags can be read at one time, and the data can be transmitted from the reader to the computer network system at one time. The speed of this data collection and the acceptance of items is tens of the bar code scanning collection and acceptance speed. Times, it is much faster than the traditional method of using receipts to collect data and check the name of the goods to check and accept the goods. Through the multi-reading of this RFID reader, the efficient and rapid circulation of items can be realized.
Good penetration
Articles with RFID radio frequency tags attached to packaging materials that are non-metallic or non-transparent materials such as paper, wood and plastic can also be recognized by the reader normally. It has good penetrability, so you don’t need to remove the items from It can be identified quickly and conveniently when it is taken out of the packaging material.
Large label storage data capacity
The data stored by RFID radio frequency tags is much larger than that of bar codes. The data stored by bar code technology can only indicate the type of the item, and cannot express the individual of each type of item. However, the RFID radio frequency tag has a large storage capacity and can store detailed descriptions of the item. information.
Strong ability to adapt to the environment
If the paper is dirty, you may not be able to see the words written on the paper. In the dark environment, the barcode scanner will not be able to scan the information of the barcode. The magnetic card is not magnetic and cannot be swiped. However, RFID technology has strong environmental adaptability. RFID radio frequency tags have strong resistance to water, oil, medicines and other substances and have strong immunity to light. They can still be easily collected in the radio frequency tag in a dirty or dark environment. digital information. Consultation hotline 400-833-1258
Labels can be reused
The data stored by RFID is electronic data, and the carrier for storing the data is an electronic chip. This chip has the function of repeated writing and can be reused, reducing the one-time investment cost of the project.
Miniaturization and diversification of label shapes
Reading RFID radio frequency tags is not limited by size and shape, and does not need to match the fixed size and printing quality of the paper for reading accuracy. This has a greater advantage than the use of barcode technology on items that need to be combined with the shape and size of the items. . In addition, the miniaturization of RFID radio frequency tags can be more flexibly applied to the production line to control the production of products.
System and data security of RFID technology
Transferring product data from the central computer to the workpiece will provide security for the system, avoid reading data directly from the system and greatly improve the security of the system, and use encryption to protect the data in the RFID radio frequency tag. Can guarantee that the data will not be read
2.3 The significance of using RFID technology in warehouse management
After years of development, RFID technology has made considerable progress at home and abroad, regardless of the technology itself or the level of application. Especially the application in the field of logistics and warehousing, due to its complete standards, high technology and application maturity, significant improvement in the level of warehousing logistics management, and gradual reduction of RFID application costs, it is becoming one of the standard application technologies for modern high-efficiency warehousing logistics. At the same time, RFID technology is also one of the key technologies in the development of modern Internet of Things technology. In recent years, with the support and vigorous promotion of national policies, it is developing at a high speed. The Internet of Things has achieved great development in many fields including manufacturing. It has gradually become an inevitable choice to solve the problems of informatization management in multiple links of enterprise production, manufacturing, warehousing, logistics and so on.
The FUWIT Warehouse Management System (WMS) solution adopts RFID technology as the key technology in the warehouse management system, which can significantly improve the technical level of warehouse and logistics management, and enterprises can obtain a good return on investment. For the present, the project has exemplary significance. It can effectively avoid and reduce the repeated investment in enterprise information upgrade.
Three, system solutions
3.1 Principles of Scheme Design
Actual effect is applicable, personalized application
Combining the actual situation of different warehouses, under the premise of grasping the general direction, the plan design will fully consider factors such as site site, operation mode, management mode, actual storage requirements, etc., so as to apply the actual application effect and avoid unnecessary functions. design. In particular, the development of software systems should fully meet the actual management needs of the warehouse, achieve personalized applications, and avoid unsuitability and impracticality.
Management mode can be copied
The system design will focus on several major main lines in warehouse management, but it can still fully consider the needs of future warehouse expansion and expansion. The warehouse management model should be able to be easily copied and defined, and it will be quickly adapted to the management needs of other warehouse areas in the future.
Controllable investment cost
On the basis of meeting management needs, investment costs should also become a key part that needs to be considered. Maximize investment efficiency. Unnecessary investment waste should be avoided, repeated investment in the future should be avoided, high investment in the improvement of management efficiency should be avoided, and the overall system construction cost should be controllable.
Application risk is controllable
The system design should ensure that application risks are controllable. Application risks mainly include new technologies and new management models, and management risks caused by changes in existing management models. It is necessary to fully study the existing management models, operating procedures, personnel quality, information level, etc., while improving operational efficiency and management effectiveness, try to achieve a gradual and smooth transition as far as possible. Avoid the negative impact of changes in management methods on business operations.
Support future expansion
In terms of equipment configuration, technical application, and software system, the system should fully consider future management development needs. When future management needs increase, it should be able to support future system function expansion and smooth transition.
3.2 System architecture

System architecture diagram
Warehouse physical layer:
The physical layer of the warehouse includes warehouses, locations, pallets, forklifts, goods, field operations, etc. On-site operations include goods in, out, inventory, sorting, allocation, splitting, moving, etc. All valid locations (storage areas) and pallets in the warehouse require the installation of RFID electronic tags in order to realize the refined management of pallets in a single location (storage area).
Collection and interaction layer:
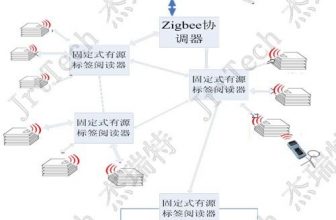
Contains a variety of on-site data collection and user interaction equipment, including RFID handheld terminals, RFID fixed readers, etc. Mainly provide user operation instructions, on-site data collection, data entry, etc. Provide real-time field data collection and interactive operation guidance for the system.
RFID data service layer:
Manage the RFID equipment and related equipment in the system, collect, cache and filter the collected data, control the collection and distribution of instructions and related data, etc. The data service layer runs on the system server in the form of system software services, and provides data services for the RFID data and related control instructions of the user application layer and the data collection interaction layer.
Enterprise application layer:
Provide computer software user management interactive interface for warehouse dispatch management center and remote management center, and provide report and data query services. The management center’s planning, management control, and data monitoring of warehouses and goods are provided through the enterprise application layer.
3.3 System topology diagram

System topology diagram
Install electronic tags (buried in the ground without shelves) in each cargo space, which can physically divide separate areas to uniquely identify the identity of the cargo space. A tray electronic label is installed on each tray to uniquely identify the identity of each tray. Each single product can be equipped with an electronic label to identify the identity of the goods. Each driver carries an electronic tag to identify the driver (optional). Install RFID fixed readers at each warehouse door/channel, and install detection antennas at the door or on both sides of the aisle to automatically detect incoming and outgoing pallets and the identity of the driver. According to the on-site terrain layout, it can assist infrared, vehicle detector, reader pairing, etc. to realize vehicle entry and exit status detection.
3.4 Warehouse Management Software Architecture

Software multi-layer architecture block diagram
3.5 Process design
3.5.1 Goods warehousing process

When the goods are purchased and received or the finished products are put into storage, an electronic label is made, and the label is written into the purchasing unit, specification and model and other enterprise-defined information, and then pasted on the goods to complete the initialization of the goods information. At the same time, install a tray electronic label on the tray to identify a specific tray information;
In the warehouse, the forklift transports the goods through the warehouse gate, and the reader installed at the warehouse gate automatically collects the RFID tag on the goods and the electronic label information on the pallet, and reads the information directly to the data center. The background realizes the goods information and the pallet. Binding, complete the warehousing scan binding, realize automatic scanning, automatic binding, without manual intervention, automatically complete the warehousing operation;
The forklift continues to transport the pallets of goods to the idle shelves. The shelf RFID electronic tags are installed on the shelves. During the shelf loading process, the forklift RFID reader will read the pallet tags and rack tags, and read the information directly to the In the data center, the background automatically completes the binding of pallet information and rack information, that is, completes the shelf operation of all goods on the pallet, and realizes accurate shelf management.
3.5.2 Goods moving process

When moving the warehouse, the forklift client can directly initiate the moving operation. The forklift directly removes the pallet that needs to be moved. When the forklift collection system reads the cargo pallet label information, the system automatically combines the pallet information with the previously bound material. The information is unbound. When the forklift picks up the goods to the new rack to complete the process, the forklift reading system will read the new rack information and upload it to the data center. The system completes the binding of the new rack and updates the inventory in real time. .
3.5.3 Process of goods delivery

When leaving the warehouse, the forklift first removes the cargo pallet from the rack. The forklift reading system reads the pallet information and sends it directly to the data center. The back-end system completes the check of the outbound information. If it is correct, the unloading operation is completed, and the system automatically Unbind the pallet information and the rack information; if it is incorrect, an early warning will be given;
After the unloading is successful, the forklift transports the goods through the warehouse gate, and the reader installed at the warehouse gate automatically collects the RFID tags and pallet tags on the goods, and sends the information directly to the data center. The back-end data center completes the goods labels and pallets. If the label verification is correct, the outbound operation will be completed, and the system will automatically update the inventory. If it is incorrect, an early warning will be issued.
3.6 Installation and layout of main hardware equipment
3.6.1 Warehouse gate forklift entry and exit inspection

The ThingMagic M6 fixed reader is used for goods in and out of the warehouse to quickly and accurately collect the label information of the incoming and outgoing goods in batches.
ThingMagic M6 is a four-channel UHF RFID reader with a high-speed reading capability of 750 tags/sec. It can be connected to up to 4 antennas at the same time for full coverage reading. It is based on ThingMagic’s core anti-collision algorithm. It realizes fast data collection while ensuring no missed readings, realizing accurate collection of goods in and out. At the same time, M6’s high stability and high anti-interference ability can ensure reliable operation in various harsh industrial environments; it supports WIFI connection and can be more easily and flexibly deployed in warehouse applications.

|
Label agreement |
EPCglobal Gen 2 (ISO 18000-6C) DRMsupport;ISO 18000-6B (*Optional); I-PX (*Optional) |
|
Antenna connector |
4ReverseTNCConnector; support4Independent antennas |
|
RFOutput |
Independent read and write mode,5to31.5dBmOutput(1.4W), ±0.5dBmAdjustable |
|
Frequency characteristics |
FCC(NA,SA)902-928MHz;ETSI(EU) 865.6-867.6MHz;MIC(Korea)910-914MHz;SRRC-MII(PRChina);920-925MHz |
|
Communication Interface |
10/100 Base-T Ethernet; HD15(GPIOinterface) |
|
Wireless network (optional) |
Built-in802.11 b/g(*Optional); |
|
Label reading rate |
more than the750Label/second |
|
Label reading distance |
more than the30feet(9 M)use6dBiantenna(36dBm EIRP) |
|
Maximum read and writeEPC IDlength |
Highest496bits |
|
operating system |
LinuxKernel version2.6 |
3.6.2 Forklift deployment plan

As a forklift client, the industrial PC completes the docking with the data center and the control and data interaction of the forklift reader.
The application of RFID readers in forklifts is different from ordinary application environments. Forklifts have more stringent requirements for RFID equipment, including dust-proof, waterproof, and vibration-proof design, which can adapt to voltage and current fluctuations. The equipment shell must Sturdy and durable, anti-corrosion, at the same time, should have good temperature adaptability, suitable for all kinds of harsh environments.

The forklift reader adopts ThingMagic-Vega. Vega is a vehicle-level RFID reader. It has passed various tests of the automotive industry quality certification standard: TS16949. It has built-in high-performance ThingMagic modules to meet harsh environmental operating standards. Requirements, very suitable for deployment in forklifts and various automotive applications.
|
Label agreement |
EPC Class 1 Gen 2(ISO 18000-6C); DRMSupport, advanced anti-collision and anti-jamming performance |
|
Antenna connector |
Three reverseTNCAntenna port support single50Ohmic antenna (when the voltage standing wave ratio is less than1.5:1Frequency range operation) |
|
RFOutput |
Independent read and write mode,5to30dBmOutput(1W),±1dBmAdjustable |
|
Operating temperature |
-40°Cto75°C; AC power adapter:0°C to40°C |
|
Environmental standards |
Confirm that the vehicle standards are met: Power thermal cycle; one thermal shock resistance& B;Durable dynamic vibration; Mechanical shock; Humidity temperature cycle; Water/Liquid inlet; connector/Use pull and push; over-emphasis of voltage; electrostatic discharge |
|
Label reading rate |
more than the190Label/second |
[ad_2]