Radio Frequency Energy Metering Asset Management System
[ad_1]
1 Overview
In order to improve the efficiency of energy metering asset management, the UHF-RFID radio frequency energy metering asset management system designed and applied by the company uses electronic tags, a new technology product, to automatically identify RFID readers and electronic tags through radio frequency signals. Scanning, can obtain the type, product name, specification, batch number, quantity, production date, expiration date, storage time, and storage time of electric energy measurement assets in a long distance, large range, and batches, and store them in the energy measurement asset management computer, automatically Record and generate bills. These meter information can be queried online on a dedicated meter management computer. To view the detailed information of which meter and the time of entry and exit, you can query it from the power measurement asset management computer at a glance, thus realizing the intelligent management of the meter library. . At the same time, the UHF-RFID radio frequency meter management system also includes the fingerprint identification security anti-theft alarm of the energy metering asset manager and the video surveillance anti-theft alarm of the warehouse area, which greatly improves the security of the energy metering asset.
2. Design plan
2.1. System design basis
1) GTB856: National Standard for Software Engineering
2) “International Integrated Wiring Standard” ISO/IEC11801
3) Video security monitoring system technical requirements GA 367-2001
4) General technical requirements for anti-theft alarm controller GB 12663-2001
5) Code for construction and acceptance of electrical installation engineering GBJ232-90,92
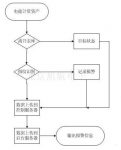
2.2. System workflow

Figure 1: System flow chart
2.3. System composition
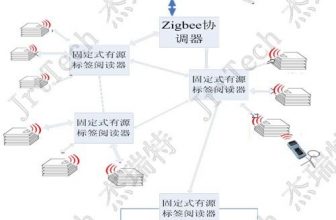
The radio frequency energy measurement asset management system designed by our company is mainly composed of five parts: RFID reading and writing equipment, electronic tags, fingerprint identification instrument, identification monitoring unit and computer software.
Figure 2: UHF-RFID radio frequency meter management system identification diagram

Figure 3: System software interface

2.3.1 Electronic label
The main considerations for electronic label selection are:
A. The actual application method and environment of the customer;
B. The read and write distance of the tag;
C. Transmission rate;
D. Read and write speed;
E. Working frequency;
F. Memory and packaging form.
According to user needs and referring to the above factors, in order to achieve accurate reading and prevent cross-reading, we choose passive single-frequency electronic tags. The working frequency of the tag is UHF frequency band, 915M; the memory of the tag adopts the EPC CLASS 1 Gen2 standard; for the complex situation of monitoring items, special material packaging is used, which is suitable for the surface of metal objects.

Figure 4 Electronic label
2.3.2 Reader
The reader/writer plays a pivotal role in the RFID system. The frequency of the reader/writer determines the working frequency band of the RFID system, and the power of the reader directly affects the distance of the RFID system. Generally speaking, a high-frequency tag has a greater reading distance, but it requires a greater electromagnetic wave energy output by the reader. A high frequency tag can be read within a distance of 3 to 8 meters.
2.3.3 Antenna:
The antenna is a transmitting and receiving device that transmits data between the tag and the reader. In practical applications, in addition to the system power, the shape and relative position of the antenna will also affect the transmission and reception of data, professionals are required to design and install the antenna of the system.
2.3.4 System Software
System software is a computer application system developed and designed for different users by our company using the above hardware. Take electric energy measurement assets as the main body of management, and the management mode based on electronic tags is flexible and convenient. It is open to enterprise information system (MIS) data, seamlessly integrated with the original MIS system and marketing management system, and can also be operated as a measuring instrument management system alone.
This system uses a fingerprint identification device to identify the personnel entering and exiting the warehouse to achieve the effect of anti-theft alarm.
2.3.6 Video surveillance
Video surveillance adopts a high-configuration large-capacity hard disk video recorder and a high-speed pan/tilt integrated camera.
(Since this part is relatively simple, the working principle of the system will not be repeated here)
2.3.7 Implementation
1. Install RFID radio frequency identification equipment at the entrance and exit of each warehouse area to form an antenna coverage area; any asset equipment installed with RFID tags will be read when passing through the antenna coverage area.
2. Install fingerprint identification instruments and access control devices at the entrance and exit of each warehouse area, and personnel entering and exiting the warehouse must pass fingerprint identity verification and access control functions.
3. The monitoring unit will realize screen capture and illegal entry and exit alarm functions.
4. The system platform performs unified and intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management functions for warehouses in various regions.
2.4 The working principle of the system
RFID technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology. Its basic principle is to use radio frequency signals and their spatial coupling and transmission characteristics to realize automatic machine identification of stationary or moving objects to be identified. In application, the electronic tag is attached to the electric energy metering asset to be identified. When the electric energy metering asset to be identified with the electronic tag passes through the read-write range, the reader will automatically take out the agreed identification information in the electronic tag from a long distance in a contactless manner (The reader can read the data of 50 or more tags at the same time), so as to realize the function of automatically identifying items or automatically collecting item identification information.
The essence of RFID technology is to exchange data wirelessly. This data exchange process requires two kinds of equipment, a device that can read/write radio frequency data, and a chip with an antenna that can be used to store and write data with it. Data can be automatically exchanged, and the RFID data reading program can be started without any operator’s participation. Compared with other forms of data collection, RFID has the following advantages:
RFID tags do not need to be targeted for reading like bar code tags, as long as they are placed in the electromagnetic field formed by the reading device, they can be accurately read. It is more suitable for use with various automated processing equipment, while reducing or even eliminating data collection due to manual intervention This brings about the reduction of human resources, efficiency, and the cost of errors and corrections.
RFID can read thousands of times per second and process many tags at the same time, which is efficient and highly accurate. This enables enterprises to greatly improve management precision without reducing (or even improving) operation efficiency and increasing (or even reducing) management costs, making the entire operation process transparent in real time, and creating huge economic benefits.
The data on the RFID tag can be modified repeatedly, which can not only be used to record and transmit some key data, but also enable the RFID tag to be recycled and reused within the enterprise, which converts one-time costs into long-term amortized costs, and further saves the operation of the enterprise At the same time, it reduces the risk and cost of enterprises adopting RFID technology.
The reading of RFID tags does not need to be visually visible, because it does not rely on visible light.Therefore, it can be used in harsh environments that barcode technology cannot adapt to, such as high dust pollution, outdoor environments, etc., to further expand the application range of automatic identification technology
RFID technology can be mixed with bar code technology to be used in their respective appropriate links in the same system. In addition to mobile computing technology, wireless local area and wide area networks are used as extensions of the enterprise’s wired network system to truly enable the entire enterprise All on-site operation procedures are seamlessly connected with various enterprise management information systems, so that every step of the operation on the job site is under the management, supervision and control of the computer management information system, so that the enterprise spends a lot of money to build the management The capabilities of the information system can be fully implemented, realizing the overall investment benefit.
In addition, the power metering asset management system introduces LED data display screens and LCD navigation screens, so that the verification and operation of power metering assets are synchronized with the information flow, and the loss of power metering assets is controlled to a large extent, and closed-loop management is fully realized; The warehouse environment is standardized and automated, dynamic touch and scrolling display humanization, intelligent control system operation stabilization, database information management and service centralization and other functions.
Normally, the frequency sent by the RFID reader is called the operating frequency or carrier frequency of the RFID system. The working frequency of the radio frequency tag not only determines the working principle of the radio frequency identification system (inductive coupling or electromagnetic coupling) and the identification distance, but also determines the difficulty and ease of implementation of the radio frequency tag and reader and the cost of the equipment. According to different operating frequencies, RFID tags can be divided into different types such as low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), ultra high frequency (UHF) and microwave. Each frequency has its characteristics and is used in different fields. , So to use it correctly, you must first select the appropriate frequency. UHF electronic tags have a very high data transmission rate, and secondly, batch reading and anti-collision capabilities are also strong. UHF electronic tags transmit energy through electric fields. Because the energy of the electric field does not decrease very quickly, the reading distance is relatively long, and the reading distance of UHF passive tags can reach about 10m.
2.4.1 System advantages
l Effectively manage the status of the electric meter and grasp the whereabouts of the electric meter in real time.
l Realize intelligent and unmanned management of electric meters, and automate the collection of electric meter information.
l Realize the electricity meter audit, without destroying the packaging form of the electricity meter during the inspection and inspection, and realize the non-contact management.
l Support batch high-speed management, the RFID identifier can identify and read several RFID tags at the same time, improving work efficiency.
l To achieve repeated recycling, the RFID tag can repeatedly add, modify, and delete the data stored in the RFID tag to facilitate the update of information.
l When covered, UHF electromagnetic waves can penetrate non-metallic or non-transparent materials such as paper, wood, and plastic, and can perform penetrating communication.
l Since RFID carries electronic information, its data content can be protected by a password, so that its content is not easy to be forged and altered.
2.4.2 System key technology
1. Passive electronic tags’ metal resistance, miniaturization, and high-sensitivity technology
2. Inlay technology of miniature electronic tags
3. Integrated RFID system middleware technology
4. Information security management technology of RFID system in different environments
[ad_2]