RFID experiment box IoT training program
[ad_1]
RFID training box goal
The Internet of Things RFID experiment box is a core experimental device that can closely integrate the teaching and research of Internet of Things related majors, and can fully meet the needs of students and teachers in learning and researching Internet of Things RFID technology.
Target:
Cultivate Internet of Things talents who are oriented to RFID applications and meet social needs.
Overview of RFID training box
The rapidly emerging Internet of Things industry is making tremendous changes in our daily lives through induction devices (RFID radio frequency identification equipment, various sensor devices, etc.) and wireless networks. The Internet of Things technology connects all materials and products to the Internet through RFID radio frequency identification, various sensors or other embedded devices, etc., to realize intelligent management, supervision and control. It is another revolution in the information industry after computers, the Internet and mobile communications. . With the rapid development of communication technology, computer technology and Internet of Things technology, general-purpose talents with knowledge of network communications, computers and Internet of Things have become a hot market demand. In order to further adapt to the development of the Internet of Things technology and related talent market needs, we suggest that colleges and universities and various vocational training schools offer Internet of Things related courses in computer and communication majors, and at the same time build Internet of Things information that matches the course teaching Platform laboratory. Its significance lies in: improving the level of teaching and research, promoting student employment, and enhancing the school’s competitiveness. Radio Frequency Identification is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, also known as radio frequency identification. It is a wireless identification technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without the need to establish mechanical or optical connections between the identification system and specific targets. get in touch with. Commonly used are low frequency (125k~134.2K), high frequency (13.56MHz), ultra high frequency (902MHz~928MHz), microwave (2.45GHz) and other technologies. The RFID training box solution built with this as the core is the first domestic solution focusing on the full application of RFID protocols. It is different from a simple RFID reading and writing experiment. Through the comprehensive interpretation of RFID protocols and supporting mainstream application development programs, students can operate the full protocol of RFID readers, as well as the programming design of common application software and the actual Internet of Things. Application design; At the same time, we provide overall solutions including equipment, teaching materials, training and services; The designed experiments are rich in content, including verification experiments, design experiments and comprehensive application experiments, which can be used for daily teaching , Can also be used for curriculum design and graduation design, to provide students with a graduation internship environment. Its laboratory solutions have the following characteristics: comprehensive RFID protocols, complete solutions, and rich experimental content.
Features of RFID training box
The RFID training box is an overall solution of modular structure that combines the characteristics of reader hardware, command analysis and application layer to carry out layered design, integrated implementation, rooted application, and contact teaching.
1. The front-end RFID reader includes:
1. Low-frequency card reader: can realize the reading operation of low-frequency tags;
2. High-frequency reader: Supports mainstream electronic tags (TI, NXP, ST, INFINEON, FUJITSU…) that comply with ISO/IEC 15693, ISO14443A/B, ICODE UID protocols, and can read and write various tags As well as some other personalized operations, support transparent commands (high-end features for cooperating with and supporting the new features of future tags and the features of various manufacturers’ tags);
3. UHF Reader: Supports electronic tags that comply with EPC CLASS1 G2 (ISO18000-6C), ISO18000-6B standards, and supports block write fast lock, EAS, long EPC, privacy operation and other protocol functions;
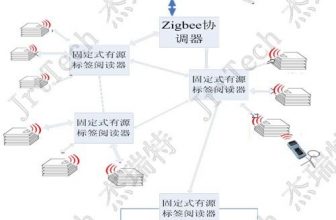
4. Active reader: It can realize the read and write operations of active tags, with low-frequency excitation, which can be used for precise positioning;
2. Electronic label recognition and production system:
1. Electronic tag cognition: List more than 40 common RFID tags, each with samples and explanatory text, and introduce the packaging form and main purpose of electronic tags.
2. Electronic label production system: Students can make labels by themselves to deepen their understanding of RFID electronic labels.
Three, reader command analysis
It mainly includes the communication protocol and command analysis of high-frequency and UHF readers. It is mainly for students to learn the underlying commands of the reader to deepen their understanding of RFID and develop appropriate applications.
4. Application system design and practice
This set of system software includes access control system, anti-counterfeiting traceability, warehouse management system, traffic membership card management system, conference sign-in system, etc. All subsystems include industry applications and source code. One interface of warehouse management is as follows:
RFID experiment box IoT training program
Purpose of RFID training box
Comprehensive technology: The Internet of Things does not involve too many new technologies. Most of the hardware, software and network involved are integrated applications of existing technologies; wireless as the root: the vast majority of the Internet of Things is the rapid and accurate identification between things, so RFID readers are the basis for building the Internet of Things; Application first: The Internet of Things is derived from applications and serves applications. Research on the Internet of Things technology that is separated from actual application requirements is meaningless; Cross-disciplinary: The Internet of Things is cross-disciplinary and cross-industry, and users and researchers must be familiar with it And master a variety of existing technologies and be able to comprehensively use them.

Reader Experiment Directory
Test box installation and connection instructions
Driver installation instructions
UHF UHF Experiment
Experiment 1 Basic understanding of UHF reader
Experiment 2 Tag data reading experiment under Gen2 protocol
Experiment 3 Tag data writing experiment under Gen2 protocol
Experiment 4 Tag key and data read protection under Gen2 protocol
Experiment 5 Set read protection, EAS, mask, destroy, and privacy operations under Gen2 protocol
Experiment 6 18000-6B label operation
Experiment 7: Experiment on the influence of reader power on tag reading distance
Experiment 8: Experiment on the influence of reader frequency on tag reading distance
Experiment 9: Inquiry experiment on the influence of tag angle on tag reading effect
Frequency point analysis experiment of experiment ten labels
Experiment 11 Three working modes of readers (active mode, response mode, trigger mode)
HF high frequency experiment
Experiment 1: The basic cognition of high-frequency reader
Experiment two: Tag data reading and writing experiment under IS014443A protocol
Experiment 3 Key operation experiment under IS014443A protocol
Experiment 4 Tag value-added and devalued experiment under ISO144443A protocol
Experiment 5 Tag reading and writing experiment under ISO144443B protocol
Experiment 6: The effect of tag angle on tag reading effect experiment
Experiment 7: Tag data reading and writing experiment under IS015693 protocol
Experiment 8 IS015693 protocol tag AFI, DSFID read and write and block lock experiment
LF low frequency experiment
Experiment 1 Low-frequency reader experiment
Experiment 2: Penetration experiment of low-frequency tags
Active experiment
Experiment 1: Read and write operations of active tags
Experiment 2 Active tag low-frequency excitation positioning experiment
RFID training box related courses
The Internet of Things laboratory can provide scientific research, teaching and practical functions for the following majors and courses: Internet of Things, software engineering, computer applications, communication principles, radio frequency identification technology, microcomputer principles, multimedia information processing, digital signal processing, radio frequency communication circuits, Network programming technology, digital and analog signals, introduction to Internet of things engineering, network security, Internet of things application system design, optical communication principles, large-scale programming, data structure, Internet of things data processing, Internet of things architecture, embedded system design, information Security, digital circuit and logic design, database system, sensor technology, wireless sensor network, wireless communication network, single-chip microcomputer principle and development, etc.
RFID training box list
(1) RFID reader
A low-frequency card reader: 125KHz frequency, UKB interface mode (YXL1036UKB)
One high-frequency reader: 13.56MHz, support ISO/IEC 15693, ISO14443A/B, ICODE UID protocol, USB interface (YX7036USB-L)
One UHF reader: 902-928MHz, supports EPC CLASS1 G2 (ISO18000-6C), ISO18000-6B protocol, supports Wiegand, RS232, RS485 interface, with trigger. (YXU1861)
One UHF reader: supports 2.45GHz frequency band. (YXR901)
One low-frequency exciter: 125K low-frequency excitation
(2) RFID electronic tag recognition system
Contains five kinds of electronic labels in different packages, with pictures and text descriptions
(3) RFID electronic label production system
Including welding tool set, anti-static gloves, original materials for label making and an instruction manual
(4) Command parsing manual
Contains high frequency, UHF command analysis and source code
(5) Applied teaching system
Contains instructions and source code for each subsystem of application teaching
[ad_2]