Shengshi Longtu RFID Smart Asset Supervision System
[ad_1]
1 System introduction
Fixed assets are an important part of the assets of government agencies. Because fixed assets have high value, long service life, scattered use locations, and many related responsible personnel, it is not easy to achieve one-to-one correspondence between accounts, cards, and objects in actual work. , It brings certain difficulties to the use, supervision, change, replacement, maintenance, loss, inventory cleaning and other tasks of the physical objects. The establishment of a fixed asset integrated management platform with accurate data and consistent accounts will have a positive impact on data report statistics, asset structure analysis, asset evaluation, and asset procurement budgets.
Our company’s RFID smart asset supervision system is based on the RFID radio frequency technology at the core of the Internet of Things. Automatic asset identification and intelligent supervision system integrating information identification, information transmission records, and optional sound and light alarm industry designation cards. The system can effectively integrate the Nissan management and anti-theft monitoring of various assets. Realize the intelligent management of important and valuable assets such as anti-theft alarm, asset inventory, inspection, loan and return, warehouse storage and statistics.
2 Introduction to RFID radio frequency technology
Radio frequency identification is a technology for automatic identification through microwave radio frequency signals. It is a fast, long-distance, non-contact automatic identification technology that can work in harsh environments.
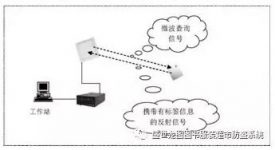
Its basic working principle is that the reader sends a radio frequency signal to the electronic tag through the antenna. After the electronic tag enters the identification area of the radio frequency signal, an induced current is generated to obtain energy, and the electronic tag information is sent out through the embedded antenna, and the reader passes The antenna decodes the electronic label information using a decoder board, and then transmits the label information to the computer through a network or RS232 interface. as the picture shows:

Figure 2-1 Basic working principle of wireless identification
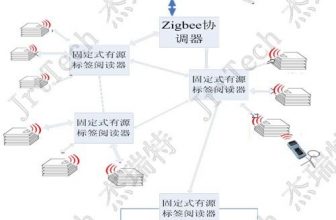
3 System structure

Figure 3-1 RFID smart asset supervision system structure diagram
3.1 Implementation method
When the relevant data of each newly purchased fixed asset is input into the computer system, an RFID electronic tag is installed on the fixed asset. The label installation method can consider the recycling and reuse of the fixed asset when it is scrapped.
According to management needs, information such as the name of the fixed asset, the date of purchase, and the department of use are written into the tag or just the tag ID number is associated.

Figure 3-2 Information Association
When using the department to receive, the staff only need to carry a handheld RFID reader to read the asset tag to be used once, and after confirmation, the read tag information is transmitted to the server through the network for registration.
During asset inventory, staff use RFID handheld readers to read the electronic tags on fixed assets. The tag information is automatically stored in the handheld readers, and then the data in the handheld is checked against the data in the database. The normal or abnormal data is processed to obtain the actual situation of fixed assets, and the inventory profit schedule, inventory loss schedule, and inventory summary table can be generated by unit and department.

Figure 3-3 Asset inventory
4 System function
4.1 Asset theft prevention management
Anti-theft of assets is realized through the cooperation of the anti-loss label attached to the article and the reader. After the tag enters the magnetic field, it receives the radio frequency signal from the reader, and uses the energy obtained by the induced current to send the product information stored in the chip. The reader reads and decodes the information, and then sends it to the central information system for relevant data processing. .
4.1.1 Principles of anti-theft application system
Technical principle:
Generally, the RFID application system mainly consists of two parts: a reader and an RFID card, as shown in Figure 4-1. Among them, the reader is generally used as a computer terminal to read, write and store data on the RFID card. It is composed of a control unit, a high-frequency communication module and an antenna. The RFID card is a passive transponder, which is mainly composed of an integrated circuit (IC) chip and its external antenna. The RFID chip usually integrates radio frequency front-end, logic control, memory and other circuits, and some even integrate the antenna Integrate together on the same chip.
Basic working principle:
After the RFID radio frequency card enters the radio frequency field of the reader, the induced current obtained by its antenna is used as the power supply of the chip through the booster circuit. At the same time, the induced current with information is detected by the radio frequency front-end circuit and the digital signal is sent to the logic control circuit for processing. Information processing; the required reply information is obtained from the memory and sent back to the radio frequency front-end circuit via the logic control circuit, and finally sent back to the reader through the antenna.
It can be seen that the antenna plays a key role in the realization of data communication between the RFID card and the reader. On the one hand, the passive RFID card chip needs to get enough energy in the electromagnetic field generated by the reader antenna through the antenna to start the circuit work; on the other hand, the antenna determines the communication channel and communication between the RFID card and the reader Way.

Figure 4-1 Principle of the application system
4.2 Asset circulation management
Fixed asset management currently relies more on traditional manual management methods and means. Data collection and entry have always been manual operations, with low efficiency and high error rates. Barcode technology can greatly improve this situation. However, due to the limitations of barcode technology (easily damaged, poor stain resistance, short reading distance, etc.), only one barcode can be scanned at a time, and asset inventory is performed each time. It requires two persons to work in a team, and one scans the nuclear data to carry out the physical inventory of assets. The work efficiency is not high.
The RFID electronic label used in the construction of the RFID asset management system of this project has a bar code printed on the surface, which can realize rapid asset inventory and management.
4.2.1 Program features
Based on the B/S architecture, the system can realize hierarchical and sub-authority management, and only need to assign the corresponding account authority to manage hierarchically. The system can configure corresponding page, function, button and other permissions for different user roles.
A unified RFID data server is used as the application middleware to realize the unified management of front-end equipment and data collection and processing. The information from various readers is summarized and integrated into a standard data format. The business application subsystem publishes electronic label data.
Considering user experience, cost-effectiveness, and application scenario requirements, high cost-effective electronic tags, RFID handsets, RFID readers and other equipment are adopted.
Fully consider the safety and ease of use of the system.Pay attention to the details of human-computer interaction and user experience in interface operation
4.2.2 Comparison of RFID and barcode/QR code application methods
The advantage of barcode/two-dimensional code is that it is cheap, but the disadvantage is that it cannot be rewritten, and it cannot be read in batches from a long distance. It is easy to be smeared and cannot be read after a long time.
The advantage of RFID technology is that it can be read in batches at a long distance, is not afraid of being damaged, and the data can be read and written. The current main disadvantage is that the cost is higher than that of barcodes.
The application of RFID technology in the field of asset management/warehouse management is mainly to realize batch data reading and improve work efficiency.
RFID electronic label application selection guide

4.2.3 Asset circulation management process
1. Asset information matching
A desktop fixed reader is used to write the item information into the label through the management platform for information matching. Labeling process, complete the card issuance link.
2. Asset scan inventory
The user holds an RFID handset to scan RFID electronic tags from a long distance. The asset management platform automatically displays the asset information according to the read RFID electronic tag information. The management platform generates reports and completes inventory tasks.
3. Asset in and out management
Deploy access control RFID reading equipment in the access channel to read the assets in the access channel. As shown in Figure 4-2, assets in and out of circulation.

Figure 4-2 Assets in and out of circulation
[ad_2]