Storage Management System of Electric Energy Meter Based on RFID Technology
[ad_1]
1. Background
The Power Metering Center is the power metering and testing organization in the power industry. It undertakes the functions of safety life cycle management of power metering instruments within its jurisdiction, including procurement, warehousing, testing, distribution, installation, operation monitoring and other links. With the deepening of the urban network transformation and the in-depth work of one household, one meter for residents, the number of newly installed meters for electricity has increased sharply, and traditional metering centers are unable to meet the requirements. New power metering centers are constantly being built, and the management of electric energy meters is “independently”, and the logistics cost is extremely high, which often triggers customer complaints. Implement full life cycle management of metering devices, including procurement, warehousing, verification, distribution, quality monitoring and other links. In order to realize intensive management, the metering center attaches a unique “barcode ID card” to each electric energy meter. From delivery, verification, inspection, lead sealing to warehouse delivery and use, every link is “scanned and managed”. The status of any electric meter can be found at any time.
The use of bar code technology for data collection of electricity meters has improved the management ability of the meters to a certain extent, but this collection method requires warehouse staff to scan each meter that needs to be in and out of the warehouse separately, and the barcode is scanned when scanning. The beam of the gun must be aimed at the bar code surface of the meter label. The bar code surface must be kept clean and tidy, with low efficiency and low accuracy. At the same time, because the meter is a four-layer meter turnover box, when scanning the meter bar code, the staff needs to turn out the bottom layer of the meter for scanning operation, which brings great inconvenience to the staff and greatly reduces the warehouse management staff. Work efficiency and increase workload. The constant flipping of the electric meter while scanning will wear out the appearance of the electric meter and affect the quality of the electric meter. Sometimes accidentally dropping the meter to the ground will cause the meter to be directly scrapped, which adds to the cost of warehouse management. Every time the warehouse management staff scans the barcode data of an electric meter, it needs to be uploaded to the data center in real time for data verification. In the case of poor network status, the in and out of the warehouse will not be able to proceed normally or the work progress will be very slow.
Bar code technology has changed the management method of power metering center assets. However, with the development of metering center business and the urgent need to improve management efficiency, the limitations of bar code technology are becoming greater and greater, and a more advanced data collection method has been constructed. It is of great significance to improve the efficiency of warehouse management.
2. System introduction
RFID is not only the barcode technology, but also the technology that has caused a revolution in the field of automatic identification. It uses wireless electromagnetic waves to identify the identified items. Compared with the traditional bar code technology, RFID has a faster data communication speed, a longer identification distance, less stringent requirements for the surface cleanliness of the identified items, and higher reading accuracy; At the same time, its unique tag anti-collision algorithm supports simultaneous reading of a large number of item information, which can read up to dozens of asset electronic tags per second, and radio frequency can penetrate the plastic box to read the data of the underlying asset electronic tags Information greatly reduces workload, improves management efficiency, and reduces operating costs.

Use RFID technology, learn from the full life cycle and logistics management model, carry out business process reengineering, establish a dynamic and refined management of the whole process of the electric meter, and establish a supporting information technology support system to realize that the electric meter can be used from storage, on-site to scrap Accurate and efficient identification, realize the dynamic management of the whole process of the electric meter logistics process and on-site work process, establish the integration of production management and marketing management, and realize the life cycle management of the assets of the electric meter.
Establish a meter asset management workflow based on RFID technology and modern logistics technology, improve and optimize the existing operation methods, gradually replace the existing method of managing equipment through bar codes, introduce new management methods and methods, and improve the level of standardized measurement operations And efficiency, establish a new management model;
Through the introduction of radio frequency identification technology, the meter can be easily identified from warehousing, on-site to scrapping, solving the problem of weak asset foundation of the meter and difficulty in collecting on-site ledger data, providing users with a full range of asset tracking management methods;
Strengthen the management and control of on-site operation and maintenance work. Through RFID technology, on-site equipment can be accurately identified. At the same time, relevant equipment and user information can be inquired in time on the site, and on-site operation and maintenance information can be entered. This improves the efficiency of on-site operation and maintenance and strengthens the Supervision and management of on-site operation and maintenance work, and customer satisfaction has been improved;
Realize the docking of the marketing system and the warehouse management system, establish a more accurate data foundation and more efficient data exchange, and comprehensively improve the efficiency of meter asset logistics management;
By pasting a composite electronic label for each meter, a unique identification is established for each meter, which lays a solid data foundation for the improvement of future marketing operations and the use of related information management methods.
3. Scheme design
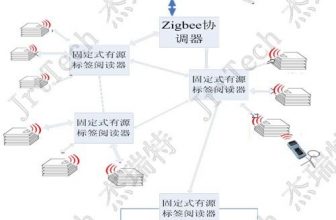
This system is an innovative project integrating RFID automatic identification technology, computer software and control technology, and network technology. Through the physical binding of the RFID electronic tag and the meter, and through the background data, the electronic tag information is associated with the identity information of the metered asset. At each subsequent node, the electronic tag information is obtained through the RFID read-write device to achieve the identity of the metered asset Recognition. This is the core of the entire system, and its frame diagram is as follows:

Establish a refined management application system for electricity meter assets based on RFID technology, optimize existing business processes, and realize a dynamic logistics management model, from leaving the factory, warehousing, verification, exporting to distribution, installation, operation and maintenance, and scrapping nodes. Refined and dynamic management of the entire life cycle. The system flow design is as follows:

The competent department assigns the serial number of the designated electric meter according to the sales demand. The serial number of the electric meter is assigned to the electronic label supplier by the competent authority. The supplier performs label printing and information writing according to the code. The printed electronic label is pasted on the production line by the meter manufacturer. The electric meter with the electronic label attached is delivered to the corresponding power supply bureau warehouse. Thus entered the RFID warehouse management information system of the grid company. For the electric meters that need to be in and out of the warehouse, RFID equipment can be used to collect data in and out of the warehouse.
When the electric meter with the electronic label passes through the scanning device, the antenna performs two-way data exchange with the electronic label through microwave communication, reads the relevant information from the electronic label (read the same information as the existing barcode), and transfers the data Information is transmitted to the data center in real time.
Code allocation
The code of the electronic label of the electric meter shall be allocated on demand by the superior department in charge. The competent superior department sends the planned electronic label code of the electric meter to the electronic label printing department. Started the first step of warehouse RFID management.
Electronic label printing, information writing
The printing and information writing of the electronic label of the electric meter can be completed by the RFID label supplier to ensure the correctness of the label information. The printing work can also be completed by the electric meter production plant, which saves the circulation link of the electronic label and reduces the operating cost of the system. Electronic label printing needs to be completed by a professional RFID printer, and the meter code is written into the electronic label data storage area while printing. Fonts and icons can be selected on the surface of the electronic label as required. In addition to the electronic label that needs to be attached to the electric meter, the electric meter turnover box of the power grid company also needs to stick a box electronic label. This work needs to be completed by the power grid company itself. The electronic label of the box is mainly responsible for bundling the data information of the electric meter, adding convenience to the working links behind the management system and providing operational efficiency.

Electronic label sticking
It is more convenient for the meter electronic label to be pasted by the meter manufacturer. The electronic label supplier sends the printed product to the corresponding meter manufacturer, and the meter manufacturer attaches the electronic label to the meter at the end of the meter production line. The electronic label pasting work must ensure the correct pairing of codes, so as not to cause confusion in the storage management of the power grid. The meter manufacturer transports the meter with the electronic label to the grid company warehouse for storage and verification.
Meter storage
The asset management team unpacks the electricity meters with the electronic tags pasted by the supplier and puts them in the turnover box. Through the RFID fixed reader installed on the warehouse conveyor belt, they automatically obtain all meter asset information in batches, and pass the information to The warehouse management system realizes the large-scale and fast warehousing operation of measuring assets.

Meter inventory
Meter inventory is mainly to check the number of meters and the number of meters in the warehouse. Meter inventory only needs to use RFID handheld device to scan the meter box number to check whether the meter is in the library and whether the quantity is complete.
Meter out of library
According to the business acceptance and inventory situation, through the outbound RFID reading device channel, the pallet-level meter assets can be shipped out of the warehouse in batches at the same time; multiple turnover box tags and meter asset tag information in the turnover box can be collected at one time, and The outbound task list is automatically checked. Provide a display of the outbound asset list, and can print the current outbound asset list; compare and verify the outbound assets. If the information between the outbound equipment and the outbound list is inconsistent, the system will give an alarm and require warehouse management After the equipment is successfully shipped out of the warehouse, the status will be changed to “pre-collected and ready to be installed”.
In other links of warehousing, according to the number of assets to be operated, RFID handheld devices and RFID fixed devices can be used to perform other operations such as verification and distribution of assets, including correction operations of electronic tag data, verification operations, and so on.
Site management
This part mainly uses RFID handhelds to perform installation, operation and maintenance and scrapping operations on the meters after being shipped out of the warehouse.
When installing on site, read the RFID tag on the device and confirm that the device information is consistent with the information on the business worksheet before allowing installation to prevent human errors in the recording and business process carry-over process. You can also download the business worksheet In the handheld, directly fill in the installed equipment information into the business worksheet after the installation is completed to ensure the accuracy of the data. After the equipment is installed, the asset status can be changed through the handheld. When the business is changing the meter, the meter change and the meter installation index can be recorded through the handheld device, and the information can be easily transmitted back to the marketing system. In daily maintenance, the staff obtains the past operation and maintenance information of the metered assets by reading the RFID electronic tags and adds and updates the latest maintenance information. For equipment that has reached the end of life treatment, the system will automatically remind the staff to scrap it, so as to complete the management of the full life cycle of the measurement asset.
4. System highlights
The system uses the latest international automatic identification technology-radio frequency identification RFID, combined with modern computers, automatic control and other comprehensive cross-domain technologies, uses ultra-high frequency RFID world-renowned brand ThingMagic M6 series products, and uses its powerful multi-tag anti-collision algorithm , High-speed information reading and processing capabilities, stable and reliable industrial-grade design, to realize automatic identification, information and intelligent management of power metering assets.

ThingMagic M6 has a reading speed of 750 tags per second, core anti-collision algorithms, high-speed information reading and processing capabilities, leading performance in receiving sensitivity, and flexible and effective parameter configuration according to the on-site environment. While improving the operational efficiency of the warehouse management of power metering assets, it also guarantees the correct rate. At the same time, ThingMagic M6 has a small size, high protection level, suitable for harsh working environments, and has a POE function, which is particularly suitable for simple and stable applications in an industrial environment. ThingMagic M6 has an enterprise-level MercuryOS embedded operating system, provides strong software support, and provides a complete RFID-based power metering asset management system for metering centers, which can bring the following benefits to power companies:
1. Establish a complete computer management system for the electricity meter warehouse to realize the management of the entire process of electricity meter electronic label printing, information writing, electronic label posting, data collection, data summary statistics, information analysis, query, and reporting;
2. The core multi-label anti-collision algorithm can read the entire box of electric meters in batches, which improves the efficiency and accuracy of the meter’s entry and exit;
3. Reduce labor intensity, improve management efficiency, and reduce operating costs;
4. The warehouse inventory can be completed quickly, and the warehouse inventory can be grasped in time.
Shenzhen Quanshunhong Technology Co., Ltd., as the leading RFID brand-Trimble’s ThingMagic general agent in China, while providing all major operators and integrators with ThingMagic’s full range of products, it is committed to cooperating with operators and integrators. ThingMagic UHF RFID equipment is applied to various applications in power grids, aviation and shipping, warehousing and logistics, clothing retail, manufacturing, anti-counterfeiting and traceability.
[ad_2]