UHF RFID technology applied to power asset management
[ad_1]
1 Overview of power asset management
Electric power companies are asset-decentralized enterprises, with many asset use departments, large use locations, complex structure classification, and large coverage. Assets can be divided into more than a dozen categories such as power transmission lines, substation equipment, power distribution lines and equipment, electricity metering equipment and communication equipment, automation equipment, tools and appliances, transportation equipment, buildings, land, and welfare facilities. In addition, usually due to the large number of power assets, large amounts, and fast update, management requires timely and accurate reflection of these changes. All of these pose challenges for the asset management of the power sector. The following analysis takes the common electric energy meter power asset management as an example.
Traditional power asset management methods generally rely on non-automated, paper document-based systems to record, track and manage; a few use barcodes to realize asset identification and management; but the efficiency is extremely low. With the increase in the number of assets, extremely The land has increased the burden on managers, a serious waste of human resources, and at the same time increased the difficulty of asset management, often causing problems such as untimely data and high error rates. Inventory management is often chaotic, and data in and out of the warehouse is wrong. If it is allowed to exist in a large area for a long time, it will bring great cost problems to the enterprise.
In terms of asset management application technologies, traditional automatic identification technologies such as one-dimensional barcodes/two-dimensional barcodes have also been widely used in item classification and labeling management. However, the barcode technology itself relies on visible light scanning reflection, low recognition rate, easy damage and staining of barcodes, and small amount of stored information. Generally, it only identifies a certain type of product, which affects its wide application in logistics management.
Compared with bar code technology, RFID radio frequency identification technology is a typical representative of non-contact long-distance automatic identification technology.RFIDThe technical identification has high accuracy, reliable performance, large amount of stored information, oil and sewage washing resistance, etc., and is especially suitable for automatic identification requirements in harsh working environments. Using RFID tags to replace bar codes and other identification products can effectively complete the automated management of assets, and realize the automatic collection, automatic processing and report output of asset information.
At present, RFID technology has been widely used in various fields such as logistics, vehicle identification, production management, and personnel card management. According to the performance advantages and disadvantages of RFID at various operating frequencies, RFID technology is mainly divided into low frequency, high frequency, ultra high frequency, microwave, etc. This article mainly uses UHF RFID technology for power asset management. Compared with other frequency bands RFID technology, its electronic label system has significant features such as long identification distance and simultaneous identification of multiple tags, which can meet the needs of the asset management process. Reliable identification of batches of multiple tags.

1.2 Construction goals of the asset management system
The modern asset management system mainly addresses the many problems faced by traditional management. It adopts UHF RFID radio frequency identification technology, computer processing technology, Internet communication technology and other information technology to realize the automatic identification of asset information and asset information in the management of power assets. Relevant operations such as acceptance, asset addition, asset disposal, asset allocation management, asset classification, asset retirement, automated/semi-automated inventory, accurate asset positioning, and automatic report output.
The main goals of using RFID radio frequency identification technology to manage power assets are to achieve:
● Timely and reliable location of assets
● Non-contact automatic identification of power attribute information
● Reduce the inventory cost of power assets, improve inventory utilization and audit frequency
● Adopt automatic/semi-automatic identification method to improve the accuracy and operation efficiency of inventory
● Realize real-time network sharing and management of power asset data, and complete report output according to needs
● Establish a unified power asset information platform to improve the level of asset supervision
1.3 Design principles of asset management system
The construction of a power asset management system should unify data standards, unify software, and unify hardware, adopt mature and reliable technologies, focus on integrity and practicability, and take into account advancement and scalability.
(1) Inheritance: to ensure the compatibility of the system with the existing test system, equipment and structure, and to maximize the use of the existing system.
(2) Advancement: The system adopts the combination of RFID technology and asset management system, which can effectively improve the efficiency of asset inspectors, and can realize real-time, accurate and effective centralized management of assets.
(3) Practicability: Starting from system requirements, meeting various functional requirements of the business to the greatest extent possible to ensure practicability. The software should be easy to operate and easy to master. It is easy to manage, maintain and repair.For the different environment and business requirements in the process of power asset allocation and transportation, it can easily and effectively complete the management of power assets, and different products must have strong targeted designs.
(4) Security: For system software and application software, attention must be paid to system security and confidentiality, and a secure network structure must be designed. RFID tags and related software must be comprehensively designed and planned for security, and electronic tags must be protected from malicious changes and cheating.
(5) Openness: System requirements should support relevant interface standards that comply with international standards and industry norms in terms of database and software development. In application development, the corresponding national standards and I/M business standards should be used. Open system internal standards and provide interface type descriptions. RFID UHF readers and electronic tags should comply with ISO/EPC and other relevant international norms and standards, and provide an open secondary development interface to support the development of mainstream RFID middleware products.
(6) High efficiency: It can ensure that the collection, transmission and use of the system have fast and effective operation efficiency, and the entire business process is brief and easy to use.
(7) Expandability: In terms of system design, it has good expandability, and can make necessary adjustments and expansions to the system according to information needs, including expansion of memory capacity and system functions. When the system software is fully upgraded, the availability of existing investment equipment can be guaranteed to the utmost. In terms of business requirements, basic data items can be expanded, and users can add relevant content according to their needs. The number of equipment can be expanded according to the needs of the business, and the overall technical solution structure does not need to be changed by the National Chiao Tung University.
(8) Reliability and fault tolerance: The reliability of the system should be considered as a whole in the design, and redundancy and error correction technologies should be used according to the function and importance of the equipment to ensure that local errors do not affect the operation of the entire network system . Equipment such as RFID readers and electronic tags must fully consider the use environment, interference factors, neighboring interference, media factors, wrong cards/bad cards and other uncertain factors, and provide various targeted solutions.
(9) Emergency response: The design of the central supervision system and the regular equipment inspection and supervision system must take into account potential emergency failures and failures, and an effective, fast and reliable emergency management system and corresponding service guarantee system must be designed. The emergency faults in the power asset management system can be dealt with in a timely and effective manner, and a set of effective solutions can be proposed.
2 The overall framework of the power asset management system
In the power asset management system, it is mainly warehouse management and data center monitoring and report output.The electronic label andReaderAll adopt the universal RFID protocol ISO/IEC 18000-6C, and its flexible scalability can ensure the application requirements for power asset management.
2.1 Overall system architecture
In the system, mobile RFID handsets and fixed readers are mainly used to complete the management of power assets (with electronic tags). In practical applications, in addition to the warehouse management of power assets, it also involves the information management of asset allocation and other links.
If a fixed reader/writer is used to manage the warehousing and exit of power assets, the basic operation is: when the asset is put in and out of the warehouse, through the radio frequency coverage area equipped with a fixed reader, the fixed reader reads To the electronic tag ID and attribute information affixed to the asset. The fixed reader/writer uploads data to the back-end workstation through the COM port/Ethernet port, and the local workstation makes a data interaction request to the back-end database. After the request is verified, it completes the database operation for in and out of the library.
If you use the handheld to perform real-time tracking and data service request processing for asset allocation and other links, the basic operation is: the handheld scans the property information of the allocated assets (scanning electronic tags), and the asset information is served through the GPRS data service of the mobile communication network Upload to the back-end server, the back-end server processes the data, and then returns the processing result to the handheld.
2.2 System design features
The power asset management system based on RFID technology can well solve a series of problems faced by traditional asset management. Its main features are:
(1) Good confidentiality
This system uses ISO/IEC 18000-6C protocol electronic tags, which have a unique 64bit ID number in the world, which can effectively identify all types of assets, down to item-level assets. Flexible encryption methods can ensure good confidentiality of the system.
(2) High reliability
Mature RFID technology and network communication technology can effectively ensure the high reliability of the system.
(3) Strong real-time data
Different from the traditional manual asset management mode, the RFID asset management system ensures real-time data through automatic identification and real-time network interaction, and has advantages in inventory and other operations.
(4) Strong scalability
The system has an open structure and a modular functional design. The system can be large or small, with more or less location points, and functions can be increased or decreased, so it has strong system adaptability.
3 System software design
The software system of the power asset management system based on RFID technology is mainly aimed at the actual needs of power asset management, and in accordance with the daily business process specifications, it has developed a stable, operable, easy to integrate and expand software system.
3.1 Main functions of system software
The functional modules of RFID-based power asset management system software are shown in Figure 2, including asset acceptance, new asset warehousing, asset use out of the library, asset report, asset query, asset inventory, asset report output, user authority management, and system management 9 functional modules such as maintenance and maintenance, the specific functions performed by each functional module are described below.
3.2 Design of main software modules
(1) Asset acceptance
Electronic tags are used as the identification of power assets (such as electricity meters, power transmission equipment, substation equipment, etc.). When the assets are checked and accepted, they complete operations such as encoding the electronic tags and inputting asset attribute information. After associating the ID information of the tag with the attribute information of the asset (name, quantity, quality, manufacturer, production date, etc.) through the tag issuance management software, upload it to the back-end database for future management.
The main operations of the asset acceptance module include:
• Count all the attributes of the labeling assets and enter them into the label issuance management system;
• The reader reads the ID information of the tag, and after uploading it to the system, the system automatically associates the two information;
• The reader writes key information into the memory of the electronic tag;
• In accordance with regulations, put the label on the specific location of the power asset
After the asset is checked and accepted, the key basic attribute information of the asset is recorded in the label, that is, the binding of the label ID and the asset attribute is completed. This information will uniquely exist in the subsequent operations.
(2) New asset storage
The storage of power assets here refers to the entry of electronically tagged assets into the warehouse.
When the asset enters the warehouse door, the electronic tag attached to the asset is read by the fixed reader to read the ID and other information. The asset information is displayed on the warehouse management system of the warehouse workstation (PC), and the warehouse administrator confirms the entry. The library information is uploaded to the back-end database, and the asset storage information entry operation is completed.
If a handheld computer is used to manage the warehousing, it is similar to the operation process of a fixed reader: the warehouse clerk uses the handheld to read the electronic tags and label information on the asset. After the warehouse clerk confirms that the asset matches the information, Upload data to the background operating system through wireless communication links such as wifi.
The judgment of warehouse entry/exit actions can be automatically determined by infrared beaming, ground sensing triggering and other technologies, or it can be obtained by confirming entry and exit through manual operation of the warehouse clerk. It can be handled flexibly according to the application environment on site. The design of the warehousing action in software processing will also vary by application.
(3) Asset use out of library
Similar to asset warehousing management, outbound attributes and warehousing information will be different, but the basic idea is the same and will not be described here.
(4) Asset inventory
The inventory of the assets in the warehouse refers to: the warehouse clerk uses the RFID handset to scan the asset tags in the warehouse one by one. When the electronic tag attached to the device is scanned, the equipment information in the electronic tag is displayed on the display of the RFID handset . After checking that the electronic label information is consistent with the actual asset attributes, the staff will upload the inspection results to the back-end server for processing in real time or at a specified time. The handset mainly uses wireless wifi communication technology to interact with the asset management back-end database.
5) Asset query and positioning
As asset management, such pseudo-problems are often encountered. Warehouse managers need to know the storage area and attributes of a particular asset in order to formulate a procurement plan or allocate such assets out of the library to achieve efficient use of assets.
The assets that can be queried are mainly obtained through the retrieval of key information, such as product firmware attribute information of the asset, and so on. The application system can quickly and accurately retrieve the queried information through the combined retrieval function of key information, and locate the relevant target asset to the position of the stacking position and shelf position. After the inquiry is over, the result of the inquiry will be submitted to the warehouse clerk for processing.
The key information that can be queried in the asset management system includes:
●Inherent attribute information of assets (product information, quality, quantity, etc.)
● Attribute information of asset warehousing (warehousing time, warehousing batch, warehousing operator)
● Asset storage information (storage location, storage change information, inventory output table)
● Asset owner information (owner unit, name, etc.)
● Asset changes and asset allocation information
● Breakdown of equipment
● Association information between assets
(6) Asset retirement
Retirement of assets refers to operations such as removing the asset information in the database to remove the asset’s use after the asset’s life cycle ends. The operations include: erasing the asset’s database information, dismantling or dismantling the electronic label, and scrapping the asset Wait to the recycling department.
(7) Asset report output
Through the automated platform system, the results of the operation are presented to customers in the form of reports. There are many forms of reports, which can be output to customers through various friendly interfaces such as images, text, and tables.
(8) User authority management
Security is an important issue to be considered in the information system. When users with different roles log in to the system, in order to prevent illegal operations and intrusion by illegal users, users must be managed by role-based authority.
For example, the user of the label issuing function has the authority to make labels, but not the authority of warehouse management, and each operator has a dedicated operating account and password to supervise and manage the operator’s work records. Illegal users will receive permission rejection and alarm prompts when logging in.
(9) System management and maintenance
System management mainly completes the correction and maintenance of system operating parameters. Complete permissions assignment, add, modify, and delete data forms, as well as system upgrade and management operations.
4 System hardware design
4.1 General description of the hardware
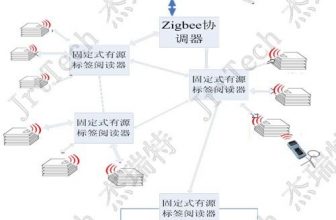
The overall architecture diagram and some network peripherals of the power asset management system are shown in Figure 1. In a mature RFID application system, the main hardware devices include: UHF electronic tags, UHF fixed readers, handheld readers, electronic label printers (printable barcodes), application servers, WEB servers, database servers, etc. . Taking a single warehouse as a unit, the warehouse access management can be managed by a fixed reader, the inventory location of warehouse assets can be managed by a handheld reader, and the issuance of electronic labels can be completed by electronic label printers.
In general, the fixed reader is installed in the warehouse gate identification area. When the asset with the electronic tag passes through the gate, the reader reads the information of the electronic tag and uploads the data to the back-end database system. After the information of the label is processed, the information of asset entry and exit is recorded to achieve the management of power assets.
In daily warehouse management such as warehouse inventory, when the portable handheld reader reads the data of the electronic tag, it uploads the data to the back-end database system through the wireless data link, and completes the data interaction with the database system. Automatic/semi-automatic operation of inventory. The following is the hardware layout design of various devices.
[ad_2]