RFID clothing anti-theft system
[ad_1]
1. System Overview
1.1. System background
With the improvement of people’s quality of life, it is the goal and ideal of most people to own valuable goods and luxury goods, but for shops, how to manage the loss of expensive goods and achieve profitability is the most important. Driven by people’s vanity and greed, some individuals will take the risk of stealing, and this behavior will bring great losses to shops. At present, many shops adopt the EAS anti-theft system, which is an electronic anti-theft product that reduces the theft of goods for retail businesses, thereby increasing sales and profits. The EAS system is used to detect when goods that are not authorized by the counter leave the designated area, and send out reminders and warning signals to remind the staff to carry out related processing. However, the existing EAS anti-theft system has shortcomings such as low detection rate, system false alarm, weak anti-interference ability, metal shielding, narrow protection width, and unrecyclable soft tags, which can no longer meet the existing anti-theft requirements.
1.2. Status Quo and Analysis
In view of some of the shortcomings of the existing EAS anti-theft system, our company recommends the use of RFID technology to realize the anti-theft of goods. The use of RFID technology can realize long-distance identification and automatic full-process monitoring of goods. It has the advantages of fast recognition speed, high recognition rate, and automatic acquisition of product information for the traditional EAS anti-theft system.
2. System Introduction
2.1. System Principle
RFID goods anti-theft management system integrates radio frequency identification technology, computer communication technology, and automatic control technology. First affix a label to each valuable item. The label contains detailed information about the item, including its production date, place of production, color, size, and price, etc. This information can be read by an RFID reader; in the store The RFID reader and RFID antenna must be installed through the passage. For example, the antenna and the reader are installed at the entrance and exit, and another desktop card issuer is placed on the counter to read and write or log off the sold products. When the unregistered tag enters and exits the door, the reader will close the IO port to control the external alarm Call the police to curb theft.
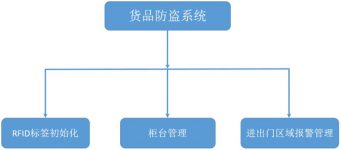
2.2. System structure
This system mainly consists of three parts: RFID tag initialization, counter management, and alarm management for entry and exit areas.

RFID tag initialization: label the product, the label contains detailed information about the product, such as: name, brand, price, status (sold or unsold), storage time, etc.
Counter management: cancel the label of the product.
Alarm management of entry and exit areas: Intelligent monitoring and management of important areas of entry and exit of goods, the system will immediately alarm when goods are illegally carried.
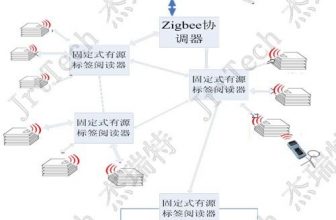
2.3. System Topology Diagram

Figure 2: System topology diagram
2.4. System Flow
2.4.1. Label selection and labeling
When using RFID technology to manage valuable goods in a store, it is necessary to select the type of tags. It is recommended to use EPC Class1 GEN2 tags. This is mainly because EPC Class1 GEN2 tags have good anti-collision properties, and RFID readers can read all within its identification range. EPC Class1 GEN2 tags, through this performance can ensure that all valuable goods within the scope of the reader’s recognition are monitored;
2.4.2. Store area division
The location and space of the actual area of the store depends on the actual situation of the store. The RFID anti-theft system of the store can be divided into three parts: monitoring area, security area and counter. The definitions of the three areas are as follows:
Safe place
In this area, the reader will not alarm when it reads any tags, that is, customers or salespersons can walk around with valuable goods in this area.
counter
The counter is an area where valuable goods are placed and displayed, and the counter is also a safe area.
Monitoring area
The areas outside the safe area (including the counter) become the monitoring area, such as the entrance of the store, and so on. When the unregistered tag passes through the monitoring area, the reader will immediately close the relay to turn on the external alarm to alarm. When the goods that have been sold (ie, deregistered or rewritten EAS data) pass through the monitoring area, the reader will not take any action.
2.4.3. Equipment installation
Reader installation
The reader can be installed anywhere in the shop.
Antenna installation
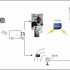
The antenna installation in the RFID store intelligent alarm system is particularly important. First, the number and size of the antenna should be selected according to the actual size of the store and the range to be monitored. Two RFID antennas can be installed in the monitoring area of the store, and the recognition ranges of the two antennas can be allowed to overlap, so as to ensure that the monitoring area is 100% covered. Install a desktop card issuer at the counter, and cancel the label on the sold goods through the antenna.

Figure 3: Schematic diagram of equipment installation
2.5. System flow chart

Figure 4: System flow chart
3. System Features
Automated monitoring
It can remotely monitor all tags within the antenna range. The antenna takes different operations on the goods after different processing methods, and activates the alarm function for the goods illegally taken out of the safe area. The whole process does not require manual operation.
Long-distance data reading and writing
The RFID reader can read and write tag information at a long distance, and can process multiple tags at a time, and can write the status of the goods into the tags, so that the antennas in different areas can perform corresponding operations.
Counter sales automation
The use of electronic tags can realize the functions of sales automation such as counter sales, return, counter inventory, inventory, and collection;
4. Other application areas
Anti-theft management for footwear and clothing stores
Anti-theft management for ceramic shops
Wallet, handbag store management, etc.
[ad_2]