Application of interactive smart electronic tags in the Internet of Things
[ad_1]
Since the concept of “Internet of Things” was put forward, both ordinary people and related professionals have paid great attention and demonstrated unprecedented enthusiasm. It is generally believed that the impact of the Internet of Things on people’s lives and social economy will far exceed the Internet. We believe that the Internet is a tool for people to communicate information through computers, and the Internet of Things is a tool for people to communicate with things or people in a passive state through computers, or the Internet of Things is The extension of the Internet from people to things.
1 The concept of the Internet of Things and related technologies
If the Internet is characterized by a network connection between a PC and a PC, the Internet of Things is characterized by a wireless connection between a PC and a low-cost microcomputer (ie, a single-chip microcomputer), and this wireless connection The way must be low cost, low power consumption, two-way and long-distance!
The Internet of Things should include at least the following aspects: perception of object information (including identity, location information, and status information), collection and transmission of perception information, information processing, and information feedback. We believe that this is also the most basic concept of the Internet of Things. According to the scope of the information transmission and processing related to “things”, the Internet of Things can be a relatively simple local area network consisting of only a short-distance information collection and transmission system and a computer with general processing capabilities, or it can include A wide area network including the Internet and “cloud” computers. When we connect thousands of these “small Internet of Things” together through various means of long-distance information transmission such as the public network and the Internet, and use the massive amounts of information they collect and gather, using the “cloud” with super processing capabilities. “When computers perform processing and provide information feedback through the network according to our various application needs, it forms the existing Internet of Things in the general sense.
The most critical link in the Internet of Things is the wireless information collection and transmission between the specific “things” below the public network and the PC. This includes the transmission of perception information and the transmission of feedback command information. Obviously, no matter it is a supercomputer, a mobile communication network, a sensor network, or the radio frequency identification system itself, none of them can meet the needs of the Internet of Things information transmission and processing alone, and none of them can represent the Internet of Things. The Internet of Things should not be a single network, but can include a combination of barcodes, passive radio frequency tags, various sensors, active radio frequency tags, mobile phones, various communication public networks, and supercomputers.
From an economical and practical point of view, it is impossible for us to install an active radio frequency tag on every toothbrush sold or on every item on the transportation pallet in the warehouse. A barcode label is obviously the best and most realistic choice. . Because the barcode recognition distance is very short, in order to transmit the information of the toothbrush or other items represented by the barcode to the network in a low-cost, simple and fast way, we can use the handheld barcode reader, including each warehouse transportation pallet Install an active radio frequency tag, and install a long-distance (over 500 m) active radio frequency tag reader connected to the mobile public network or the Internet in the warehouse. We can easily hold the barcode reader The information read about the toothbrush and the items on the tray is transmitted to and stored in the active radio frequency tag installed on the tray, and then indirectly transmitted to the active radio frequency tag reader through the active radio frequency tag, or The active radio frequency tag in the handheld barcode reader is directly transmitted to the active radio frequency tag reader. Then through the reader, the information is transmitted to the public network or the Internet. In this way, we can use a networked computer to grasp the relevant information of the toothbrush or the items on the tray, including their location information, anywhere.
Here we involve short-distance bar code recognition (also can be the collection of other sensor information such as infrared temperature measurement), long-distance wireless transmission of active radio frequency tags, computer and public information transmission networks, and the Internet. In this simple example, we can clearly see that the entire information transmission is not just a single transmission system or network, it is a combination of multiple information collection and transmission methods, which should be counted as a “ubiquitous network” .
From top to bottom combing the entire information connection and transmission process of the Internet of Things, it is not difficult to find: We have various supercomputers for information processing; we also have various public networks, mobile networks, and the Internet for long-distance information transmission; information; Perception We have barcode label recognition technology, passive radio frequency tag short-distance recognition technology, and various common sensor technologies (temperature, humidity, pressure, etc.) that collect item status information. But how to transfer the basic information about objects and people collected by sensors, barcode labels, and passive radio frequency tags to tens of meters or even 1 km away from the public network in a simple and low-cost manner , And the feedback instruction after information processing is returned to the “thing” in time has not been solved, and the key to the problem lies in: this transmission method must be low-cost and wireless, and it must be low-power and reliable.
Since the active radio frequency tag itself has the basic characteristics of simple structure, small size, low cost, low power consumption and long-distance transmission, it has naturally become people’s hope for solving the key problem of Internet of Things information transmission. However, due to the various limitations of the existing active electronic tags, it cannot meet the various needs of IoT applications, and a new generation of interactive smart electronic tags I-RFID has also emerged.
2. Interactive smart electronic tag I-RFID
Although there is no difference between I-RFID and existing general active electronic tags in structure, the working methods are completely different between the two.

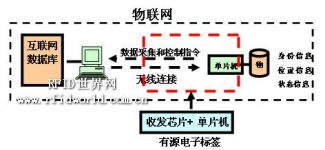
Figure 1 Application of I-RFID in the Internet of Things
As we can see in the figure, the key information transmission part of the Internet of Things is the wireless connection between the PC and the microcontroller. And this part must be composed of a single-chip wireless micro-power transceiver and a single-chip microcomputer. This is actually the basic structure of an active electronic tag. I-RFID uses an ultra-low power consumption method to maintain a fast two-way communication connection between the computer and the single-chip microcomputer connected to the “thing”; at the same time, by pre-writing various required application programs in the single-chip microcomputer, and The method of invoking these applications through wireless instructions when needed, enables the I-RFID tag to perform various tasks required by various IoT applications including identification, positioning, sensor data collection, etc., at any time and place needed. ! In this way, a key problem in the information transmission of the Internet of Things is solved in a low-cost way.

Figure 2 The working principle of I-RFID
The figure described is the active electronic tag in the low power consumption state of periodic monitoring-sleep-re-monitor-re-sleep. After receiving the command signal from the coordinator at the moment of wake-up monitoring, it will immediately follow the instructions and follow the pre-written instructions. Enter the state of information exchange with the reader, and complete the scheduled work tasks in a short period of time, and then return to the periodic monitoring-sleep-re-monitor-re-sleep low-power state. Waiting for the next work arrangement.
3. Application of I-RFID in the Internet of Things
Since I-RFID solves the key problems of low-cost and low-power wireless long-distance information transmission in the application of the Internet of Things, it naturally opens up the broad application space of I-RFID. Below we explain the example of the urban traffic intelligent management plan.
3.1 Urban traffic intelligent management plan
Intelligent management of urban traffic is the key to improving the efficiency of urban traffic management. The key issue of the intelligent management of urban traffic is how to realize the real-time collection and transmission of urban vehicle and road traffic information in an economical, effective and reliable way. Electronic tags, especially active electronic tag technology, are the most hopeful technologies. However, because the existing active electronic tag technology cannot solve the problem of achieving long-distance and on-demand bidirectional work under the premise of low power consumption and low cost, it also hinders its wider application and promotion. It has become a major obstacle for the Internet of Things to enter thousands of households and all walks of life.
After nearly six years of hard work in the practice of short-range wireless communication applications including Zigbee and RFID, West Valley has invented an interactive intelligent electronic label system with completely independent intellectual property rights in the key technology of active electronic tags. The existing active electronic tag technology is upgraded to a whole new level. Through the method of automatically jumping to the working channel of the label, the two-way communication problem of the interactive smart radio frequency tag is solved at low cost; the fast filtering technology of invalid signals solves the ultra-low power consumption problem of the interactive smart radio frequency label; the ultra-low power The combined working mode of consumption standby state and fixed action solves the problem of on-demand and flexible working of interactive smart radio frequency tags; through the automatic time division, frequency division and code division methods of interactive smart radio frequency tags, it solves the problem of massive radio frequency label information. Deal with the problem; through the use of new advanced and original positioning technology, the problem of precise positioning in different size application environments is simply and effectively solved. In addition, the communication distance of our active electronic tags can range from a few centimeters to 2 kilometers, far exceeding the existing general active electronic tags. Please refer to the attachment “Internet of Things and Interactive Smart Electronic Labels”.
3.2 Construction of basic urban data collection system
(1) In a fixed position on each car, install an anti-disassembly I-RFID smart electronic tag, which has a unique ID number in the world (of course, it can be renumbered by the user as needed).
The I-RFID smart electronic tag usually does not emit any signal, but periodically monitors the channel every 1 s or 0.5 s as needed, monitors, receives and records the signal sent by the coordinator by broadcasting (the Intersection location information and time information), after receiving and recording the signal of the coordinator, immediately jump to the working channel of the reader, and send back its ID number and the ID of the last intersection coordinator to the reader at the intersection Number (used to identify the direction of the vehicle), and after receiving the receipt signal sent by the reader, stop transmitting, and after a certain period of sleep, jump back to the monitoring channel to monitor the coordinator signal of the next intersection. If the system also needs to understand the traffic jam at the intersection, after receiving the receipt signal sent back by the reader, it will continue to transmit its own ID number to the reader several times every 10 to 30 s. In this way, the number of ID numbers from the same tag received by the reader at the same intersection can clearly understand the traffic jams in all directions at the intersection.
The I-RFID smart electronic tag has the function of preventing disassembly. It is driven by a AA lithium battery. Under normal circumstances, it can be used for six years without battery replacement. The two-way communication distance between it and the fixed reader at the intersection is adjustable from 5 to 300 m (uplink) / 5 to 700 m (downlink), and the communication distance with the handheld reader is adjustable from 1 to 100 m.
(2) Install a coordinator and an I-RFID tag reader that works on different channels and is connected to the network at each road junction that needs to be monitored for vehicles and traffic. Each reader uses 220V mains power supply. , The power consumption is less than 1W, and the information processing capacity of each I-RFID reader is 30 vehicles/sec=108000 vehicles/hour.
There are 83 independent channels available for readers at each intersection, and as many as 3,822 independent channels to avoid mutual interference with other 2.4G communication devices that may exist on site. The coordinator writes the position number of the intersection and the time of passing the intersection to all vehicles entering or about to enter the intersection by broadcasting. After the vehicle-mounted I-RFID tag receives and records the received information, it immediately returns its own ID number and the ID number of the coordinator at the front of the road. After the reader/writer receives the information sent by the vehicle-mounted I-RFID tag, it will transmit it to the system server together with the ID of the tag, the ID of the reader itself, and the time information through the network connected to it. The reader and the coordinator work on different channels, using 220V AC or other DC power supply, the maximum power consumption is <1W.
(3) Each reader (including the coordinator if necessary) is connected to the management control center database through a wired or wireless way (optical interface, ADSL or GPRS, etc.).
(4) The database and computer of the management control center will use the real-time vehicle information collected at each intersection to calculate the real-time flow of vehicles in the entire city and the specific location and driving direction of each vehicle at any time.
3. 3 basic functions of the system
Using the above information, combined with the patented wireless traffic light control technology (patent application number: 2007100488725), we can easily realize the function of urban traffic intelligent management:
Real-time and effective dispatch and command of traffic signal lights, including automatic green light release for state guest cars, emergency vehicles, etc.;
Provide the most true and reliable valuable information for city road planning;
According to the time that the vehicle stays in different areas of the city, without any other hardware investment, the collection of traffic congestion charges in the central city can be realized;
Provide paid service services of vehicle attendance and dispatch management to the owners of various vehicles in the city. (Such as buses, taxis, ambulances, delivery vehicles, maintenance service vehicles, public vehicles of government agencies, etc.);
According to the traffic conditions of the intersections of the whole city, the vehicles will be effectively and automatically guided;
Locate and track stolen vehicles, illegal vehicles, vehicles in arrears, and cloned taxis;
Since our data collection is 24 hours a day, when a traffic accident or a possible criminal offence involving a vehicle occurs, we can easily investigate and deal with the relevant vehicle based on time and location.
Due to the installation of intelligent electronic license plates on each vehicle, this will bring many other vehicle management benefits. It can easily solve many traffic management problems, such as the problem of cloning license plates, toll evasion, and non-parking charges. I-RFID electronic license plate is a kind of intelligent electronic license plate. It can not only provide ID number, but also directly provide any information about the vehicle itself required for management according to the command signal of the coordinator.
Conclusion: The basic concept of the Internet of Things should be the “perception” and transmission of the identity information, location information and status information of the “things”, as well as the processing and feedback of these information. The key to the promotion and application of the Internet of Things technology lies in how to realize the wireless long-distance two-way transmission of relevant information between specific “things” and PCs under the public network at low cost and low power consumption.
[ad_2]



