Automatic control system for bus dispatching and station reporting
[ad_1]
Chapter 1 Document Introduction
1.1 Document purpose
This document is a detailed description and preliminary design description of the overall framework and various functional subsystems of the bus dispatching and station reporting project, and serves as a functional summary description of the entire system, as the core basis for future transformation into system design, development, testing and acceptance .
1.2 Document scope
This document mainly completes the detailed description of the system status, overview, overall design, hardware, software, function and other modules involved in the system, and serves as the target of the system.
1.3 Audience
Responsible person of relevant department of Party A
Relevant technical person in charge
Party B’s project leader
Project designer of Party B
Party B project developer
Party B project tester
Party B’s project maintainer
Chapter 2 Status of Public Transport
2.1 Background introduction
With the rapid development of the national economy and the acceleration of urbanization and motorization, the scale of cities has continued to expand, and the number of motor vehicles and road traffic flow has increased sharply. Especially in large cities, the increase in public transport vehicles, the extension of lines, and the increase in the number of vehicles, traffic operation Not smooth. Despite the construction of a large number of transportation facilities, traffic congestion is still very serious. Many years of practical experience at home and abroad have shown that an important way to solve urban traffic problems is to develop public transportation, establish an advanced public transportation system APTS (Advanced Public Traffic System), and improve road capacity and bus operation management. The urban public passenger transport system has not yet introduced (or is in the process of) introducing advanced high-tech, and basically still adopts the manual dispatching method of “fixed departures and stuck points at both ends”, which causes the speed of public transportation vehicles to drop, and the driving interval is not balanced, which often occurs.” The phenomenon of “crossing of cars” and “large gaps” has seriously affected the service quality of public transport passenger transport. In particular, due to the lack of modern communication means, dispatchers cannot understand the conditions of operating vehicles in real time, and it is difficult to take dispatching measures in a timely and effective manner. Bus dispatching is in a backward status of “invisible and inaudible”, with greater blindness and lag. With the continuous development and progress of various science and technology and application technologies, urban transportation has gradually begun to move towards an intelligent and humanized road, which has led to the concept of Intelligent Traffic System (ITS), which is Advanced information technology, data communication transmission technology, electronic control technology, sensor technology and computer processing technology are effectively integrated into the transportation system, so as to achieve more accurate, real-time and efficient integrated management and control of the transportation system. Maximize the harmony and unity among people, vehicles and roads. Among them, an important direction of the development of intelligent transportation is the accurate positioning and navigation of vehicles in urban traffic, which has become an inevitable demand for the development of many industries (such as public transportation, fire fighting, emergency rescue, traffic accident handling, etc.).
2.2 Analysis of existing urban traffic positioning and navigation systems
2.2.1 GPS vehicle positioning and navigation system
GPS (Global Positioning System, Global Positioning System) is currently a relatively mature positioning and navigation technology, and has been widely used in practice. It uses 24 (including 3 spare) space satellites of the United States to achieve global coverage, thereby realizing global, all-weather, and omni-directional positioning and navigation functions. The GPS system mainly includes three components: the ground control part, the space satellite part and the ground user device (GPS receiver terminal). At present, it has been widely and successfully applied in urban vehicle positioning and navigation, and its positioning accuracy is generally 20m~300m.
2.2.2 A-GPS positioning and navigation system
A-GPS (Assisted GPS, network assisted GPS), it is an improvement to the GPS system, which adds a communication base station on the basis of GPS, so as to use the exact location of the base station and the received GPS satellite related information to achieve more accurate The accuracy of positioning and navigation can reach about 10m.
2.2.3 Beidou positioning system
The Beidou Positioning System is a regional satellite positioning system independently developed by my country. It is a system specially established for domestic positioning and navigation in my country. It consists of two geostationary orbit satellites, a backup satellite, a central control system, a standard comparison system and User terminal and other parts. However, due to the special working principle of the system, the positioning accuracy of the system is not as good as GPS, and the dependence on the ground network is also very large, so it is not suitable for the precise positioning and navigation applications in the special area of the city. It can only be realized in a large range. Rough positioning and simple navigation.
The above various current traffic vehicle positioning and navigation systems all have their own advantages, but they all have the following common shortcomings for the urban traffic positioning function:
1. All belong to the open positioning system, that is, once the network or satellite signal has a problem, the positioning function cannot be realized;
2. In some specific areas of the city, such as areas with densely distributed buildings, underground parking lots and other places and areas, the above system cannot achieve good positioning, that is, there are “dead corners” areas for positioning;
3. The accuracy of spatial stereo positioning is too low. Although GPS and A-GPS can achieve positioning accuracy within 10m, in terms of space, such a large error range cannot distinguish the position difference of the upper and lower lanes at the same place;
4. All GPS satellite systems belong to the United States. Once a special event (such as the United States because of war needs, it may limit the accuracy and coverage of civilian GPS), it may seriously affect the positioning of our urban civilian systems; Our country’s Beidou system is also completely dependent on the communication network, which is also not very reliable.
It can be seen that although most of the current positioning systems can meet the basic needs of urban traffic vehicle positioning, they are used in many special areas (such as densely-built areas, large underground parking lots, and positioning between the upper and lower floors of the same overpass, etc. ) Cannot be well satisfied and realized.Because of this, this document proposes a method based onRFID Technical urban traffic positioning and navigation system.
2.3 Current status and problems of the existing public transportation system
2.3.1 Status Quo of Public Transport System
Under the current management environment, after several years of development and construction, some public transportation groups have basically completed the internal network construction of the company, forming the IC card management center as the network center, radiating to various office and production places, as the company’s information Chemical construction provides the necessary hardware conditions. At present, the company has made some attempts in the construction of enterprise informatization, and has also implemented some independent and simple information management systems. However, the selection of this system is relatively isolated. It is a complete MIS system structure and framework, which has not really played a role. The purpose of information circulation and sharing is basically the printing and statistical functions in some links that are realized, which cannot reflect the detailed information sharing of the entire company, nor can it track and analyze the entire management process. Through detailed research on some companies, some companies still rely on manual information transmission methods, especially the reported information is very large, and multiple links often do the same work, resulting in a great waste of human labor. At the same time, because the company’s informatization construction is basically blank, many departments understand the enterprise informatization work as a simple printing and electronic process. For this purpose, there is still a lot of training and communication work to be done in the construction and implementation of informatization.
2.3.2 Existing problems
Through investigation and analysis, it is found that some group companies have some typical problems in terms of informatization, which are explained separately below.
Information island
The so-called information island means that between various functional departments and various positions, everyone’s information resources cannot be shared. Everyone enjoys their own information alone, and cannot be conveniently and timely provided to the relevant collaborative departments, even if this information is right. Other links are very important. For example: the main station and the company cannot grasp each other’s information in time.
Repetitive work
The so-called heavy repetitive work: It means that after the work of one link is completed, it needs to be processed and sorted again in another functional department. It is particularly obvious that the daily reports and other related reports of many functional departments have been repeatedly input and processed for many times, and the workload is very large. In fact, these tasks can be easily avoided in the information system, because in the information system, the entire information is shared. As long as you have the legal authority, you can enjoy the relevant information instead of going to various functional departments yourself. Collect and sort, or report to each functional department for sorting.
Problems that need to be solved urgently
Based on the status quo and on the basis of making full use of existing resources, the key and prioritized main problems of the bus company are the accurate monitoring of vehicle operation and the construction of a supporting on-site dispatching management system.
Chapter 3 System Overview
3.1 Goals achieved by this system
The main goal of establishing this system is to improve the intelligent management of XXX bus company’s dispatch and stop reporting. According to the data collected by the equipment, timely feedback the number of trips and kilometers of the vehicle, as well as the analysis of the vehicle operation benefit, provide a basis for the leadership decision-making. The specific goals are as follows:
1. Record and count the number of trips and kilometers of the vehicle: use data collection equipment to accurately record the time the vehicle departs from the starting station and arrive at the terminal. The system counts the number of trips and kilometers of the vehicle daily, and can be based on attendance data Corresponding to the number of kilometers the driver has traveled, so that human error and modification can be avoided, and objective and true data can be provided for use by relevant departments.
2. Attendance management of vehicles and drivers: Statistics and analysis of the attendance of vehicles and personnel based on collected data.
3. Vehicle operating status monitoring: It mainly monitors vehicles passing through the monitoring point. Data such as the time of the monitoring points passed by the vehicle and the number of trips can be monitored for use by various departments of the company.
4. Automatic vehicle station reporting: According to the monitoring point information collection equipment, vehicle identification card, and existing station reporting system, it automatically announces the station that the vehicle is about to arrive, and analyzes and predicts the time when the vehicle arrives at a station for passengers’ reference;
5. Parking lot management: It can count the number of vehicles parked in the parking lot with monitoring points, the parking time, and it is convenient to count or query the relevant information of parked or unparked vehicles.
6. Maintenance and fuel consumption management. Set up monitoring points in maintenance and refueling stations, and the system provides software interfaces to report maintenance and fuel consumption data to the dispatch center database for vehicle benefit analysis, effectively plugging man-made cost loopholes.
7. Analysis of vehicle operation benefits. Through the analysis of the actual vehicle mileage, fuel consumption, repair costs and other data, the vehicle operating benefits can be calculated, and the vehicles with lower benefits can be prompted for analysis by the relevant departments. Benefit analysis can also be carried out on the terminus and lines.
8. On-site scheduling information management. Information management such as attendance and violations of drivers and sales personnel, and information management of vehicle accidents, vehicle conditions, insurance, etc., and the above information can be automatically transmitted back to the center for relevant departments to call.
9. Data installation and authority management. Convenient and flexible rights management methods, authorized users can use which functions. A department can only see the data related to the work of its department, and the security of the data is strictly guaranteed.
10. Query, statistical analysis. Convenient and flexible query on all kinds of data for use. Calculate the attendance and operational benefits of all operating vehicles to form daily, monthly, and annual reports. The number of trips and kilometers of vehicle operation can be counted by route, terminal, individual, etc., to form daily, monthly, and annual reports.
3.2 Principles of System Construction
System construction includes both software and hardware. When developing, purchasing and integrating software and hardware, Shanghai Renwei Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. follows the following principles:
1) Advanced
The main construction idea of the automatic management system for bus dispatching and station reporting is to use wireless induction technology, embedded mobile computing technology and software technology to construct an adaptive wireless control system covering a large area. It has the advantages of advanced products, mature products and high cost performance.
2) Economical
On the premise of ensuring that the technical requirements are met, the system design uses products with the best performance-to-price ratio as much as possible. The construction of the system maximizes the role of some of the original equipment, such as computer networks, equipment, software, etc., saves investment for users to the greatest extent, and protects existing user investments.
3) Practicality
The construction of the system fully meets the application requirements and actual conditions of this project, highlighting strong practicability, friendly interface and simple operation.
4) Scalability
In the system plan, the system capacity and network development plan are designed according to the viewpoint of system analysis and overall planning, which not only considers the current ease of use, but also has appropriate advancement.
3.3 System design features
1) Highly automated. The system can automatically detect the time and location information of the controlled target passing through the controlled area, and automatically realize the attendance, statistics and safety management of the controlled target.
2) Mature and reliable network communication system. The wireless identification base station installed in the deployment control area transmits the collected information to the central centralized control system through the 485 industrial communication network or TCP/IP, GPRS, WIFI, etc. in real time, without human intervention in the whole process.
3) Complete data statistics and information query software. The system software has a dedicated database management system, including controlled target information collection and statistical analysis system, attendance statistics and management analysis system, display and print various statistical reports, and provide a full range of queries and management for senior managers Serve.
4) The safety, stability and reliability design of the system. The system products are designed to work continuously and reliably all day long in an outdoor environment.
Chapter 4 System Overall Design
4.1 System hardware composition
The main components of the system are as follows:
Information collection unit: long-distance reading and writing equipment;
On-board unit: remote electronic tag;
Information transmission unit: GPRS+GPRS antenna;
Site relay unit (site unit);
Bus dispatch center platform;
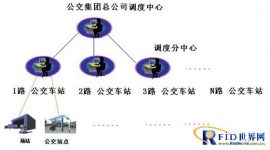
4.2 System network structure diagram
4.2.1 The overall topology of smart public transport construction

Intelligent bus systemConstruction is a long-term work, and it is a considerable scale project to complete the information construction of the entire link. Including investment in hardware construction and software system construction. Taking into account factors such as funding and ease of promotion, informatization construction should follow the principles of “comprehensive planning, step-by-step implementation, benefit-driven, and key breakthroughs”. Out of experience.
The so-called comprehensive planning means that in the construction and architecture of the entire system, we must fully start from the comprehensive informatization construction of the entire company, and cannot be limited to an existing partial goal. We must base on the overall informatization goal of the entire company. To build the system, so that the system will also have good scalability and integration in the future.
The so-called distributed implementation means that any set of information system is not a simple system engineering, which involves all aspects of the enterprise, not a partial problem. When we are in the previous system, we have to proceed in steps and cannot fully blossom. In this way, all aspects of the system can be slowly implemented and implemented. Especially in this public transportation intelligent system, we can first grasp the most urgent link of the company’s informatization requirements, parking lot and unmanned scheduling to focus and advance, and directly bring visible benefits to corporate information sharing, thereby driving others. Part of the system implementation.
The so-called benefit-driven and key breakthroughs means that we must grasp the core links of the company and make key breakthroughs so that the advantages of the system can be fully utilized. Once everyone sees the advantages and benefits brought by the system, the implementation of the system will be much easier , But also laid a good foundation for the overall rationalization of the system. Especially the company’s parking lot and unmanned dispatch. If these two links are implemented well, the company’s vehicle monitoring situation can be straightened out immediately and some human factors can be prevented. The company can fully analyze the entire process, find problems and Solve problems and provide reasonable and scientific management.
4.2.2 Bus dispatching and station reporting system diagram

System flow chart
The bus dispatching and reporting system has two parts in the management process: first, the bus station access control system (on-site management); second, the bus stop automatic identification system (off-site management);
1. The bus station access control system (site management)
Ⅰ. The topological structure diagram of the system
Including long-distance reading and writing system, background processing system, LED display system.
Ⅱ. The workflow and characteristics of the system
When the bus enters the parking lot, the remote reader reads the electronic tag number placed on the vehicle. The reader automatically transmits the globally unique number or vehicle-related information that it reads to the background computer for processing. This information is recorded and processed to record the entry time of the vehicle and vehicle-related information. The background determines which parking space the vehicle should be parked in, and transmits this information to the LED display. The driver can know through the LED display. Which parking space should be parked and some additional information, such as the next departure time (this time is the result of automatic calculation by the background computer), etc. When the bus leaves the field, the vehicle information is read by the remote reader, and the back-end system records the time and other information of the field and writes the records to the back-end database. The management of the whole process avoids human intervention, minimizes the operating cost of the system and reduces the inevitable losses caused by manual operation.
The functions and features implemented in the bus station management system include the following aspects: remote automatic recognition without stopping, real-time fixed-point collection of bus entry and exit times, determination of the parking lot location of the bus, dispatch center and parking lot LED display The card guides the parking space where the bus should stop after entering the station. This system avoids the situation that the bus is parked in other social parking lots and other nights and does not return at night. At the same time, it also prompts vehicle scheduling, traffic statistics, vehicle attendance, task assessment, and maintenance period. , Automated management of vehicle maintenance records, inspection records, etc.
Second, the automatic recognition system of bus stop signs (off-site management);
Ⅰ. The topological structure diagram of the system
Including remote readers, remote electronic tags, background processing systems, GPRS systems, and broadcasting systems.

Ⅱ. The workflow and characteristics of the system
When the bus leaves the bus station, it is recognized by the reader installed at the entrance and exit of the bus station. When the reader outside the entrance and exit recognizes the remote electronic tag attached to the bus, the reader will issue a special instruction to change the tag. Another special ID is activated. After the ID is activated, it will output a signal to the broadcasting system. At this time, the broadcasting system can broadcast the site information on time, such as: “Next stop at Gongzhufen Station, please prepare passengers to get off the train and get off. “; When the bus is 100-200 meters away from Gongzhufen Station of the bus station, the station-side reader will recognize the electronic tag on the vehicle at a long distance, and the remote reader installed at the station will issue a special instruction to attach it. Another special ID of the electronic tag on the bus is activated. After the ID is activated, it will output a signal to the broadcasting system. At this time, the broadcasting system can accurately broadcast station information, such as “Arrival at Gongzhufen Station in front, please get off the bus. Prepare and get off”; At the same time, GPRS will transmit the site equipment IP address and tag ID to the bus station dispatching sub-center, and the dispatching center will compare the site’s reader IP address and tag ID with the pre-stored information, so You can clearly know the specific location, driver, stop time and other information of a certain bus.
[ad_2]



