BRT traffic signal priority control scheme
[ad_1]
1. Reference basis
This solution refers to the following specifications:
GAT 527-2005 Applicable specification for urban road traffic signal control methods
GAT 509-2004 Urban Traffic Signal Control System Terminology
Traffic signal control guide-current German regulations
GB 25280-2010 Road traffic signal control machine
Signal Controller Manual
2. Principles of bus priority control

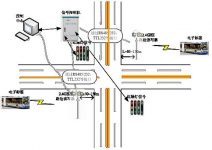
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of bus signal priority control
3. BRT signal priority control system scheme
Bus Rapid Transit (BRT for short) is a new type of public passenger transportation system between Rapid Rail Transit (RRT) and Normal Bus Transit (NBT). The volume of transportation is usually called “the subway system on the ground”. It is a unique urban passenger transport system that uses modern bus technology to cooperate with intelligent transportation and operation management, opens dedicated bus roads and builds new bus stations, realizes rail transit operation services, and reaches the service level of light rail.
Bus positioning and signal priority are key parts of the BRT system. The BRT signal control system is composed of a bus detection module, a traffic flow detection module, a communication module, a signal control machine processing module, and a signal light output module. The structure of the BRT signal control system is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 Structure diagram of BRT bus priority control system
Bus detection module
This solution uses RFID (radio frequency) detection system to detect and locate public transport vehicles. RFID vehicle detectors are installed near the intersection to detect public transport vehicles. When a bus approaching a road intersection, the RFID reader installed on the roadside will read the electronic tag information, identify the bus, and at the same time transmit the signal and time information of the bus’s arrival at the road intersection to the signal controller, and control the signal According to the number of public transportation vehicles arriving at the intersection, comprehensive consideration of information such as the queuing of social vehicles and the saturation of other lanes, the device judges the timing of the signal light, and extends the green time of the current release phase or breaks early, so as to realize the bus at the intersection. The signal is given priority, and social vehicles are also taken into consideration.
The RFID bus detector is usually composed of a vehicle-mounted electronic tag (also called a vehicle-mounted mobile unit) and a roadside reader (also called a fixed unit). The electronic tag is composed of an antenna and an RFID chip, and each chip contains a unique identification code to indicate the bus to which the electronic tag is attached. The reader is used to read and write the information in the electronic tag. The reader communicates with other computers or systems through the network to complete the information acquisition and data management of the electronic tag. Through the roadside reader near the intersection, the distinction and detection of public transportation vehicles are realized, so the signal controller can perform intelligent control of public transportation priority on this basis.
Install active electronic tags on BRT buses. The tags are placed on the upper right corner of the windshield of the front of the vehicle, and the equipment is placed on the top of the front of the vehicle.
The reader needs to get power from the signal machine, and the reader communicates with the intersection signal machine through the signal line. The installation location of the identification device is determined according to the maximum length of the green light that can be extended at the intersection in the traffic direction. Once determined, the location of the identification device is difficult to modify, and it is generally used on traffic arterial lines with relatively stable traffic flow. The construction of the reader does not need to break the road, but the construction from the installation position of the reader to the intersection road needs to be constructed on the green belt. After arriving at the intersection, use the pipeline of the intersection signal lamp to connect the reader to the signal machine.

Table 1 Installation specifications for readers

Table 2 Installation specifications of electronic tags
3.1.1 Main functions
Detect the arrival information of public transport vehicles. Including bus arrival time, direction and other information.
Detect the number of buses at the intersection. Each electronic tag has a unique code, and the tag uses “active” to send information and is in a state of always sending.
The electronic label information read by the reader is stored in the buffer, and the information is uploaded to the PC or controller through “active” or “passive”.
It can be used in conjunction with GPRS to perform real-time positioning of public transport vehicles, facilitating the monitoring and dispatching of public transport vehicles.
3.1.2 Main technical parameters
Reader
Working frequency: 2.4GHz-2.5GHz;
Working mode: The communication with PC and controller is passive;
Communication interface: RS232, RS485, Wiegand 26/34/66;
Horizontal lobe width: 75°
Vertical lobe width: 55°
RS485, RS232 communication rate can be set (9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600 (recommended), 115200);
With multi-label identification function: using anti-collision technology, the identification interval of tags can be adjusted according to needs;
Gain: 0~31dBi adjustable;
Reading distance: The reading distance of the reader is positively correlated with the gain. As the gain increases, the corresponding reading distance also increases. The total reading distance is the reading distance of the reader and the identification distance of the electronic tag. Sum.
Multi-buffer technology is used internally (the buffer capacity can read 512 tags at the same time);
Read tag type: comply with specific tag communication protocol;
Dimensions: 320mm×200mm×100mm;
3 indicator lights: (power light: always on as long as the power is turned on; working normally light: flashing once every 1 second; label indication: the label is on when it is read);
Weight: 2.5kg;
electronic label
Working frequency: 2.4GHz-2.5GHz;
Working method: active;
Transmitting power: less than 1mW;
Reading method: read-only;
Reading distance: 0-100 meters; 0-50 meters; 0-25 meters; 0-10 meters;
Water resistance: waterproof;
Working life: 5 years;
Static working current: <10uA;
Maximum working current: <15mA;
Working voltage: 3V;
Collision ability: It has a strong anti-collision ability, and the number of cards that can be read at the same time>200;
Size: 54mm×86mm×4.5mm
Vehicle flow detection module
In order to detect data such as traffic flow and vehicle occupied coil time, it is necessary to bury a detector at the intersection, and use Renwei’s centralized and coordinated signal control machine for flow detection and analysis. Renwei centralized and coordinated signal control machine is equipped with a vehicle detection module by default, which is used for vehicle flow detection in the four directions of north, south, west and east. The detection module can be used to interface with any other vehicle detector that uses dry contacts or OC transistors as output, and can also be directly connected to the detector provided by Renwei through a network cable.

Figure 3 The position of the detection module in the 4U control box of the signal machine
The location of the detector is about 1-60 meters away from the parking line, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4 Intersection detection layout
The coil detector is used in conjunction with the signal control machine and does not require third-party equipment or software conversion.
3.2.1 Main functions
Traffic information collection and processing function: Traffic information collection is the basic function of the detector. The detector judges the presence or absence of the vehicle by detecting the change of the coil induction, and then the CPU calculates the data to obtain the traffic volume, average speed, and time occupancy rate , Average vehicle length, average distance between vehicles and other traffic data. The sensitivity of the detector can be set manually.
Data storage function: The detector can store the calculated data. If the communication is interrupted, once restored, the historical data can be uploaded to the portable computer or control center via the communication port to keep the data intact.
Fault detection function: The detector has the detection of coil open circuit and short circuit faults. When a fault is found, the detector can upload fault information. The stored information can be displayed and consulted on the detector or an external device connected to the detector (the device can retrieve and display the stored information). Record the fault type and details L in the form of code or text; the time and date when the fault occurs, and the time and date when the fault is cleared can be queried through the maintenance tool and the central system.
3.2.2 Main technical parameters
Automatic compensation for environmental drift, which can automatically track environmental changes to achieve dynamic balance
Strong anti-interference ability, can work in strong electric field environment
With 8-level sensitivity adjustment, reliable vehicle detection sensitivity is 0.1% to 0.9% (threshold/base value)
Automatic sensitivity enhancement, and can automatically track the slow change of the sensor’s working environment, and can automatically adapt to sudden changes in sensor hardware conditions and sudden changes in sensor working environment
Can avoid interference between coils
Coil induction indicator, communication indicator
It has a complete self-check function, which clearly indicates the failure phenomenon, once the failure disappears, it will automatically resume work
Detection of multi-lane vehicles, up to 32 lanes
The detector has two functions: automatic reset after power-on and manual reset
Hardware watchdog to ensure long-term stable work
The detection response time is 15ms, and the inductance self-coordination range is 50uH~1000uH, so that the feeder length range is 5m~500m
Working outdoors all-weather, able to withstand harsh environmental conditions for a long time, vehicle false detection rate <±2%; occupancy detection accuracy: ≥95%; speed range 0~150km, vehicle speed detection error ≤5% (20~120km/h);
MTBF: 50000 hours
Input voltage: DC 5V ±10%
Input power: 1 W
Input current: 0.2 A
Working temperature: -20 ~ +70 ℃
Storage temperature: -40 ~ +85 ℃
Relative humidity: <95% non-condensing
Dimensions: L*W*H 200×110×45(mm)
Bus signal priority calculation module
The bus signal priority calculation module is the realization part of the BRT signal priority control algorithm. Including preprocessing module and intelligent decision-making module. The input information of this module is the vehicle information provided by the bus FRID detector and the lane coil detector, and the output is the signal priority control decision: whether to adjust (phase jump, end early or extend, etc.) the current phase time and adjustment range.

Figure 5 Signal bus priority control module
The function of the intelligent decision module is: based on the output of the preprocessing module, through the traffic demand intensity fuzzy inference technology, combined with the bus priority control strategy, calculate whether the green light time is adjusted (advanced, delayed or phase jump), and determine the adjustment value.

Figure 6 Intelligent decision-making module
The function of the traffic demand intensity fuzzy controller is to complete the fuzzy judgment and reasoning process of traffic conditions, that is, to determine the traffic demand intensity corresponding to each phase or each lane according to the detected traffic flow parameters, and then complete the function of a fuzzy classifier. The task of the green light adjustment fuzzy inference system is to compare the current green light pass phase with the next candidate pass phase, and give a green light adjustment (delay/advance/phase jump, etc.) decision and adjustment time.
Bus priority control mainly adopts the following strategies (as shown in Figure 7): green light time extension strategy, green light time advance strategy and phase jump strategy.

Figure 7 Bus priority signal control strategy
Green light time extension strategy
This strategy achieves bus priority by extending the green light time of the priority phase. When the bus arrives at the intersection (referring to the vehicle detector and is detected), but the phase is still a green signal and the remaining green time is not enough for the bus to pass through the intersection, in order to make the priority bus wait without stopping To pass an intersection, you need to extend the green time of this phase.
Green light time advance strategy
That is to shorten the red light time when the vehicle waits for the green light signal. When the bus arrives at the intersection, the phase of the direction of the bus is in the red light state. At this time, the green light execution time of the current phase of the intersection is shortened, so that when the bus arrives at the intersection, the green light signal can pass the intersection smoothly. Under this control strategy, under the condition that the cycle length is unchanged, the previous phase can be compensated with green light in the subsequent implementation of the phase sequence scheme.
Phase jump strategy
That is, the green signal of a certain phase is ignored. When the bus arrives at the intersection, the traffic direction of the bus is a red signal, and the execution green light time of the current phase of the intersection is about to end, and the next execution phase is still not the phase of the bus traffic direction, only wait until the phase is completed. After that, the bus can be allowed to pass. Since there are fewer social vehicles waiting to pass in the next execution phase of the intersection, on the basis of weighing the benefits, skip the next execution phase and directly execute the phase green light of the direction of the bus traffic, so that the bus will pass the intersection smoothly with the green light signal mouth.
[ad_2]



