Transportation one-card system solution
[ad_1]
Program overview
background
With the rapid development of the national economy today, the consumption index of various industries is constantly rising, and the number of people taking buses, light rails, subways, and taxis every day is countless. Therefore, a large amount of daily cash transactions and circulation are inevitable. With the development of technology, various cash payment methods have appeared on the market. As an emerging payment tool, IC card has the characteristics of high security, not easy to damage, can use one card for multiple purposes, and supports offline consumption. Has been widely used. However, public utility charges such as transportation have the characteristics of a huge number of customers, relatively low consumption, and high consumption frequency.
Therefore, using IC card payment methods to replace traditional cash payment methods in transportation and other fields is particularly important for user convenience, reducing operating costs, quickly collecting operating data, improving management efficiency and level, and providing auxiliary decision support for transportation management. Significance: The close integration of IC card and the application of public charging must become the general trend for a long period of time in the future.
Target
Based on the above background, local governments have been soberly following the principles of “integrating resources, one card for multiple uses, unified planning, and unified deployment” for municipal planning and construction. Centers, settlement banks, terminal applications, and card manufacturing centers are systematically integrated. The goal is to improve the transportation service environment of the entire city, reduce operating costs, prevent various risks, and provide citizens with more convenient, thoughtful and more humane services.
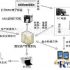
Traffic Card System Data Flow
.jpg)
Overall design
As a professional equipment provider in the industry, Zhuhai Zhongzhi Technology Co., Ltd. has established a complete, safe and stable card manufacturing center for different industries.
Design Principles
High security
The data required by the card making system is uniformly generated and encrypted by the data center, and transmitted directly to the making end through the network, without involving data copying. The data is assigned to the designated card making terminal according to the authority. After the card is made, the card-making result needs to be recovered in time, and the card-making situation should be tracked in time.
The card adopts the GP standard Java card, and the card is initialized according to the EMV card issuance process.
Good scalability
Card-making equipment can add different modules according to the needs of customers;
The card-making software can flexibly intercept the data and distribute the data to the designated module;
The application of different industries can be initialized by adding smart card modules.
The card adopts Java card, which can add different applications to realize one card with multiple functions.
Management standards, risk control
The card-making center uses a secure card-making management system to avoid data transmission through disks, which may lead to data loss and duplication.
In the process of making a card, you must log in to the card making management system safely, and perform the steps of blank card storage registration, card collection registration, and finished card mailing registration.
Network structure diagram of card system
.jpg)
Personalized content for cards
Chip content: including PBOC2.0 standard debit and credit application, transportation application, social security application
Card face information: print card number, name, expiry date
Card personalization process
The bank generates account opening data, and the branch uploads the industry data to the bank data center.
The data center integrates bank data and industry data to generate card issuance data.
The data center uses the secure card system to download the data to the card issuing center of each branch through the network.
The branch receives the card-making data, and the operator operates the card-making equipment to make the card.
Put the finished card into the mailing system, package the card and mail it.
Hardware Configuration
Card-making equipment selection
Datacard? MX6000? Card Issuing System
The overall speed of the MX6000 system can reach 1500 sheets per hour, and the operating speed is between 625 sheets and 1000 sheets per hour according to the different modules and module types used, and the amount of data processing. In particular, it depends on the amount of personalization data processing, such as embossing, smart card personalization, and laser engraving. And the design of MX6000 also allows adding modules to increase the speed of personalization.
MX6000 system configurable modules: including card entry box, card output stupid, magnetic writing, smart card module, embossing module, hot stamping module, flat printing module.
Packaging equipment selection
MXD card distribution system
Encryption equipment selection
Choose the appropriate model according to the customer’s own needs.
Software configuration
Security card software
Data management module-ciphertext data generation, storage, splitting, network transmission, use, destruction, etc.
Device management module-punch card machine status, enable and disable management
User management module-post, teller and transaction authority management
Blank card management module-management of purchase, summary, order, warehousing, inventory, query, requisition, inventory, allocation, destruction, etc.
Card-making management module-card-making task generation and authorization, card-making link linkage management, card issuing equipment selection and drive, task recovery management
Statistical report module-generate various required statistical reports
Affina? Data preparation software (optional)
The data generation process usually starts with a record containing cardholder data. For financial cards, it is a traditional magnetic stripe card personalization data file. The file contains different information for each cardholder. The Datacard data preparation system reads the information in the file and generates the required EMV parameters and new encryption elements, including keys, certificates and digital signatures.
The sensitive part of this data is encrypted and protected. The newly generated smart card data is appended to the cardholder data record and safely transmitted to the card issuing system for card personalization.
Affina? Personalized management software
Affina Personalization Management Software (APM) is a system based on the Microsoft® Windows® platform that centrally manages smart card personalization applications and other smart card “objects” on a central network server. The personalization management software also provides an application operating environment. The application runs on a central server and realizes the personalization of smart cards on remote personalization devices through the network. APM software supports GlobalPlatform?, MULTOS? and other proprietary card standards.
APM software centrally stores and manages keys used in the personalization process, various smart card applications and other smart card objects.
Smart card selection
IC card selection: fully consider compatibility, support EMV specifications, and support one card with multiple applications in a true sense.
Recommend Java Card
Java Card is a Java system structure for smart cards launched by SUN. The use of Java cards can speed up the progress of application development, avoiding developers to study the underlying structure of specific smart card chips, and can support multiple card applications and applications in a more flexible manner. Application addition and deletion after the card is issued. There is a firewall between different applications, and the secure communication between the card and the terminal can be realized through a secure channel.
Of course, if only from the functional point of view, the various functions of the Java card can also be implemented on the Native card. However, the methods for implementing the above functions of the Native card will be very different between different manufacturers, which increases the user’s personalization, Difficulties in application development.
The Java card has clear definitions in application download, deletion, personalization, card life cycle management, etc. This is the content of the GP (Global Platform) specification. Many smart card manufacturers, chip manufacturers, bank card organizations and telecom operators are all members of GP. The GP specification was originally the Open Platform developed by Visa. Therefore, the personalization of EMV cards refers to the GP specification.
[ad_2]