Military vehicle management based on 433MHz RFID
[ad_1]
Background needs analysis
At present, vehicle management mainly uses video recognition, 900MHz passive RFID, and 2.4GHz active RFID technologies. However, these technologies have the following problems in military vehicle identification:
1. Video recognition technology:
A. Because military vehicles are inconvenient to recognize by license plate, and some vehicle license plates need to be masked, the video recognition technology through license plate has no practical significance.
B. License plate recognition limits the speed of vehicles to a certain extent, which is not convenient for vehicles to move quickly.
C. Video recognition technology is inconvenient to use when performing tasks in the field.
2. 900MHz passive RFID technology:
A. Due to the short recognition distance (6M) of passive RFID technology and the characteristics of frontal recognition, the recognition of vehicles in the field is greatly restricted, which is not convenient for rapid recognition of vehicles performing field missions.
B. Since the recognition of passive RFID technology requires front reading to ensure the recognition rate, it is necessary to install a gantry at the entrance and exit so that the antenna is facing the vehicle RFID card to ensure a high recognition rate; if the antenna is mounted on the side, the recognition rate There will be a relatively large reduction. The gates of military barracks are generally inconvenient to install gantry gates. Therefore, this scheme has the disadvantage of low recognition rate.
C. Due to the large number of special military vehicles and the large number of vehicle models, the height and angle of the RFID card installed in different vehicles are quite different, which is another reason for the low recognition rate.
3. 2.4GHz active RFID technology:
A. Although 2.4GHz active RFID has a long identification distance (up to 80M) and good directional performance, it basically solves the problem of entering and exiting the camp, but compared with 433MHz active RFID technology, due to the poor diffraction performance of 2.4GHz active RFID, Vehicle recognition that performs tasks in a complex environment in the wild has the shortcoming of short recognition distance.
B. For some special vehicles, due to the insufficient penetration performance of 2.4GHz active RFID, the recognition distance of some special vehicles is short, which results in unsatisfactory recognition rate for entry and exit of some special vehicles and affects field recognition.
Features and advantages of 433MHz active RFID technology in military vehicle management
1. It has the characteristics of strong penetration, strong diffraction, and long transmission distance. It is suitable for various complex environments. It is particularly effective for vehicle identification for tasks in the field. It can quickly and remotely identify vehicles in the field through the handheld.
2. In view of the penetrability and strong diffraction of 433MHz, the electronic tag can be adapted to a variety of special vehicles at the same time, solving the problem of the recognition rate of 2.4GHz active RFID for some special vehicles.
3. Automatic long-distance recognition, long reading distance (adjustable from 1 to 150 meters), suitable for rapid vehicle identification, theoretical calculation, vehicle speed can be effectively recognized within 200KM/H.
4. Effectively solve the shielding problem of vehicle explosion-proof metal mesh and automobile film in the passive RFID solution.
5. Ultra-low power consumption, no radiation damage, safe and reliable to use.
6. It is easy to install and does not need to be installed on the front, which solves the installation problem of the electronic tag in the passive RFID solution that must be aligned with the antenna.
7. Allow vehicles to enter and exit in parallel (maximum parallel capacity is 100) without adding reader/writer equipment.
8. Due to the powerful long-distance characteristics of 433MHz RFID, it gives great convenience to the application of handsets. For the management of vehicles performing tasks in the field, only the handheld device is used, and the command vehicle passes along the vicinity of the convoy to scan the information of nearby vehicles.
9. For large-scale convoys, the handheld device can be used to check whether the vehicle is left behind, and the handheld device can also be used to check the vehicles that have entered the fork by mistake, intercept and direct the relevant vehicles to return to the correct road.
10. In addition, if all military vehicles are uniformly equipped with 433MHz tags, handheld phones can also be used to conveniently check fake military vehicles running on the road.
Scheme principle
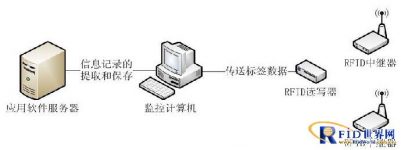
The system consists of “application software server”, “monitoring computer”, “RFID repeater”, “RFID reader” and “RFID electronic tag”.
The main realization idea is: stick the “RFID electronic tag” on the front windshield of the vehicle to realize one car and one card. Install “RFID repeaters” in the camp area or garage gate road, and the guard duty room will distribute management computers and install “RFID readers”.
When a vehicle with an “RFID electronic tag” needs to enter or leave the camp or garage, the “RFID repeater” obtains the signal of the “RFID electronic tag” and forwards the signal to the “RFID reader”. According to the “RFID electronic tag” information fed back by the “RFID reader”, the monitoring computer can learn the current vehicle entry and exit information and the vehicle entry and exit status, and match the information with the application server data to obtain the vehicle exit task information. If there is an exit task, the barrier will be opened to release the vehicle. If there is no exit task, the barrier will be closed (if the vehicle is a return unit, the barrier will be opened by default).
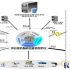
Schematic diagram of the overall structure:

Schematic diagram of vehicle entry and exit:

Schematic diagram of hand-held inspection of vehicle forks:

[ad_2]