RFID-based modular intelligent warehouse system
[ad_1]
1. Background
RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology realized by radio frequency communication. RFID tags are small in size, large in capacity, long in life, and reusable. They can support fast reading and writing, multi-eye identification reading, non-visual identification, mobile identification, positioning and long-term tracking management. The purpose of the RFID technology-based storage system design is to realize the automation of item out/in-warehouse control, item storage location and quantity statistics, and information query process, so as to facilitate management personnel to perform statistics, query and grasp the flow of materials, so as to achieve convenience, speed and safety. , High efficiency and other requirements.
Compared with traditional barcodes, RFID technology can store more information in the inventory management system, guarantee the reliability of storage, quality assurance and product category management on a larger scale, and can read any number of RFID tags from a certain distance , Which greatly reduces the workload and error rate of goods registration.RFIDIt also realizes the function of tracking products from the production of products to the consumers buying products from beginning to end, which can help companies find and solve problems in the supply chain as early as possible. In addition, real-time inventory and smart shelf technology based on RFID ensure the correctness of shipments and returns and the timeliness of replenishment; RFID solutions can provide accurate information about inventory conditions, and managers can quickly identify and correct inefficiencies. Operational situation.2. Introduction to RFID
2. Introduction to RFID
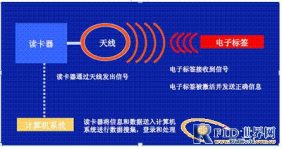
The most basic RFID system consists of three parts:
(1) Electronic tag (Tag)
Electronic tags, also known as radio frequency tags and transponders, are generally composed of coupling elements (antennas) and dedicated chips.
The electronic tag is the real data carrier of the radio frequency identification system. Each tag has a unique electronic code (ID number), and the tag generally stores electronic data in an agreed format. In practical applications, RFID tags are usually affixed to the surface of objects of different types and shapes, or even embedded inside the objects, so they will be made into different shapes as needed.
(2) Reader
A device that reads (and sometimes writes) tag information can be designed as a handheld or fixed type; the reader can read and identify without contactelectronic labelThe electronic data stored in, so as to achieve the purpose of automatically identifying objects. Usually the reader is connected to the computer, and the read label information is transferred to the computer for further processing.
(3) Antenna: Transmit radio frequency signals between the tag and the reader.
An antenna is a device that receives or radiates radio frequency signals from a radio transceiver in the form of electromagnetic waves.
2.2 The working principle of RFID
The reader sends out a certain frequency radio frequency signal through the antenna. When the tag enters the antenna radiation field, it generates an induced current to obtain energy, sends out its own coding and other information, which is read and decoded by the reader and sent to the host computer for relevant processing.

2.3 Advantages of RFID
Convenient and fast reading: Data reading does not require a light source, and can even be carried out through the outer packaging. The effective identification distance is longer. When the active tag with its own battery is used, the effective identification distance can reach more than 30 meters;
Fast recognition speed: as soon as the tag enters the magnetic field, the reader can read the information in it instantly, and it can process multiple tags at the same time to achieve batch recognition;
Penetration and unobstructed reading: The barcode scanner must be at a close distance and there is no object blocking the situation before it can read the barcode. RFID can penetrate non-metallic and non-transparent materials such as paper, wood, and plastics for penetrating communication. It does not require a light source and has a longer reading distance. But it does not recognize through conductive objects such as metals.
Large data capacity: the capacity of the one-dimensional barcode is 50Bytes, the maximum capacity of the two-dimensional barcode can store 2 to 3000 characters, and the maximum capacity of RFID is several MegaBytes. With the development of memory carriers, the data capacity also has a trend of continuous expansion. In the future, the amount of information that items need to carry will become larger and larger, and the demand for tags that can expand the capacity will increase accordingly.
Long service life and wide application range: The carrier of traditional bar codes is paper, so it is easy to be contaminated, but RFID has strong resistance to water, oil, chemicals and other substances. In addition, because the barcode is attached to the plastic bag or the outer packaging carton, it is particularly vulnerable to damage; the RFID label stores the data in the chip, so it can be protected from contamination, and the RFID has strong anti-pollution ability and durability.
The label data can be changed dynamically: the programmer can write data into the electronic label, thus giving the RFID label interactive portable data file function, and the writing time is shorter than printing a bar code;
Better security: RFID electronic tags can not only be embedded or attached to products of different shapes and types, but also can set password protection for the reading and writing of tag data, thus having higher security;: because RFID carries electronics Information and its data content can be protected by a password, so that the content is not easy to be forged and altered, and the security is higher.
Dynamic real-time communication: The tag communicates with the reader at a frequency of 50-100 times per second, so as long as the object attached to the RFID tag appears within the effective recognition range of the reader, its position can be dynamically tracked and monitored.
Small size and diversified shapes: RFID does not need to match the fixed size and printing quality of paper for reading accuracy. It is more suitable for the development of miniaturization and diversified forms to facilitate embedding or attaching to products of different shapes and types.
Three, system introduction
3.1 System management objects
1) The main body of warehouse management is the warehouse administrator, and its management objects include:
(1) Inventory: Items stored in the warehouse are the fundamental object of warehouse management; inventory is divided into three forms: pallets, boxes and bulk, limited to the current RFID is not suitable for management to each Small single items, so the unit of using RFID to manage items is the whole box and the entire pallet;
(2) Storage location: the area in the warehouse that is used to store inventory items and does not overlap each other in space. Generally, one storage location can store multiple inventory; it can also occupy several storage locations for a larger inventory. .
(3) Warehouse management equipment: equipment used for warehouse management, such as forklifts, trolleys, etc.; these equipment need to be reasonably scheduled and real-time positioned in large, busy warehouses to improve equipment utilization.
2) Warehouse management tasks
The main tasks of warehouse management are:
(1) Warehousing (incoming inspection)
(2) Delivery (selection)
(3) Move warehouse (replenishment)
(4) Disk library
(5) Generate various inventory reports according to needs
[ad_2]



