3PL Logistics Informationization Solution
[ad_1]
With the development of modern logistics industry, independent companies that provide logistics transportation and distribution services for Party A and Party B have developed rapidly, forming a third-party logistics industry. Striving to become a more specialized third-party logistics company with lower overall costs and higher distribution efficiency has become the development trend of the international logistics industry, as well as the direction of social division of labor and the development of modern logistics.
However, in the rapid progress of the logistics industry and logistics informatization, the overall planning, business characteristics, and implementation steps of the enterprise’s implementation of informatization will all have a direct impact on the effects of informatization. For example, the requirements of the various modules of the logistics system are also very different, the most prominent of which is inventory management; from an industry perspective, the fastest growing field of logistics information will be chain distribution; in terms of product characteristics, those products The areas where the update cycle is particularly short and the turnover rate is particularly fast are definitely the most concerned about logistics informatization. Therefore, the focus of informatization is determined by the business characteristics of the enterprise and is carried out under the guidance of industry characteristics. In addition, we must pay attention to the significant impact of logistics technology and information technology itself on the construction of logistics informatization.
Project Objectives
Through the implementation of the information system, logistics enterprises will eventually form a closer strategic alliance with customers and suppliers, realize a wider range of information sharing, save costs, and create a win-win situation in the logistics supply chain for Baosu, customers and suppliers. The overall planning and goals of logistics enterprise informatization are shown in the figure.
In terms of information system construction, it is necessary to realize the coordination of logistics, information flow and capital flow, and ensure the following goals:
1. Information is highly shared and interactive. In order to meet the needs of the joint logistics cooperation plan of various third-party logistics departments and their outsourced logistics partners, the system must have a certain degree of openness. In other words, the third-party logistics management information system should no longer be a closed island system, but must be an open and integrated supply chain information system built on the Internet, through a high degree of information sharing and interaction and supply Maintain good communication and contact with business partners, outsourcing logistics partners, and customers.
2. The scalability of the platform. The scalability of the platform includes two levels: one is scalability in space; the other is scalability in time. Spatial scalability means that the platform can achieve scale expansion in different geographic locations. Because logistics system facilities (such as warehouses) vary greatly in space, logistics information platforms must adapt to the geographic changes of logistics facilities. Time scalability means that when user needs, technological progress, and corporate organizational structure change over time, the system can transform some existing functional modules or add some functional modules to adapt to the new Variety.
In the development and optimization of logistics enterprises’ own business, the following goals need to be achieved:
1. Demand forecasting and management. Specifically, it is necessary to achieve the following two goals. One is to conduct market research before the demand side’s “order” is issued, collect historical data and related information of the demanding customer’s enterprise, and use various forecasting tools and methods to conduct market research on the demand side. Predict the needs of customers more accurately, so as to achieve “knowledge in mind”. The second is to integrate the information and data of the three aspects (the demander, the supplier and the resource conditions of the enterprise) after the “order” of the demander is issued, determine the order quantity, make a decision, and combine the supplier’s supply status and The company’s inventory conditions, make all preparations for receiving the goods.
2. Inventory optimization management. Inventory management is an intermediate link in the whole process management of third-party logistics companies. Reasonable inventory can not only ensure uninterrupted supply and meet customer needs, but also reduce unnecessary costs and expenditures of logistics companies. It is to achieve high-quality and efficient management of third-party logistics companies. key. Inventory optimization and management should achieve the following management objectives: First, organize the supply of goods according to order requirements. The second is to optimize inventory based on existing inventory and order requirements, and decide how much (quantity) to purchase? How to purchase (bulk)? And when to purchase (time)? The third is to manage a series of business activities such as inspection, loading and unloading and handling, sorting and processing, temporary storage of goods, and out of the warehouse based on relevant information.
3. Optimal management of transportation and distribution. Transportation and distribution management is the last link of third-party logistics management, and it is also a direct means to ensure the smooth flow of goods and fulfill customer needs. High-quality and efficient transportation and distribution management is extremely important to realize the optimization of the entire process of third-party logistics management. The following goals should be achieved: distribution according to customer needs; optimization and management of transportation methods and transportation routes, etc.
2 Analysis of logistics management system
2.1 Analysis of the business process of the third-party logistics (3PL) management system
Generally speaking, the functions of a logistics management information system include the following parts:
(1) Order management: use communication technologies such as email, fax and EDI or EOS to log in and maintain order information.
(2) Warehousing management: including items warehousing, material movement in the warehouse, sign for receipt and other links.
(3) Transportation management: including the formation of transportation documents, loading plans, and route development.
(4) Packaging management: including repackaging, sub-packaging, repackaging and other activities.
(5) Intelligence function: including plans, forecasts and related expenses related to the above-mentioned activities.
(6) Financial management: design cost accounting, freight calculation, etc.
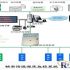
Business flowchart
Business process description: (1) The customer submits the delivery order: (2) The customer center authenticates the customer, and then enters the next step after the verification is passed. The customer center can also feedback logistics information to the customer in time to facilitate customer inquiries: (3) Order The module stores order information and sorts it out; (4) Sends relevant information to the decision center according to the order requirements; (5) The decision module consults inventory information, personnel and equipment information, and other transportation and warehousing outsourcing partners and suppliers data, and Analyze the historical data of operation and management, and then make a decision-making response, and submit it to the distribution center; (6) The distribution center negotiates with the corresponding distribution station or outside to carry out distribution, delivery, return and return of the goods, etc.: (7) Transportation point Perform distribution tasks; (8) The financial management module conducts financial settlement through the Internet or other means.
2.2 System characteristics
The third-party logistics management information system is a platform and system for logistics enterprises and large-scale manufacturing enterprises to conduct modern logistics business electronic management and operation. It has the following characteristics:
1. High openness. Based on INTERNET technology, there is no time and space limitation; the client uses a browser, no distribution is required, which reduces the workload of system maintenance to a minimum.
2. High adaptability. It can exchange information with third parties and customers through various communication channels such as XML/EDI, WEB, E-MAIL, FAX, and mobile phones.
3. High integration. The system integrates transportation systems, GPS systems, warehouse management systems, and other trade website connections to form a smooth supply chain management.
4. Highly intelligent. In the supply chain management, it is necessary to send instructions and real-time monitoring of automatic warehouses, GPS systems, barcode recognition, etc.
3 System design scheme
3.1 System structure
3.2 System development model and technology
Three-tier system architecture:
The three-tier structure is the development of the traditional client/server structure and represents the future of enterprise-level applications. Typical applications under the Web are B/S structure and multi-layer C/S applications. As shown below:
(1) The interface layer provides users with a visual interface. Through the interface layer, users input data and obtain data. The interface layer also provides a certain degree of security to ensure that users will not see confidential information.
(2) The logic layer (also known as the middle layer, intermediary agent) is the bridge between the interface layer and the data layer. It responds to user requests in the interface layer, performs tasks and grabs data from the data layer, and transmits the necessary data to the interface layer . Use clear language to state the argument.
(3) The data layer. The data layer defines and maintains the integrity and security of the data. It responds to the request of the logic layer and accesses the data. This layer is implemented by a large Oracle database server.
The advantages are:
(1) It has flexible hardware system composition and better support for distributed computing environment.
(2) Improve the maintainability of the program.
(3) The thin client model.
(4) Carry out strict safety management.
In addition, the system is easy to manage, supports heterogeneous databases, and has high availability.
4 System software design
4.1 The overall functional structure of the system
The functional structure of the third-party logistics management information system can be divided into four levels: data management layer, business processing layer, decision-making management layer and strategic management layer. The overall function description of the logistics management information system of the third-party logistics is shown in the figure:
Overall functional structure
4.2 Overview of the main functions of the system
(1) Customer Relationship Management: customer login management, customer information management, customer identity verification, customer inquiry, and customer relationship management;
(2) Order Management Subsystem (Order Management): order receiving, sorting, and querying;
(3) Warehouse Management Subsystem (Warehousing Management): Inbound Management, Outbound Management, Inventory Check, Warehouse Optimization Management, Goods Inquiry Management
(4) Distribution Management Subsystem (Logistics Distribution): Contains various functions closely related to the distribution business process, such as carrier management, settlement, intermodal transportation planning, vehicle scheduling, distribution and loading management, route selection, in-transit monitoring, and distribution planning Management, stowage of goods, receipt of goods on arrival, etc.
(5) Decision-making subsystem (DS): feedback information management, partner management, supplier management, market forecast management, market information management, enterprise internal information release management (including company introduction, business philosophy, laws and regulations, market quotations, etc.) ;
(6) Accounting management subsystem (Finance Management): cost budget management, customer financial settlement, supplier financial settlement, partner financial settlement, financial statistics management, human resource management of each subsystem, personnel attendance management, equipment maintenance management ;
(7) System Management: Initialization, user management, data backup, operation authority management, data collection interface management, system settings, etc. Permission setting function interface:
5 System safety design
The logistics information management system ensures the security of the system by making full use of the security of OS, Application Server and database, combined with strict user, role and authority management.
Each information system user (that is, each natural person) has a unique login code and password. Once the user logs in to the system, the system can learn the system user category (customer, logistics center, warehouse, code and Name).
Each information system user can only access authorized information, and any information accessed without authorization cannot be accessed. The system access authority is granted only when needed, and functions without access authority are not visible to information system users at all.
6 concluding remarks
Reasonable design and implementation of logistics management informatization, relying on modern methods to help manage logistics enterprises, and provide accurate, timely, and abundant information are the basic requirements for the development of modern logistics as a third-party logistics enterprise. Logistics enterprises can combine their respective scales, strengths and characteristics to implement informatization in a timely and forward-looking manner, and rationally allocate resources such as storage, transportation, equipment, and human resources, so as to ensure the effective connection and efficient operation of all links of the enterprise, so as to build a collection of transportation and storage. Lay the foundation for a large-scale network logistics enterprise that integrates multiple functions such as distribution, packaging, loading and unloading, handling, circulation processing and information processing.At the same time, through the construction of a powerful, complete and practical information system, the management level and economic benefits of the logistics industry are improved, the intermediate links of logistics are reduced, the logistics cost is saved, and the gap with the advanced level of international logistics is shortened.
[ad_2]