Kelu Electronic Asset Management System Solution
[ad_1]
1. System overview
With the popularization of computer and barcode recognition technology, the warehouse assets of most companies have begun to use computer data systems and barcode scanning for management, but the data is still recorded on paper and then manually input into the computer; or scan the assets one by one with a scanner Barcode, and then transfer the data to the computer for collection and statistical collation. This not only causes a lot of waste of time and human resources, but also due to human factors, data entry and barcode scanning speed is slow, and the accuracy rate is low. This traditional method has been difficult to meet the fast and accurate requirements of warehouse asset management, which has seriously affected the work. Efficiency has become a major obstacle restricting the development of enterprises.
This system is based on the most advanced Internet of Things RFID radio frequency identification technology and computing information processing technology to complete the automation, batching and information management of goods in and out of the warehouse, to ensure the rapid and accurate data input in each link of the warehouse asset management To ensure that the company can grasp the real data of the inventory in a timely and accurate manner, and reasonably maintain and control the company’s inventory. Through scientific coding, it is also convenient to manage the batches of items. Using the system’s warehouse map location management function, you can also grasp the current location of all inventory equipment in time, which is conducive to improving the efficiency of warehouse asset management.
2. Technical advantages
The technical principle of the project is the Internet of Things RFID technology. RFID is the most advanced object recognition technology in the world. As a representative of the latest technology, it is a new growth point and development driving force for the world economy. RFID is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification, that is, radio frequency identification. RFID technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology, which automatically recognizes target objects and obtains related data through radio frequency signals. It consists of two parts: electronic tags and readers, which can realize long-distance, large-scale automatic identification. The reader can identify electronic tags within a distance of several centimeters to tens of meters, and can read and identify objects, equipment, vehicles and people with electronic tags in batches, regardless of whether they are stationary or in motion. Recognition, which has become a dazzling new star in the field of automatic recognition.
RFID technology has the following advantages:
(1) Quick scan
With traditional barcode recognition, only one barcode can be scanned at a time; RFID readers can simultaneously identify and read multiple RFID tags.
(2) Small size and diversified shapes
RFID does not need to match the fixed size and printing quality of the paper for reading accuracy, and is more suitable for the development of miniaturization and various forms to facilitate embedding or attaching to products of different shapes and types;
(3) Anti-pollution ability and durability
The carrier of traditional bar codes is paper, so it is susceptible to contamination, but RFID is highly resistant to substances such as water, oil, and chemicals. In addition, because the bar code is attached to the plastic bag or the outer packaging carton, it is particularly vulnerable to damage; RFID tag is to store the data in the chip, so it can be protected from contamination.
(4) Reusable
Nowadays, the barcode cannot be changed after it is printed. The data stored in the RFID tag can be dynamically updated, and it can be recycled and used multiple times.
(5) Penetrating and barrier-free reading
Bar code scanners must be close and without obstructions before they can read bar codes. RFID can penetrate non-metallic and non-transparent materials such as paper, wood, and plastics for penetrating communication. It does not require a light source and has a longer reading distance.
(6) Large data memory capacity
The capacity of a one-dimensional bar code is 50 Bytes, the maximum capacity of a two-dimensional bar code can store 2 to 3000 characters, and the maximum capacity of an RFID is several megabytes. With the development of memory carriers, the data capacity also has a trend of continuous expansion. In the future, the amount of information that items need to carry will become larger and larger, and the demand for tags that can expand the capacity will increase accordingly.
(7) Security
Since RFID carries electronic information, its data content can be protected by a password, making the content less likely to be forged and altered, and has higher security.
3. Application prospects
Today, with the rapid development of the Internet of Things, apply the Internet of Things technology to enterprise warehouse management, make full use of the Internet of Things RFID technology (Radio Frequency Identification), and establish an asset management system that meets the requirements of modern enterprises, so that the enterprise’s asset equipment management can be realized. Automatic, fast, and batch operation can not only greatly improve work efficiency, increase the economic efficiency of the enterprise, and demonstrate the advanced management level of the enterprise, but also implement the “energy saving and emission reduction” and “vigorous development of materials” proposed by the country in the 12th Five-Year Plan. Established policies such as “Networking” and “Building Smart Grid” conform to the general trend of international and domestic development.
At present, the power asset management system based on the Internet of Things RFID technology has been practiced and applied in metering centers and meter libraries in many provinces and cities such as Beijing, Tianjin, Shandong, Henan, Hubei, and Guangdong, and achieved very ideal results. There is no need to manually scan the barcodes for power assets in and out of the warehouse. The centralized identification device (reader) at the entrance and exit of the warehouse can automatically identify the electronic tags on the assets and upload the label information to the main station system in real time. The assets in and out of the warehouse are truly automatic, With fast and large-scale operation, managers can also keep track of the status of asset entry and exit at any time to achieve efficient management. This system greatly saves the manpower, material resources, and time of the power supply enterprise, improves work efficiency and economic benefits, and has broad application prospects.
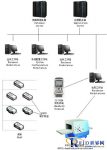
Four, system composition
The system consists of three parts: electronic tags, readers (handheld terminals, centralized identification devices) and master station management software. The electronic label is pasted on the asset equipment; the handheld terminal can individually identify the number of electronic labels in the designated area, and communicate with the main station software through GPRS or USB, upload and download related parameters and data; the centralized identification device is responsible for centralized identification of electronic Label and store data; the master station management software is responsible for system data storage, business logic processing, system parameter configuration, data browsing, and query functions.
4.1 Electronic label
Electronic tags replace traditional barcodes and are the data carrier of the asset management system. They are composed of antennas and chips. Each tag has a unique electronic code (ID number), and the tag can store electronic data in the agreed format. According to the requirements of the power supply company, the factory Write the device number and other information into the electronic label before. The electronic label will be made into different shapes according to actual needs, affixed to the surface of the device, or embedded in the device. The electronic tag can also be used as an identifier to identify the operator who enters and exits the warehouse.
4.2 Reader-Handheld Terminal
As a small handheld reader, the handheld terminal is mainly used to read electronic tags in a small area. Compared with the fixed centralized identification device, the handheld terminal has the characteristics of flexibility, mobility, and convenience to carry. Find assets, single tag identification, information records, and other operations. In addition, the shelves can be numbered according to the area. The handheld terminal can read the electronic label information on all the devices in the area, and send the read information to the main station system server through USB, GPRS, WIFI, etc. The main station management software can Perform asset inventory and draw warehouse maps based on this information.
4.3 Centralized identification device
When the equipment enters and exits the warehouse, the equipment must pass through the RFID centralized identification device to enter and exit the warehouse. The reader in the RFID centralized identification device reads the electronic tag information in the equipment to automatically enter and exit the warehouse; when the equipment enters and exits the warehouse,RFIDThe reader in the centralized identification device reads the electronic label information in the equipment, and if it is not authorized to enter and exit the warehouse, it will alarm, otherwise it will complete the automatic entry and exit operation.
4.4 Master station management software
The main station management software is divided into three parts: business program, system configuration program and database server.
4.4.1 Business procedures
The business procedures are divided into two sections, one is asset storage and exit management, and the other is business expansion and new installation project management.
Asset warehousing management includes the following main menus: daily operations, archive data, information query, statistical reports, and system settings.
1. Daily business. Daily business operations, mainly including asset storage, asset verification, asset exit authorization, asset exit, asset damage registration, asset maintenance, asset retirement, shelf position management, etc.;
2. File data. Mainly provide detailed file information of assets. Including the asset number, asset type, storage time, warehousing person, verification information, asset status, storage time, leaving the storage person, applicant, user unit, etc. Each item of the archive data is a drop-down menu that provides options and the content can be modified. Therefore, this menu is only authorized by the system administrators, warehouse administrators and other high-level management personnel, and ordinary operators have no right to open this menu.
3. Information query. Mainly provide asset equipment information query, shelf warehouse information query, work order query, etc. The content provided by the asset equipment information query is similar to the content of the above-mentioned archive information. The difference is that the information queried in this menu is unmodifiable, and it is a general menu that can be used by any operator; multiple query conditions are provided, including assets Number, operator, storage time, etc.; support single and list query. Inquiry of shelf warehouse information, mainly provides contents such as shelf and warehouse usage, asset location, remaining warehouse positions, and equipment distribution map inquiry. A work order will be generated for each warehousing operation, with a corresponding work order number. The work order query can be based on the work order number to query the operation record, or according to the time or the operator to query all the work orders and print the work orders.
4. Statistical reports. Count the current equipment quantity, storage quantity, outgoing quantity, remaining positions, etc. The following reports can be provided, such as a statistical table of warehousing and exit conditions, a statistical table of assets by number, a statistical table of operation records, a statistical table of asset status, a statistical table of asset usage, and a statistical curve of business volume.
5. System settings. Mainly refers to the general settings of the business operating system, including operator password settings, shortcut key settings, serial port settings, etc.
4.4.2 System configuration program
The system configuration program is used to configure various parameters of the system. It mainly includes the following main menus: system parameter configuration, system management, and system maintenance.
1. System parameter configuration. Mainly configure the power, frequency, data receiving mode settings of the reader, read and write mode, time and related menu definitions, etc.
2. System management. Mainly include operator authority setting, operator role definition, warehouse definition, etc.
3. System maintenance. Mainly include dictionary table maintenance, data source maintenance, system administrator setting, etc.
4.4.3 System configuration program
The database server is used to store data.
5. System implementation plan (take power supply company as an example)
5.1 Establish master station and substation
The main station server of the asset management system is located in the headquarters, the database and main station system are installed on the server, and the system clients are installed in the headquarters warehouse, related operator computers, power supply stations, and business halls, through the internal LAN of the power supply company, each client You can access the master station system according to your own authority, and view and use different information and data according to different authority.
5.2 Put an electronic label on the device
Attach electronic labels to power meters, collectors, transformers and other equipment. Electronic labels are usually affixed before the equipment leaves the factory. They can be affixed to the surface of the equipment or embedded in the equipment as needed. The shape and size of the labels can be changed as needed. And customization. Equipped with a label printer in the warehouse, if the label on an individual device is damaged and cannot be read, a new label can be printed on the spot to replace the damaged label.
5.3 Establish an identification device (read-write device) in the warehouse
Identifyelectronic labelThe device is also called a reader. Usually four-channel fixed readers and handheld readers are used in warehouses. The four-channel fixed readers are usually placed at the door of the warehouse and made into open radio frequency doors or closed centralized readers. The identification device, when the equipment enters and exits the warehouse, it can identify dozens to hundreds of electronic tags in batches within a few seconds, and upload the tag information to the main station server, management personnel and business through the data line and the network. The operator can inquire about the equipment in and out information through the client terminal on the personal computer.
5.4 The overall structure of the system
[ad_2]


