Application of Radio Frequency Identification Technology in Mobile Payment Technology
[ad_1]
In recent years, with the continuous advancement of technology and the popularization of mobile phones, the role and function of mobile communication has not only ensured smooth communication, but has become multi-purpose and multi-functional. Mobile phones will also become people’s information terminals and carriers. RFID-based mobile payment technology is a technology that uses mobile phones as a carrier to realize multiple applications such as mobile payment, identity verification, and all-in-one cards. As the carrier, the mobile phone combines a variety of applications of contactless cards, allowing users to enjoy a variety of services anytime and anywhere, enriching the connotation of products and services of all parties, and enabling all parties to provide customers in a convenient, efficient and safe manner. Existing and innovative products and services.
1 Radio frequency identification technology
1.1 Radio frequency identification technology
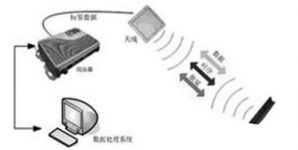
Radio Frequency IdentificaTIon (RFID) technology is an application technology that is easy to control, simple and practical, and is particularly suitable for automatic control. It uses magnetic or electromagnetic fields to perform non-contact two-way communication using radio frequency to achieve the purpose of identification and Exchange data, can identify high-speed moving objects and can identify multiple targets at the same time. The basic principle is to use the transmission characteristics of radio frequency signal coupling or radar reflection to realize automatic identification of the identified object. The RFID application system includes three parts: tags, readers and RFID application platforms. Its working principle is: the reader sends a radio frequency signal of a certain frequency through the transmitting antenna. When the radio frequency card enters the working area of the transmitting antenna, an induced current is generated, and the energy obtained by the radio frequency card is activated; the radio frequency card encodes itself and other information through the built-in transmitting antenna of the card. Send out; the system receiving antenna receives the carrier signal sent from the radio frequency card, and transmits it to the reader through the antenna adjuster. The reader demodulates and decodes the received signal and then sends it to the background main system for related processing; The system judges the legitimacy of the card according to the logic operation, makes corresponding processing and control for different settings, and sends out instruction signals to control the action of the actuator.

Figure 1 RFID system structure diagram
1.2 Application status of radio frequency identification technology
In recent years, with the development of technologies such as large-scale integrated circuits, network communications, and information security, RFID technology has entered the stage of commercial application. Due to the characteristics of non-contact recognition, multi-target recognition and high-speed moving object recognition, RFID technology shows great development potential and application space. It is considered to be one of the most promising information technologies in the 21st century and has been highly regarded by the global industry. Pay attention, especially in the United States, Britain, Germany, Sweden, and other countries that have relatively mature and advanced RFID systems. At present, RFID has been widely used in many fields such as industrial automation, commercial automation, and transportation control management, such as:
Manufacturing: real-time monitoring of production data, quality tracking, automated production, personalized production, etc. can be applied to the production process. The application in the production of precious and sophisticated goods is even more urgent.
Anti-counterfeiting: RFID technology has the characteristics of being difficult to forge, but the cost is relatively high. The current application areas include: anti-counterfeiting of valuables (tobacco, alcohol, medicine), and anti-counterfeiting of tickets.
Transportation: High-speed non-stop, taxi management, bus hub management, railway locomotive identification, etc. There have been many successful cases with great application potential.
Military: identification and tracking of ammunition, guns, materials, personnel, trucks, etc.
2 Application of RFID technology in mobile payment
2.1 Application of RFID technology in mobile payment
At present, RFID-based mobile payment mainly includes four solutions: NFC, eNFC, SIMpass, and RF-SIM, all of which are derived from the development of RFID technology.
NFC (Near Field CommunicaTIon) near field communication technology is evolved from the integration of non-contact radio frequency identification (RFID) and interconnection technology. It combines inductive card readers, inductive cards and point-to-point functions on a single chip. Identify and exchange data with compatible devices within a short distance. The working frequency is 13.56MHz. However, users who use this mobile phone payment solution must change to a special mobile phone. At present, this technology is widely used in Japan and South Korea. Mobile phone users can travel across the country with their mobile phones equipped with payment functions: their mobile phones can be used for airport boarding verification, building access keys, transportation cards, credit*, payment cards, and so on.
The “e” in eNFC stands for “enhanced”, which means enhanced, and eNFC means enhanced NFC technology. In addition to being 100% compatible with NFC technology, the enhanced version also includes support for two other widely used ISO standards, namely: ISO 14443B and ISO 15693. eNFC is a combination of mobile phones and smart cards, using SIM cards As the core, the smart card application is placed in a single-chip SIM card, and the non-contact function is implemented by the NFC chip built into the mobile phone, and communicates with the SIM card through the SWP protocol.
SIMpass is a dual-interface SIM card payment solution that integrates antennas and radio frequency chips. It supports contact and non-contact working interfaces. The contact interface realizes the SIM function, and the non-contact interface realizes the payment function. It is compatible with multiple smart card application specifications.
RF-SIM expands the functions of traditional mobile phone SIM cards by building a short-range identification chip in the SIM card. RF-SIM can be installed on a mobile phone to achieve short-range wireless communication. The communication distance can be automatically adjusted from 10-500cm. It supports 100M in one direction and its working frequency is 2.4GHz. But this technology does not support ISO14443.
2.2 Application prospects of mobile payment based on radio frequency identification technology
With the development and popularization of mobile technology, mobile payment has gradually become a new form of electronic payment service. Mobile payment has the characteristics of mobility, timeliness, personalization, convenience, etc., enabling users to complete transactions with various objects anytime and anywhere as long as they hold the phone in hand. According to data released by China UnionPay, as of the end of 2009, the total number of customized mobile payment users in my country exceeded 21 million. In the first half of 2009 alone, 62.685 million transactions were completed with a total payment amount of 17 billion yuan. According to data released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the number of mobile phone users in my country reached 747 million in 2009. This makes mobile payment more and more popular among banks, mobile operators, merchants and consumers. Compared with traditional mobile payment (SMS, WAP, etc.), RFID-based mobile payment has great advantages in user acceptance, convenience, and payment security. First of all, due to the technical characteristics of RFID, it is easy to complete the simulation of various cards (bus card, silver **, membership card, etc.). Therefore, after using the mobile phone payment technology based on RFID, the mobile phone integrates the functions of various cards, and a mobile phone can meet the needs of people in all aspects of food, clothing, housing and transportation. Secondly, whether traditional mobile payment is SMS, WAP or other methods, it needs to pass through the wireless network. How to ensure the security of transmission in the wireless network has become an obstacle that restricts traditional mobile payment. For RFID-based mobile payment methods, although the mobile phone and the acceptance terminal (such as POS machine) are also wirelessly transmitted, because the distance is very short (within 10 cm), the possibility of intercepting the signal is very low, and the acceptance terminal and The back-end uses the standard PBOC2.0 specification for data transmission, and the information security is guaranteed. Moreover, the RFID-based mobile payment process is to use the mobile phone close to the surface of the accepting terminal (such as POS machine). This payment process is undoubtedly simpler and more convenient than traditional mobile payment methods such as SMS and WAP, making users more willing and accepting This way of operation.
The development of RFID technology has given technical support for mobile payment, and the huge market prospect of mobile payment in the future also provides a broad market space for mobile payment technology based on RFID. At present, China Mobile has successively launched pilots of mobile phone micropayment services in Shanghai, Beijing, Chongqing and other places, mainly using RFID-SIM technology. After China UnionPay and China Unicom also launched smart card mobile payment services in Changsha, they launched a commercial trial of UnionPay card mobile payment in Shanghai, and will jointly accelerate the promotion and application of a new generation of mobile payment across the country.
3 Restrictive factors and suggestions for development in our country
Although RFID-based mobile payment technology has bright prospects and has successful cases in Japan, South Korea and other countries, there are still some problems that need to be resolved if it is to play an important role in my country’s future third-party payment market.
First of all, my country currently lacks a unified mobile payment industry standard. Due to the different international mobile phone payment technology standards, the three major domestic operators and UnionPay have their own choices. If they are allowed to develop independently, incompatibility is likely to occur, which restricts the user’s use and experience and is not conducive to mobile phones. Large-scale development of the payment industry. Therefore, the early promulgation of industry standards is particularly necessary. Moreover, the acceptance terminals (cash registers, POS machines, vending machines, etc.) that consumers contact when making transactions require the formulation of a series of industry technical standards and reach consensus with related industries and enterprises. Only when standardization is achieved and the market scale is expanded, the truly easy-to-use, safe, cheap, and standardized mobile payment technology products will become more abundant and gradually penetrate into all aspects of people’s work and life, so that users can truly appreciate the convenience of mobile payment.
The second is the divergence of business models. Mobile operators value mobile payment because most mobile phones have to go through its network; UnionPay values mobile payment because the most ideal form of mobile payment is to integrate credit* functions. As all parties in my country’s mobile payment industry chain are still in a “fuzzy” state of rights and status, the existing business model has the problem of “ineffective cooperation”. For mobile payment to take shape, full integration of the communication and financial industry industrial chains is required. However, both parties want their own advantages to dominate the entire industrial chain, which is not conducive to the development of the market. Only when all parties work together can the mobile payment market develop rapidly in the future.
In addition, the construction of supporting environment cannot be ignored. This not only includes investment in “hardware” such as the construction of mobile payment networks, the laying or transformation of relevant acceptance terminals, and personnel training, but also the support of relevant policies, commercial promotion of the entire mobile payment business, and reaching a unified settlement standard with banks Such as the construction of “software”, these are also one of the keys to the successful promotion of mobile payment.
As the combination of mobile electronic payment and RFID technology continues to mature in the future, combined with the successful experience of foreign countries, the mobile payment industry has shown us a bright future.
[ad_2]



