Dual-band mobile phone mobile payment solution
[ad_1]
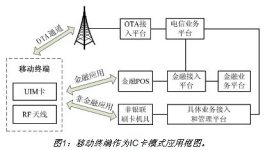
At present, mobile terminals based on mobile phones as IC card models can be divided into two types according to application scenarios: financial applications and non-financial applications (Figure 1).
The financial application scenario is based on the payment application in the SIM card certified by UnionPay as the main body, and cooperates with UnionPay or bank POS devices to realize the financial payment function. Mainly include PBOC/qPBOC debit and credit application, PBOC e-wallet/passbook application, electronic cash application, etc.
Non-financial application scenarios refer to non-UnionPay-certified or compatible SIM card applications that cooperate with non-UnionPay POS devices to achieve electronic money payment, points, ID recognition, security control and other functions. Mainly include public transportation application, industry application, small area (enterprise, campus all-in-one card) application, security identification application, etc.

Mobile payment market demand and major problems
China is a mobile payment market with huge potential. There are currently more than 500 million mobile phone users, 150 million credit card users, and a huge number of all-in-one card users. With the evolution of the 3G era, these users will shift from traditional cash or credit card payments to new non-contact mobile phone mobile payments. The huge market demand has brought pressure to many manufacturers in the mobile payment industry chain, such as operators, card developers, mobile phone manufacturers, and chip suppliers, as well as new opportunities. At present, mobile payment based on mobile phones continues to rise in the world, such as buying drinks, buying tickets and so on. Mobile phone-based mobile payment applications are highly valued by mobile operators and service providers. Mobile payment has its own advantages: it has a large potential user group and the low penetration rate of credit cards in China; the portability of mobile phones provides a basis for developing various mobile payment services, and the operation is simple and fast; at the same time, with the help of mobile communication networks, mobile payment It can be carried out anytime, anywhere, across time and geographical constraints.
According to the space and time characteristics of payment, the current mobile payment service can be divided into off-site non-real-time remote payment and on-site real-time payment (Figure 2). Off-site non-real-time remote payment is a commonly used payment method at present. This method generally initiates a transaction request through SMS. From the perspective of the payment speed, there is an obvious time delay. It takes a few seconds when it is fast, and even a few when it is slow. minute. The mobile phone bills, shopping, mobile banking, etc. currently carried out in China all belong to this type of off-site non-real-time remote payment.

Due to the obvious time delay, off-site non-real-time remote payment has been unable to meet the application areas of urban all-in-one cards such as bus tickets, rail transit, and taxi fares. In this case, on-site real-time payment transactions are required, and the payment transactions can be quickly completed through non-contact communication between the mobile phone and the payment device, so that it only takes a few hundred milliseconds to complete a transaction.
Dual frequency mobile payment solution
There is an urgent need in the market for a mobile payment product that meets this feature: it supports both 13.56M and 2.4G, and can achieve high security, scalability and low-cost deployment. Therefore, the dual-band mobile phone mobile payment solution came into being and stood out among many technologies, becoming the best technology choice for telecommunications and financial operators to easily carry out their business.
The dual-band mobile payment solution is a completely independent research and development by Shanghai Huahong Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd., a contactless mobile payment solution formed by combining China’s national conditions and international advanced technology. It also supports contactless mobile payment and mobile payment based on 13.56M SWP technology. 2.4G contactless mobile payment.
Hua Hong’s dual-band SIM card technology solution includes hardware circuits, SWP/HCI protocol stacks and multi-interface priority relations developed by COS.
Dual-band SIM card composition and circuit
The dual-frequency SIM card is similar to a normal SIM card in external physical form, except that it encapsulates a chip that supports multiple functional entities inside the card body.
The payment chip (security master control chip) provides payment functions, other value-added service functions, and radio frequency chip control functions. It also provides a physical channel between the SIM card chip and the user terminal and provides telecommunication functions.
The 2.4G radio frequency chip is controlled by the payment chip, which can realize radio frequency function, basic radio frequency protocol, and provide radio frequency communication channel of dual-frequency SIM card reader.
SHC1228 chip can provide dual ISO7816 interface function, or provide ISO7816 plus SPI interface function. Abundant interface resources enable SHC1228 to adapt to a variety of security control chips and radio frequency modules, greatly expanding the functions of the SIM card, providing a new carrier for mobile operators and developing value-added services other than communications, and greatly increasing card developers The flexibility to choose a variety of contactless mobile phone mobile payment solutions (Figure 3). The advantages of its application are very obvious, including:

1. Meet the latest international standards. It adopts the single-wire communication protocol SWP and supports the latest eNFC mobile payment architecture. The solution has been tested for commercial use in Europe and China, and it has become a widely recognized solution in the industry.
2. Support dual-band mobile payment solutions. It has the advantages of 13.56M and 2.4G, and has a very wide range of applicability.
3. High security. It supports DES/3DES, RSA1024, and provides multiple security protection mechanisms to ensure its strong security and anti-counterfeiting capabilities. Support a variety of mainstream encryption authentication algorithms to improve the security level of smart cards; authentication: EAL4+.
4. Strong flexibility and adaptability. The password and access conditions of each storage sector can be defined according to different applications, so as to meet the requirements of different occasions and different purposes without affecting each other. It can realize independent storage and security management of bus transportation, micropayment, mobile banking, commodity consumption and other industry applications.
5. Strong performance compatibility. Complete business application testing with most domestic and foreign mainstream brand mobile phones, and joint debugging with a number of financial and ticketing terminal POS machines, and its performance is excellent.
The circuit connection of the dual-frequency scheme is shown in Figure 4. The connection of SHC1228 and mobile phone terminal: SHC1228 connects the mobile phone baseband chip through 7816 to realize telecommunications applications; connects the mobile phone CLF chip through SWP to realize 13.56M channel contactless mobile payment applications. SHC1228 and RF chip connection: SHC1228 and 2.4G RF are connected by serial interface. 2.4G RF transmitter and receiver wake up SHC1228 with external interrupt.

SWP/HCI protocol stack
Hua Hong dual-band solution provides SWP/HCI protocol stack, which enables card manufacturers to save time and R&D costs.
SWP (Single Wire Protocol) is a single-wire connection scheme based on the C6 pin, which is a physical layer protocol. Simply put, it uses a data cable to communicate the user card and the NFC chip, and then connects to the outside through the NFC chip.
In the SWP scheme, the interface interface includes three lines: VCC (C1), GND (C5) and SWP (C6). The SWP signal line realizes full-duplex communication based on the principle of voltage and load modulation, so that the user can be stuck in The ISO 7816 interface definition supports both 7816 and SWP interfaces at the same time.
The HCI (Host Controller Interface) protocol belongs to the network layer protocol. The HCI protocol defines the interface between Hosts, including: different hosts exchange commands, responses and events by establishing Pipes between Gates; defines a set of HCP (Host Controller Protocol, host control) Protocol) message mechanism; defines a set of HCP routing mechanism, responsible for the transmission of messages between different hosts, and fragmentation of messages when necessary (Figure 5).

Multi-interface priority relationship
The dual-frequency solution has traditional 7816 telecommunication interface, SWP interface and 2.4G radio frequency interface. The priority relationship needs to be handled correctly in the COS development process.
When telecommunications applications and 2.4G applications occur at the same time, 7816 telecommunications applications are given priority, but 2.4G applications are not affected. When telecommunications applications and SWP (13.56M) applications occur at the same time, 7816 telecommunications applications are given priority, but 13.56M applications are not affected.
Supportable applications
The dual-frequency solution combines the advantages and characteristics of 13.56M and 2.45G technologies, and can integrate multiple applications, and each application is isolated from each other. The specific functions of these applications include: school/enterprise all-in-one card application, identity recognition, mobile online banking, electronic wallet, Bank Card application, bus all-in-one card application, coupon function, and wireless communication function.
[ad_2]