The application scheme of RFID radio frequency identification in the management of seed resource bank
[ad_1]
Preface
Faced with the severe changes in the global climate and the threat of future wars, all countries are striving to build their own national seed bank for the continuation of their own agricultural species. For example, the “Rice Gene Bank” seed bank established by Thailand holds 24,000 kinds of rice. Seeds, the “Global Seed Bank” built by Norway is known as the Noah’s Ark of human agriculture, and China’s largest seed resource bank was established in Kunming; seeds are important agricultural production materials that have vitality and are a special commodity. It is the core driving force of agricultural development, and it is the “commanding height” that stabilizes grain production and develops modern agriculture.
Strengthen seed information management measures to increase the utilization of good varieties. The management unit should standardize the quality supervision of a series of procedures for seed production, processing, packaging, inspection, and storage, and resolutely prevent fake and inferior seeds from entering the market. With the rapid development of information technology today, how to use advanced information technology to improve the level of seed resource management has become an extremely urgent need. With the rapid development and application of RFID radio frequency identification technology in recent years, domestic and foreign seed resource companies have begun to apply RFID technology to manage seed repositories. Monsanto in the United States, Limagrain in France, and domestic Wanxiang Denon and Denghai Seed Industries Large-scale seed companies at home and abroad have begun to use RFID radio frequency identification technology to implement full-process monitoring and traceability in all aspects of seed production, processing, transportation, storage, packaging, inspection and sanitation.
1
, my country’s seed industry development
Since the “Seed Law” was promulgated at the end of 2000, the seed industry has truly entered the stage of marketization. The state abolished the control of major crop seeds, breaking the former state-owned seed company’s dominance of the world. Various private seed companies were established one after another and foreign seed companies entered my country, which opened the prelude to fierce competition in the Chinese seed industry. Seeds are classified according to the business varieties, which can be divided into grain crop seeds (corn, rice, soybean, wheat, etc.), cash crop seeds, vegetable seeds and flower seeds. Corn seeds and rice seeds are highly commercialized. The value of my country’s seed market has grown from 20 billion yuan in 2001 to more than 50 billion yuan at present, and my country has become the second largest seed market after the United States.
2. Design requirements for seed resource bank
2.1. Seed bank classification:
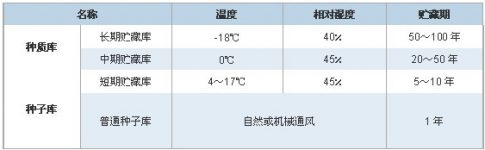
The seed bank is a special warehouse used to store important species resources. The storage environment (mainly temperature and humidity) has a great influence on the lifespan of seeds. According to the different temperature and humidity environment in the warehouse, traditional seed storage buildings can be divided into 4 categories:

2.2. Design basis for seed bank:
Seed life span refers to the period of time that seeds can maintain their viability under certain environmental conditions. Heredity and development environment determine the inherent life span of seeds; harvest, drying, processing conditions, and storage conditions determine the aging speed of seeds. According to storage behavior, crop seeds are divided into traditional (orthodox seed), recalcitrant seed and middle seed. For the storage of traditional seeds, the key is to control the moisture and storage temperature of the seeds. As long as one of them is low, the storage life of the seeds can be prolonged. Harrington proposed the following guidelines:
1) Seed moisture content is in the range of 5~14%, every 1% decrease, the seed lifespan will be doubled;
2) The storage temperature is in the range of 1-50℃, and the seed life will be doubled for every decrease of 5.6℃ (100F). During storage, the differences between different seeds can be ignored, so most types of seeds can be stored under standard conditions.
3) First, the seeds must be dried before entering the warehouse to reduce the moisture content of the seeds. Too high drying temperature will damage the seeds, and the high temperature resistance of wet seeds is lower than that of dry seeds.
The IBPGR Advisory Committee (IBPGR Advisory Committee) recommends drying conditions for seed storage as follows: temperature 15°C (59°F) and relative humidity 10-15%. For seeds that do not need to be stored for a long time, The DANIDA Forest Research Centre recommends a maximum drying temperature of 30~35°C, which reduces the moisture content of the seeds to 10~12%.
4) Secondly, proper storage temperature and relative humidity should be ensured during storage. The two key factors of moisture and temperature are complementary. Low-temperature storage of seeds must combine low water content and air relative humidity; under high temperature conditions, even seeds with safe water content will age faster. Harrington believes that the index of safe seed storage (<5 years) is: RH%+?F ≤100. 5) During production, the longevity of seeds, especially long-lived seeds, must be measured. It takes an extremely long time and often requires prediction. The current estimation of the longevity of ancient seeds is based on the use of 14C isotope; the prediction of the future life of the seeds is commonly used by mathematical statistics. 6) Successful seed storage requires attention to the whole process of storage, that is, the whole process of seeds from maturity of the mother plant to sowing. 2.3. Issues for attention in the application of RFID in the seed resource bank: 1) Temperature. RFID electronic tags are used in the seed resource bank. The storage temperature is -20℃~+60℃, and the working temperature is -20℃~+60℃. If used in a special ultra-low temperature environment, RFID electronic tags need special design. .
2) The working temperature of RFID reading and writing equipment, the storage temperature is between -20℃~+80℃, and the working temperature is between -10℃~+60℃. If used in a special ultra-low temperature environment, RFID reading and writing equipment needs special design.
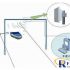
3) RFID working environment is required to avoid as much as possible. Metal objects and liquids attenuate or even block the RFID signal. Therefore, the correct selection and placement of tags and antennas in the implementation of the project plan is related to the final implementation effect of the project.
2.4. Requirements for seed packaging bags:
Common seed packaging bags on the market include plastic bags, aluminum foil bags, paper-plastic composite bags, woven bags, kraft paper bags, etc. Since metal materials can shield RFID signals, choose as much as possible when making seed packaging bags with RFID tags. For packaging bags made of non-metallic materials, such as special packaging bags made of metal materials, in the selection of RFID tags, metal-resistant RFID tags must be used.
2.5, the design of the seed resource library shelf
It can be arranged and displayed according to the requirements of seed management in the seed resource bank, and it is convenient for the RFID technology to play the advantages of better radio frequency reading in the seed resource bank. Customized metal shelves and seed resource management intensive shelves can be used.
2.5.1, shelf type design
A larger warehouse is needed to meet the storage of seed resources, and it takes up a large area of the warehouse.
The advantage is that it is convenient to implement the RFID system, and has more advantages in the arrangement of the RFID antenna and the reading of the tag.

2.5.2, Dense rack type design
The use of dense racks can save the area occupied by the warehouse, and the seed resource bank is more standardized and tidy. It is easy to find and can prevent the seeds from being misplaced and misplaced to a certain extent. The implementation requirements and cost of RFID technology are higher.
The reading requirements for RFID tags are higher, the amount of reading increases, and the reading environment is higher. In order to ensure the reading effect and no missed reading occurs, the number of RFID antennas arranged in dense racks increases, making installation more difficult. Implementation costs will also increase. Shenzhen Wanquan Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. has developed an advanced UHF multi-antenna splitter for application environments that require a large number of densely arranged readers and antennas in file management, seed resource library, etc., which can greatly reduce project implementation costs.

3. Application of RFID technology in seed resource bank management
3.1. Necessity and advantages of using RFID technology
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has the advantages of easy to use, no manual intervention for identification, long-distance reading in batches, low environmental requirements, long service life, data encryption, and storage of information can be changed. Combined with an effective application management system, It can help realize the monitoring of seeds from the source of production to the final consumer. This project applies RFID radio frequency identification technology to the management of crop seeds to track the entire process of seed production, storage and sales, which greatly improves the traceability of seeds, effectively improves the protection of seed intellectual property rights, and improves the prevention of counterfeit and inferior seeds Ability to protect the interests of consumers and improve food safety.
Realize the full-process monitoring and traceability capabilities of seed resources, which is particularly important for seeds, which are the most basic means of production in agricultural production. It is a very important issue to effectively carry out seed management work, to prevent the occurrence of fake and inferior seed pits, and to ensure the safety of food production.
Improve the efficiency of seed resource bank management and ensure the correct and shared management of seed resource information.
Improve the efficiency of seed resources import and export, inventory check and write-off.
The sales and circulation of seed resources can be monitored and traced.
Through RFID seed resource bank management, it is easy to realize the information management of stock seed resources.
3.2. Application of RFID technology in the whole process of seed resource management
When RFID is applied to seed management, the most important thing is to apply the characteristics of RFID tags to ensure the realization of “source” seed tracking solutions and the ability to provide complete transparency in the seed supply chain. In order to achieve this goal, different label formats and label reading formats are selected in different stages and different logistics processes.
3.2.1. Production link:

In the production stage, RFID soft tags are used on the seed sample packaging, which corresponds to the large seed packaging. The producer stores the product name, variety, origin, batch, pesticide application, producer information and other necessary content in the computer server , Use RFID tags to record the initial product information and production process; when purchasing products, use the content of the tags to quickly sort the products, and give different purchase prices according to the different conditions of the products. The staff is equipped with handheld RFID reading and writing equipment, which is convenient for inventory, tracking, improving the efficiency of seed acquisition and direct information storage, forming historical records and statistical information, which is convenient for research and analysis.
3.2.2. Processing link:
For the seeds delivered directly from the production base, after the processing company reads the RFID information on the agricultural products, the information is kept in the computer, and the processing information of the agricultural products is further added to the processed agricultural product electronic tags. The agricultural product electronic tags The use of RFID is the same as in the production process. A single RFID electronic tag is applied to agricultural products with high value and strict environmental requirements, while labels are applied to products of lower value, transported pallets and large packages, and for individual agricultural products. Apply barcode technology.
3.2.3. Warehousing link:

In the seed storage link, the production time, location and other related information of the seeds are recorded through RFID tags, and the storage warehouse, location, and entry and exit records of different batches of seeds are formed in the management software, which effectively improves the efficiency of warehouse management and maximizes the satisfaction of corporate dynamics Requirements for warehouse management. For example, use the information recorded in the RFID tag to quickly determine whether the product is suitable for storage in a warehouse, and how long it can be stored; when leaving the warehouse, choose the product that is first out of the warehouse according to the storage time to avoid economic losses; at the same time, the use of RFID can also achieve The quick inventory of the warehouse helps managers to keep abreast of the status of the products in the warehouse. In this link, the transported seeds with RFID electronic tags need to be stored, so it is necessary to install RFID read-write equipment at the entrance of the warehouse that automatically judges the seeds in and out of the warehouse and records the seed information, and install multiple read-write devices in the warehouse. The device records the seeds in different regions. When counting goods or inquiring about goods, you can use RFID handheld readers to directly inquire about goods information. The application of RFID in the warehousing link focuses on the reading and management of RFID information.
[ad_2]