Application of RFID technology in clothing anti-counterfeiting management
[ad_1]
1 Introduction
In the famous Maslow’s five levels of needs, the most basic needs are physiological needs, and the most basic physiological needs are the needs of food, clothing, housing, and transportation. These are mentioned to emphasize the point that clothes are the most basic needs of human beings.
It is this rigid demand for clothes that has created an extremely broad apparel industry and market, and has spawned millions of apparel companies. If such a huge industry is not well managed, the industry will be chaotic. Unbearable, and China’s clothing industry has been chaotic for a long time.
2 The biggest problem facing clothing management
2.1 Counterfeit products are flying all over the sky
If any of the above Peugeots is added to a piece of clothing, who can tell me for sure that he can judge the authenticity of the dress. Why does this happen? There are three reasons:
First, consumer demand is large, and there is a large demand for such a large supply. Many consumers who want to wear famous brands but are unwilling to spend more know that fake fakes are bought, which encourages the arrogance of fake sellers and disrupts normalcy. The order of market competition has violated the legitimate interests of real brand-name clothing operators.
Second, driven by interests, there is a certain profit margin between genuine products and counterfeit products. In order to obtain this part of the benefits, the counterfeiters do things that harm others and benefit themselves.
Third, the reproducibility of existing technology
Counterfeiters can easily master some of the conventional anti-counterfeiting methods. They are not only satisfied with making a fuss on the product packaging, but also affixed with fake and counterfeit marks, which make it more difficult for consumers to distinguish the authenticity. After the counterfeiting technology is mastered, counterfeiters have even developed from going it alone to gangs. The gangs have more sophisticated methods of making counterfeit products, and their exquisite packaging is even more attractive to consumers than genuine products.
The first two reasons are very difficult for us to overcome, and the third point, I believe that many manufacturers have made various degrees of efforts, but the specific effects should be experienced by those who have used it.
2.2 The entry and exit of clothing and inventory is a huge project. According to incomplete statistics, the total amount of clothing per year is 80 million. According to preliminary estimates, it costs a person to count one piece every second day and night. The time is 926 days. That is to say, it is a simple inventory. A pure company needs to form a dedicated team to complete it. In the absence of advanced inventory technology, many companies cannot even manage their own clothes well. I don’t even have the energy to manage other people’s imitations.
3 Some existing clothing management methods
At present, most clothing anti-counterfeiting uses anti-counterfeiting labels (laser anti-counterfeiting, telephone query anti-counterfeiting). These methods have good practicability and have received certain effects in the field of anti-counterfeiting, but the openness and reproducibility of these technologies determine Therefore, they are only a temporary solution to counterfeit clothing manufacturers.
Existing warehouses and inventory are usually advanced bar code technology, which can improve efficiency to a certain extent, but bar code scanning must be aligned one-to-one, and only single products can be identified at a time , And is greatly affected by the environment.
4 New Ideas for RFID Clothing Management
With the rapid spread of the concept of the Internet of Things, RFID technology has evolved from being little known at the beginning to now being popular in all walks of life. The introduction of RFID technology into clothing management can provide clothing anti-counterfeiting, warehouse management, inventory, and logistics. Transportation provides new ideas for management.
5 RFID can solve the technical principle of clothing management problems
5.1 Introduction to RFID technology
Microwave radio frequency automatic identification (RFID) technology is a new technology that has emerged in the world in recent years and has been rapidly promoted and applied. It is a brand-new method for automatic collection of characteristic data such as the attributes, status, and number of objects in order to realize digitization and informatization. It can be widely used in automatic identification of persons, animals, and objects.
Key equipment
The key equipment of microwave radio frequency automatic identification (RFID) mainly has the following three components:
(1) Electronic Tag or Label (Electronic Tag or Label) that stores the data information of the marked object:
The core of the electronic tag is an integrated circuit chip with information transceiver and storage functions, with a storage capacity of 1Kbits or more. Since it is affixed to the recognized object like a normal label when in use, the device is visually called an “electronic label”.
In the automatic identification management system, each electronic label saves an object’s attribute, status, number and other information. Electronic tags are usually installed on the surface of an object with a certain angle of view without metal obstruction.
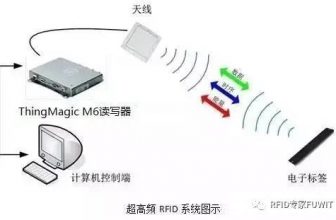
(2) Reader OR Scanner (Reader OR Scanner) used to read and write tag data, its main function is: write the data information to be stored in the blank electronic tag; check the data information currently stored in the electronic tag; Modify (rewrite) the data information in the electronic label.
(3) The reader is connected to the microwave antenna (Microwave Antenna) that sends and receives signals to and from the electronic tag.
One of the most important indicators of a microwave antenna is the gain of the antenna. Generally, the higher the gain, the longer the distance between reading and writing tags; the stronger the directivity; and the larger the antenna volume.
working principle
The principle block diagram of the microwave radio frequency automatic identification application system is as follows:
The basic working principle is:
(1) When an object equipped with an electronic tag approaches the microwave antenna, the reader will send out a microwave inquiry signal under control;
(2) After the electronic tag installed on the surface of the object receives the query signal from the reader, it reflects the data information in the tag back to the reader according to the command requirements in the query signal.
(3) After the reader receives the microwave synthesis signal reflected by the electronic tag, it can separate the identification code and other information stored in the electronic tag through the internal demodulation and processing of the reader.
(4) The identification information is transmitted to the control computer as the characteristic data of the object for further processing, so as to complete the application of information inquiry, charging, release, statistical management and so on related to the object.
5.2 The technical principle of realizing the anti-counterfeiting function
The EPCC1G2 label is divided into four areas:
EPC area: the area to store EPC code, currently the maximum can store 96Bits EPC code. Read and write.
TID area: Store the ID number set by the label manufacturer. There are currently two ID numbers of 32 and 64 Bits. Readable, not writable.
User area: This area is different for different manufacturers, readable and writable.
Password area: There are 32Bits access (access) password and 32Bits destruction (kill) password. Read and write.
Among them, the ID number of the TID area is unique in the world and cannot be copied under the existing technical conditions. Therefore, it is the most ideal way to use this area for anti-counterfeiting of single products.
5.3 The technical principle of realizing the warehouse entry and exit and inventory function
The EPCC1G2 protocol reader integrates the most advanced anti-collision data algorithm, which can identify multiple electronic tags at the same time, that is, it can handle the in and out and inventory of multiple clothes at the same time, which can greatly improve work efficiency and save manpower and material resources.
5.4 The technical principle of realizing logistics transportation
RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology. Its basic principle is to use radio frequency signals and electromagnetic coupling to transmit data to realize automatic identification of identified objects. That is, communication is realized by emitting electromagnetic waves. According to the principles of physics, the shorter the wavelength of electromagnetic waves, the longer the transmission distance. It happens that the frequency band occupied by EPCC1G2 is 902-928MHz, and the wavelength of this frequency band is very short (only a few centimeters) , So the reading and writing distance of this frequency band reader is usually about 1-20 meters.
In logistics and transportation, each vehicle is equipped with a vehicle electronic tag to achieve long-distance rapid entry and exit, and it can track the approximate itinerary of the vehicle in real time.
[ad_2]