Fast and Agile Supply Chain Management System for Apparel Enterprises
SaveSavedRemoved 0
Deal Score0
[ad_1]
Based on rfid technology
Fast and agile supply chain for apparel companiesManagement system
suggestion
Haohai Yitong Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
June 2007
The overall goal of this project:
1) Use RFID technology to build a local intelligent information environment for fabrics, semi-finished products, finished products, customer orders, etc., to achieve rapid positioning and rapid processing of goods, improve logistics speed, and effectively support garment production management.
2) Through the development of RFID-based distribution management system applications, the automated management of logistics distribution and allocation in the chain system is realized, and the data collection and analysis capabilities of sales information, customer information, promotional data, product price change information, etc., are improved, especially for key points Customer service capabilities.
3) The on-time delivery rate of products has increased from the current 95% to 98%, the production cycle has been shortened by 15%-20%, the order processing time has been shortened from 1-2 days to 1-2 hours, and the inventory days have dropped from 206 days to 150 days.
The overall goal of this project:
1) Use RFID technology to build a local intelligent information environment for fabrics, semi-finished products, finished products, customer orders, etc., to achieve rapid positioning and rapid processing of goods, improve logistics speed, and effectively support garment production management.
2) Through the development of RFID-based distribution management system applications, the automated management of logistics distribution and allocation in the chain system is realized, and the data collection and analysis capabilities of sales information, customer information, promotional data, product price change information, etc., are improved, especially for key points Customer service capabilities.
3) The on-time delivery rate of products has increased from the current 95% to 98%, the production cycle has been shortened by 15%-20%, the order processing time has been shortened from 1-2 days to 1-2 hours, and the inventory days have dropped from 206 days to 150 days.
The project involves the implementation level:
To build a complete clothing supply chain management system based on RFID technology to realize automatic collection of relevant material data in the entire life cycle of clothing requires not only the establishment of an RFID application environment within the company, but also suppliers, distributors and customers, Logistics and transportation companies, etc.
The company’s implementation of a supply chain management system based on RFID technology can be divided into three stages as a whole:
1) Departmental demonstration stage. At this stage, according to the actual situation and status of the company, select departments or links with urgent needs, mature conditions, relatively independent, and certain representativeness to implement RFID technology, such as finished product warehouses, a certain production line in the sewing workshop, and specialty stores. The main goal of this stage is to achieve partial results through departmental RFID application demonstration, and to explore the experience of applying RFID technology in clothing enterprises, and to play a demonstrative role in the comprehensive application of RFID technology in enterprises.
2) Enterprise application stage. After the department’s demonstration is successful, apply RFID technology to other departments of the company, such as raw material warehouses, cutting workshops, other production lines in the sewing workshop, ironing workshops, and other specialty stores, forming the whole process of clothing production and sales based on RFID technology. Apply the system and realize the integration with other information systems of the enterprise, thereby comprehensively improving the comprehensive level of enterprise informatization and enhancing the market competitiveness of the enterprise.
3) Application extension stage. On the basis of the successful application of RFID technology by enterprises, from the perspective of the clothing supply chain, extend the application of RFID technology to the front-end and client-end of suppliers, apply RFID technology in procurement, distribution, after-sales service and other links, and cooperate with suppliers and third parties. The information system integration of external companies such as logistics and after-sales service providers constitutes a clothing supply chain management system based on RFID technology, thereby improving the market competitiveness of the clothing supply chain with the company as the core.
1) Departmental demonstration stage. At this stage, according to the actual situation and status of the company, select departments or links with urgent needs, mature conditions, relatively independent, and certain representativeness to implement RFID technology, such as finished product warehouses, a certain production line in the sewing workshop, and specialty stores. The main goal of this stage is to achieve partial results through departmental RFID application demonstration, and to explore the experience of applying RFID technology in clothing enterprises, and to play a demonstrative role in the comprehensive application of RFID technology in enterprises.
2) Enterprise application stage. After the department’s demonstration is successful, apply RFID technology to other departments of the company, such as raw material warehouses, cutting workshops, other production lines in the sewing workshop, ironing workshops, and other specialty stores, forming the whole process of clothing production and sales based on RFID technology. Apply the system and realize the integration with other information systems of the enterprise, thereby comprehensively improving the comprehensive level of enterprise informatization and enhancing the market competitiveness of the enterprise.
3) Application extension stage. On the basis of the successful application of RFID technology by enterprises, from the perspective of the clothing supply chain, extend the application of RFID technology to the front-end and client-end of suppliers, apply RFID technology in procurement, distribution, after-sales service and other links, and cooperate with suppliers and third parties. The information system integration of external companies such as logistics and after-sales service providers constitutes a clothing supply chain management system based on RFID technology, thereby improving the market competitiveness of the clothing supply chain with the company as the core.
The company’s functional requirements: WEB-based supplier collaborative work platform, detailed requirements are as follows
Company Apparel Co., Ltd.’s main requirements for a web-based supplier collaborative work platform include:
(1) Maintenance of basic information. Provide suppliers with a basic information maintenance function, mainly the supplier’s production capacity data, delivery cycle, etc., and provide a reference for when the company issues purchase orders (including fabric orders and garment OEM manufacturing orders) to suppliers.
(2) Coordination of production schedule. After the company issued a purchase order to the supplier, the supplier lacked a channel for reporting the production progress to the company, making the company unable to understand the supplier’s production progress in real time.
(3) Hope to learn more about the fabric market through fabric suppliers and provide more fabric choices for the company to design new products.
(4) Establish a channel for information exchange between the company and suppliers.
Requirements for production and logistics management systems based on RFID technology
The main requirements of the company apparel co., Ltd. for the production and logistics management system based on RFID technology are:
(1) Real-time understanding of work-in-process inventory. Keep abreast of the current WIP inventory of Gela, including the total WIP inventory of Gela and the WIP inventory of each work section.
(2) Real-time understanding of production progress. Keep abreast of the current production progress of Gela, including the completion of Gela’s production plan and the progress of each section.
(3) Reduce the workload of workshop management. Apply RFID technology and establish information system to reduce the workload of workshop management.
(4) Realize the monitoring of the production process. Realize the monitoring of the sewing process of the suit, including the monitoring of orders and plans, the monitoring of each piece, etc.
(5) Quality data collection and management. Timely collect quality problems in the sewing process of suits, and carry out timely statistical analysis and control of sewing quality.
Demand for finished product warehouse management system based on RFID technology
The main requirements of the company apparel co., Ltd. for the finished product warehouse management system based on RFID technology are:
(1) Improve the efficiency of finished products in and out of warehouse.
(2) Improve the efficiency of finished product warehouse inventory.
(3) Reduce the error rate of finished product shipments.
Demand for store management system based on RFID technology
The main requirements of the company’s clothing company for the management system of the RFID technology-based specialty store are as follows:
(1) Improve the efficiency of finished products warehousing.
(2) Improve the efficiency of store inventory
(3) Anti-theft and alarm
Company Apparel Co., Ltd.’s main requirements for a web-based supplier collaborative work platform include:
(1) Maintenance of basic information. Provide suppliers with a basic information maintenance function, mainly the supplier’s production capacity data, delivery cycle, etc., and provide a reference for when the company issues purchase orders (including fabric orders and garment OEM manufacturing orders) to suppliers.
(2) Coordination of production schedule. After the company issued a purchase order to the supplier, the supplier lacked a channel for reporting the production progress to the company, making the company unable to understand the supplier’s production progress in real time.
(3) Hope to learn more about the fabric market through fabric suppliers and provide more fabric choices for the company to design new products.
(4) Establish a channel for information exchange between the company and suppliers.
Requirements for production and logistics management systems based on RFID technology
The main requirements of the company apparel co., Ltd. for the production and logistics management system based on RFID technology are:
(1) Real-time understanding of work-in-process inventory. Keep abreast of the current WIP inventory of Gela, including the total WIP inventory of Gela and the WIP inventory of each work section.
(2) Real-time understanding of production progress. Keep abreast of the current production progress of Gela, including the completion of Gela’s production plan and the progress of each section.
(3) Reduce the workload of workshop management. Apply RFID technology and establish information system to reduce the workload of workshop management.
(4) Realize the monitoring of the production process. Realize the monitoring of the sewing process of the suit, including the monitoring of orders and plans, the monitoring of each piece, etc.
(5) Quality data collection and management. Timely collect quality problems in the sewing process of suits, and carry out timely statistical analysis and control of sewing quality.
Demand for finished product warehouse management system based on RFID technology
The main requirements of the company apparel co., Ltd. for the finished product warehouse management system based on RFID technology are:
(1) Improve the efficiency of finished products in and out of warehouse.
(2) Improve the efficiency of finished product warehouse inventory.
(3) Reduce the error rate of finished product shipments.
Demand for store management system based on RFID technology
The main requirements of the company’s clothing company for the management system of the RFID technology-based specialty store are as follows:
(1) Improve the efficiency of finished products warehousing.
(2) Improve the efficiency of store inventory
(3) Anti-theft and alarm
Schematic diagram of the overall scheme:
Figure 1.1 The overall structure of a supply chain management system based on RFID technology
Figure 1.2 The overall model of the clothing supply chain management system based on RFID technology
Figure 1.3 The overall structure of the project system
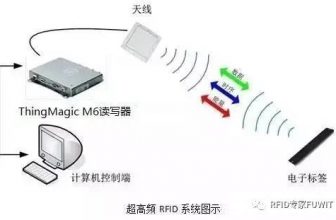
Figure 1.4 Schematic diagram of the logical structure of the RFID application system
Due to the integration of RFID technology logistics and information flow, logically it can be roughly divided into seven steps, starting from the information system such as ERP, DRP, etc., through the processing of the application system of this project, and returning to the information system layer. The following takes the RFID application in the sewing workshop as an example to briefly explain the processing logic of each step of the RFID application system.
① Planning release and execution: Information systems such as mySAP ERP generate various production plans, such as raw material procurement and inventory planning, cutting operation planning, sewing industry planning, ironing operation planning, finished product inventory planning, transportation planning, sales planning, etc., and Reach to relevant departments for execution.
② RFID data collection: Before the application of RFID technology, data collection in the sewing industry was mainly carried out by manual accounting. After applying RFID technology, the clothing bag attached with RFID tags can be read by the RFID tag reader after passing through a certain RFID reader to complete the automatic collection of original data.
③ RFID middleware: Due to the technology and application environment, the data collected by RFID has a lot of redundancy or misreading. The RFID middleware processes the collected raw data appropriately to ensure the correct identification of RFID tags. Sex and uniqueness. At the same time, the RFID middleware is also responsible for the processing of the read data, such as the interpretation of the EPC code.
④ Real-time data: Since the RFID card reader can collect the RFID tags that enter its reading range at any time, the data read has the characteristics of real-time and mass, and a database independent of the business system should be used to manage these most primitive data.
⑤ Business data generation: The real-time raw data is analyzed through multiple layers to form data related to business processing, such as parsing RFID tags into specific materials, analyzing RFID card readers into specific locations, and combining time sequence to combine certain The RFID tag passes through the data of multiple card readers in turn, and parses it into the technological process of a certain material.
⑥ RFID application system: Use the business data generated before to develop corresponding systems to realize business and job management, such as logistics monitoring, job scheduling, and progress monitoring.
⑦ Application system interface: timely feedback logistics data to information systems such as ERP system, and provide on-site data for ERP to make accurate plans.
① Planning release and execution: Information systems such as mySAP ERP generate various production plans, such as raw material procurement and inventory planning, cutting operation planning, sewing industry planning, ironing operation planning, finished product inventory planning, transportation planning, sales planning, etc., and Reach to relevant departments for execution.
② RFID data collection: Before the application of RFID technology, data collection in the sewing industry was mainly carried out by manual accounting. After applying RFID technology, the clothing bag attached with RFID tags can be read by the RFID tag reader after passing through a certain RFID reader to complete the automatic collection of original data.
③ RFID middleware: Due to the technology and application environment, the data collected by RFID has a lot of redundancy or misreading. The RFID middleware processes the collected raw data appropriately to ensure the correct identification of RFID tags. Sex and uniqueness. At the same time, the RFID middleware is also responsible for the processing of the read data, such as the interpretation of the EPC code.
④ Real-time data: Since the RFID card reader can collect the RFID tags that enter its reading range at any time, the data read has the characteristics of real-time and mass, and a database independent of the business system should be used to manage these most primitive data.
⑤ Business data generation: The real-time raw data is analyzed through multiple layers to form data related to business processing, such as parsing RFID tags into specific materials, analyzing RFID card readers into specific locations, and combining time sequence to combine certain The RFID tag passes through the data of multiple card readers in turn, and parses it into the technological process of a certain material.
⑥ RFID application system: Use the business data generated before to develop corresponding systems to realize business and job management, such as logistics monitoring, job scheduling, and progress monitoring.
⑦ Application system interface: timely feedback logistics data to information systems such as ERP system, and provide on-site data for ERP to make accurate plans.
Figure 1.5 Web-based supplier collaborative work platform framework
Schematic diagram of the logistics of suit sewing process
Sewing production RFID reader layout plan
Figure 1.6 The structure of the production and logistics management system based on RFID technology
Sewing production RFID reader layout plan
Figure 1.6 The structure of the production and logistics management system based on RFID technology
Figure 1.7 The structure of a distribution management system based on RFID technology
Figure 1.8 Logistics schematic diagram of suit sewing process
Note: Management issues of traditional clothing production workshop
(1) Large management workload
Apparel production has obvious seasonal characteristics. According to the survey, there are about 13,000 pieces of work in production during the peak season and more than 7,000 pieces of work in the off-season. The list contains 5 pieces. Every day, each administrator needs to process 400 incidental work orders, and at the same time, there are more than 40 employees on one list. It can be seen that the administrator needs to process 16,000 pieces of information only for employee piece-rate statistics, which is estimated to take several hours, and does not include quality problem statistics, work-in-progress management, production schedule management, etc.
(2) Poor real-time performance
Since the workshop mainly uses the manual recording method on the work order, the original vouchers for statistics are the work order and the quality problem record sheet. Therefore, the batch data can be summarized and summarized only when the suit is fully sewn and the shift is handed over. Statistics cannot accurately grasp the workshop site in real time.
(3) Information is not smooth
At present, when the work order is printed in the cutting workshop, the specific sewing production line has been designated, and the actual completion status can be fed back to the information system before the sewing is completed or transferred to the ironing workshop. There is a large lag in information feedback. That is to say, after the plan arrives at the workshop, there are information gaps or blind spots, which have a certain impact on the rationality of the production plan.
(4) Difficulty in order tracking
Because an order or plan often corresponds to multiple accompanying work orders, each accompanying work order corresponds to multiple suits, the products in progress are scattered in each station of each workshop, and the production statistics are lagging. Or plan to track, that is, it is difficult to know the progress of the order or plan at any time.
(5) Information utilization rate is not high
Attached work orders and quality problem records are the main sources of information in the sewing workshop. The data is mainly used for employee piece counting and salary calculation. How to better use this information in workshop management and increase the utilization rate of the above data? At present, there is room for improvement in the management of the company’s sewing workshop.
(1) Large management workload
Apparel production has obvious seasonal characteristics. According to the survey, there are about 13,000 pieces of work in production during the peak season and more than 7,000 pieces of work in the off-season. The list contains 5 pieces. Every day, each administrator needs to process 400 incidental work orders, and at the same time, there are more than 40 employees on one list. It can be seen that the administrator needs to process 16,000 pieces of information only for employee piece-rate statistics, which is estimated to take several hours, and does not include quality problem statistics, work-in-progress management, production schedule management, etc.
(2) Poor real-time performance
Since the workshop mainly uses the manual recording method on the work order, the original vouchers for statistics are the work order and the quality problem record sheet. Therefore, the batch data can be summarized and summarized only when the suit is fully sewn and the shift is handed over. Statistics cannot accurately grasp the workshop site in real time.
(3) Information is not smooth
At present, when the work order is printed in the cutting workshop, the specific sewing production line has been designated, and the actual completion status can be fed back to the information system before the sewing is completed or transferred to the ironing workshop. There is a large lag in information feedback. That is to say, after the plan arrives at the workshop, there are information gaps or blind spots, which have a certain impact on the rationality of the production plan.
(4) Difficulty in order tracking
Because an order or plan often corresponds to multiple accompanying work orders, each accompanying work order corresponds to multiple suits, the products in progress are scattered in each station of each workshop, and the production statistics are lagging. Or plan to track, that is, it is difficult to know the progress of the order or plan at any time.
(5) Information utilization rate is not high
Attached work orders and quality problem records are the main sources of information in the sewing workshop. The data is mainly used for employee piece counting and salary calculation. How to better use this information in workshop management and increase the utilization rate of the above data? At present, there is room for improvement in the management of the company’s sewing workshop.
Attached:
For clothing, the demand for personalized services of products is extremely strong and the product updates and changes are rapid. The brand clothing industry is the most suitable industry for applying RFID technology due to its characteristics. When various industries around the world are experimenting with RFID, the world’s apparel industry has also emerged as direct beneficiaries of RFID technologies such as Gap, Benetton, Prada, Levis, and Gargeur. Their various explorations and attempts around RFID technology will surely serve as a touchstone for the large-scale application of RFID in the apparel industry.
For clothing, the demand for personalized services of products is extremely strong and the product updates and changes are rapid. The brand clothing industry is the most suitable industry for applying RFID technology due to its characteristics. When various industries around the world are experimenting with RFID, the world’s apparel industry has also emerged as direct beneficiaries of RFID technologies such as Gap, Benetton, Prada, Levis, and Gargeur. Their various explorations and attempts around RFID technology will surely serve as a touchstone for the large-scale application of RFID in the apparel industry.
U.S. Gap’s efficient and convenient clothing tracking management
The American Gap company is in a leading position in the global professional retail industry. Its products mainly include clothing and accessories for adults, women, children and babies. In addition to selling in the United States, Gap has thousands of branches all over the world. Gap’s total sales in 2000 alone reached 13.6 billion U.S. dollars.
Gap has experience in applying RFID technology to inventory management and clothing tracking management. In the past few years, the company has been committed to creating a complete system around the entire business process-from the initial production stage to the in-store tracking, ordering, inventory, and control links that assist sales staff. Electronic chips are installed on each piece of clothing during the production process using clothing tags as carriers. These labels store electronic information such as clothing style, size, color, and intended destination. Through the real-time tracking of goods, Gap has greatly improved the management efficiency of all major aspects from production, circulation to inventory control in thousands of chain stores around the world.
In inventory management, the size and specifications of all inventory clothes can be managed and classified through the ID number Gap of the electronic tag. Once the shipment order is received, company employees can immediately know the exact location of the required specifications of clothing storage by reading the equipment. RFID technology eliminates the factors of human error and does not require visual reading, making inventory management simple and fast. At the same time, the delivery time and inventory control are optimized to minimize the delivery error rate.
Gap company also uses RFID tracking system to implement effective management of sales terminals. The label of each piece of Gap clothing is tracked by the system, regardless of whether the clothing is placed in a box in a warehouse or on a shelf in a shopping mall. As long as customers have demand, sales staff can tell consumers how many colors are available for their fancy styles through portable barcode readers, and can find the target products for customers in the first time, avoiding traditional manual search. Time spent and loss of customers. According to statistics from relevant departments, since Gap applied RFID technology to effectively track and manage clothing, the company’s sales have increased by 20%.
German Gardeur excavates the industry’s best performance with RFID
Gardeur, a well-known German clothing manufacturer established in the early 1920s, mainly produces men’s and women’s trousers and denim, and mainly distributes goods to clothing specialty stores and high-end clothing stores. Their main customers are from Eastern European countries. In 2005, sales reached 93 million euros and garment production reached 2.8 million pieces. The company also operates more than 630 clothing specialty stores worldwide.
Gardeur is a supplier of the German Metro Group. Metro Group’s stride RFID promotion plan prompted Gardeur to introduce RFID technology into its supply chain management in 2003 to implement supply chain monitoring. In a few years, Gardeur continued to use the savings to invest in the development of the RFID system. Currently, Gardeur is cooperating with Fashion Group RFID and the German Article Numbering Center (GS1 Germany), hoping to jointly develop a universal RFID solution for the textile industry. (Note: Fashion Group RFID is located in Munich, Germany. It is an industry group organization with great influence in the textile industry).
Gardeur’s goal is to build the best RFID system for global use. It hopes to develop a mini tag embedded in clothing, and it also hopes to reduce costs and solve customer privacy issues. The original intention of Gardeur to support Fashion Group RFID is because they hope to form an industry-wide unified standard and compatible technology to protect the investment of clothing manufacturers. Thomas Ballweg, President of Garduer, said: “We are convinced that the successful application of RFID in the apparel industry can drive the overall adoption of this technology in the textile industry.”
A new attempt at RFID by Prada, Italy
Prada, a world-renowned Italian clothing brand, has always been unique in international fashion with its simple and calm design style. The first brand that started as travel leather goods has now successfully constructed a complete boutique kingdom “from leather goods to clothing and shoes”, and its sales territory has now expanded to the world.
Prada Advanced Garment Group began to install RFID electronic tags on clothing in November 2001. The electronic tags are printed on electronic substrate materials and then embedded in plastic or paper clothing tags. The label used by Prada on the merchandise of the Epicenter flagship store in New York records relevant information about the style, size, color and other details of the clothing as well as the price. When customers pass their store wearing Prada clothes, the RFID system will control the display in the store to show the model showing the same clothes on the T-shaped stage in Milan. The use of this technology greatly increases consumers’ sense of accomplishment after purchasing Prada products.
From the above cases, it is not difficult to see that RFID technology can exert significant advantages in the integrated management of industrial logistics, anti-counterfeiting and anti-theft of retail terminal products, fast POS settlement, VIP member management and multimedia clothing demonstrations. Facing the successful attempts of many well-known international companies on RFID, what is the situation of Chinese local companies?
RFID strategy of Chinese companies
RFID strategy of Chinese companies
Looking at the intensive attempts of well-known foreign companies in RFID technology, some large domestic enterprises and public utilities departments have already become “crab-eaters” and have begun the exploration of RFID applications.
China’s railway dispatching and statistics system is currently the largest RFID application system in China. Hundreds of thousands of domestic locomotives are equipped with RFID, and the network is spread all over the country. The label on the bottom of the locomotive contains information such as vehicle type, model, vehicle number, and cargo. When the train is running, the readers along the railway can quickly read the vehicle information and transmit the read data to the national railway Department’s central server. Through the RFID platform, China’s railway system has improved the level of statistical dispatch and improved operational efficiency. Compared with the promotion of RFID technology by the foreign retail giant Wal-Mart Group, in China, the first to try RFID is not the retail industry but the manufacturing industry. The powerful Haier Group has established two fully automated logistics centers to optimize its supply chain management. By deploying RFID technology, Haier Group has not only reduced 200,000 square meters of warehouses, but also reduced stranded materials by 90%, and reduced inventory funds by 63%, which greatly reduced operating costs.
Chinese clothing companies have also begun to explore step by step, driven by the RFID boom. China’s well-known menswear brand “Kimba” deployed the RFID management solution of Symbol Technology Corporation of the United States in its warehouses and specialty stores in 2006. Through the implementation of wireless management of Rinba’s logistics warehouse and finished product warehouse, real-time data collection in various specialty stores and stores through the electronic bar code identification system, and timely information sharing and communication with the headquarters, it solves the problem of Rinba’s warehouse management and supply chain management. Long-standing problems.
Compared with some large domestic enterprises with relatively limited capital and scale, the penetration rate of RFID in the industry is relatively low. Apparel companies that have successfully applied RFID are even rarer. The main reasons behind the analysis phenomenon are the following bottlenecks that need to be broken through:
High cost
For most companies, the input-output ratio determines to a large extent whether a business technology can be quickly adopted. Cost is still an important bottleneck for the failure to popularize RFID in apparel companies. Traditional one-dimensional and two-dimensional bar codes only cost a few cents, while better RFID tags cost tens of cents. If hundreds of thousands of goods need to be labeled a day, the cumulative cost is indeed staggering. At present, the huge cost pressure of electronic tags has led companies to finally abandon RFID and look for other low-cost but not efficient information solutions.
high risk
Although the industry still holds a positive attitude towards the long-term prospects of RFID, the high cost of RFID has made some companies think that implementing RFID is a high-risk move. At present, the software and hardware technologies provided by many RFID solution developers are still in the laboratory and simulation application stage, and they are not yet able to meet the needs of real-world applications on a large scale. It can be seen that the commercial basic strategy of applying RFID technology will take at least a period of time to mature.
Standards are not uniform
At present, the special technology adopted by RFID companies uses different system frequencies, storage rules, and data encoding content. Once RFID readers and tags cannot be used in common use, the companies will not be able to smoothly exchange data and work together. Limit RFID technology within the enterprise. When the data in one link of the supply chain cannot be reused in the next link, it will greatly increase the cost of technology development. It is precisely because of the lack of a set of widely-used standards that RFID technology has not been widely used in supply chain management. It can be seen that a detailed, unified, standardized and open technical standard is the top priority for the development of RFID technology.
From a domestic perspective, most of the successful RFID applications are promoted by the government, accounting for 70 to 80%. Since RFID currently has many technical and cost constraints, it is very difficult to rely solely on corporate behavior to promote it. In addition, it is also important to drive the industry’s internal demonstration and create an overall technological atmosphere for the enterprise. At present, there are not only those who test the waters of RFID technology in China, but also those who are on the sidelines and opponents. For Chinese apparel companies in need, RFID is both close by and out of reach. It is necessary for Chinese apparel companies to increase their acumen in this regard and locate their role in the RFID wave based on their actual conditions. The practice of blindly following the trend, accepting it entirely or ignoring it, and resisting it altogether is too extreme.
Industry authorities believe that China is the world’s largest potential market for RFID. In the next 3 years, RFID technology will bring a revolution to China’s industry. Regardless of the results of this change, one thing is certain: in the RFID tide, only those who are rationally observant and have the courage to practice have the possibility of success and benefit. (Source: “China Clothing”)
Attached:
What hinders the advancement of RFID in China?
According to the latest report provided by IDTechEx, it is estimated that in 2006, the sales of RFID tags will almost triple the total sales in the 60 years since their invention, and the global RFID market will reach 7 billion U.S. dollars by 2008. The future of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is promising. But in China, in the face of the storm that RFID has set off in the global market, it seems that many companies are in the wait-and-see stage and are reluctant to take this first step. What is it that makes them so worried? What is hindering the advancement of RFID in China?
* Moderator: Yue Haixia, editor of ileader website:
RFID-unlimited radio frequency identification, has become the focus of international pursuit. It has formed a mature market abroad and is constantly developing. The application companies of this technology range from the global giant business empire Wal-Mart to the international IT giants IBM, HP, Microsoft, etc. However, compared with the huge momentum of RFID in foreign markets, the domestic market seems a bit too calm. What causes RFID How slow is progress in the Chinese market? With this question, we organized this discussion to listen to the opinions of these companies on this issue.
* Giordano/Giordano Group CIO Hou Tong
The application of RFID in China currently has great obstacles, but I think these obstacles are not unique to China, but are faced by the whole world.
1) The price of the label is high and can only be used on high-value products;
2) Standards issue: There is no standard for UHF frequency bands in China, which prevents companies from investing in RFID. Different brands of readers and tags are not compatible;
3) There are few suppliers, it is difficult for us to compare and choose, and the services and products that suppliers can provide are few;
4) RFID is still an immature technology, and its accuracy and usability need to be further improved. Not as many problems can be solved as most people imagine. There is a big gap between user expectations and reality when using RFID.
What hinders the advancement of RFID in China?
According to the latest report provided by IDTechEx, it is estimated that in 2006, the sales of RFID tags will almost triple the total sales in the 60 years since their invention, and the global RFID market will reach 7 billion U.S. dollars by 2008. The future of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is promising. But in China, in the face of the storm that RFID has set off in the global market, it seems that many companies are in the wait-and-see stage and are reluctant to take this first step. What is it that makes them so worried? What is hindering the advancement of RFID in China?
* Moderator: Yue Haixia, editor of ileader website:
RFID-unlimited radio frequency identification, has become the focus of international pursuit. It has formed a mature market abroad and is constantly developing. The application companies of this technology range from the global giant business empire Wal-Mart to the international IT giants IBM, HP, Microsoft, etc. However, compared with the huge momentum of RFID in foreign markets, the domestic market seems a bit too calm. What causes RFID How slow is progress in the Chinese market? With this question, we organized this discussion to listen to the opinions of these companies on this issue.
* Giordano/Giordano Group CIO Hou Tong
The application of RFID in China currently has great obstacles, but I think these obstacles are not unique to China, but are faced by the whole world.
1) The price of the label is high and can only be used on high-value products;
2) Standards issue: There is no standard for UHF frequency bands in China, which prevents companies from investing in RFID. Different brands of readers and tags are not compatible;
3) There are few suppliers, it is difficult for us to compare and choose, and the services and products that suppliers can provide are few;
4) RFID is still an immature technology, and its accuracy and usability need to be further improved. Not as many problems can be solved as most people imagine. There is a big gap between user expectations and reality when using RFID.
If you have any questions, please contact
Haohai Yitong Technology(Beijing)Limited company
Address: Yumin East Road, Xicheng District, Beijing5No Ruide Building0811room
Product Director: Mr. Tian Ruiqing
telephone:010-58572638 13241931667
Mail:[email protected]
1
[ad_2]