Semi-active RFID radio frequency identification technology personnel access control entry and exit management area positioning system
[ad_1]
1.Semi-active RFID system development background
With the gradual improvement of the intelligent management system and the continuous updating of information facilities, the ability of security prevention and control has been greatly enhanced. In response to the current archives, large factories, prisons, nursing homes, hospitals, schools, enterprises and institutions, large squares, large shopping malls, government departments, smart communities and large public places, the needs for personnel entry and exit management and intelligent regional positioning and precise positioning Combining the advantages of our company’s semi-active RFID technology, our company deliberately developed this system “personnel access control area positioning system based on semi-active RFID radio frequency identification technology”, which solves the problem of automated personnel access judgment management. Accurate positioning of personnel, regional positioning management. The system can also realize intelligent monitoring and management, personnel information management, cross-border alarm, button for help alarm, tracking and other functions. Significantly improve the internal security and management efficiency of important places such as archives, improve management efficiency, and reduce the work intensity of management personnel. At the same time, the system interface is open and has many extended functions, such as linkage with video surveillance systems to achieve refinement manage.
2.Semi-active RFID technology introduction
2.1 Introduction to RFID technology
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Technology) is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically recognizes target objects and obtains related data through radio frequency signals. Conceptually, RFID is similar to barcode scanning. The barcode scanning technology attaches the encoded barcode to the target and uses a dedicated scanning reader to use photoelectric signals to transmit information from the bar magnet to the scanning reader; and RFID Use a dedicated RFID reader and a dedicated RFID unit that can be attached to the target, and use RF signals to transmit information from the RFID unit to the RFID reader.
At present, there are roughly three types of products derived from RFID technology: passive RFID products, active RFID products, and semi-active RFID products.
Passive RFID products are the first to develop, and are currently the most mature and widely used products in the market. For example, bus cards, canteen meal cards, bank cards, hotel access cards, second-generation ID cards, etc., which can be seen everywhere in our daily life, belong to the category of close contact recognition. The main operating frequencies of its products are low frequency 125KHZ, high frequency 13.56MHZ, UHF 433MHZ, and UHF 915MHZ.
Active RFID products have been slowly developed in recent years, and their long-distance automatic identification characteristics determine their huge application space and market potential. At present, there are major applications in the field of long-distance automatic identification, such as smart prisons, smart hospitals, smart parking lots, smart transportation, smart cities, smart earth, and the Internet of Things. Active RFID has sprung up in this field and belongs to the category of long-distance automatic identification. The main operating frequencies of the products are ultra-high frequency 915MHZ and microwave 2.45GHZ.
Active RFID products and passive RFID products have different characteristics, which determine different application fields and different application modes, and they also have their own advantages. But in this system, we focus on introducing semi-active RFID products between active RFID and passive RFID. This product integrates the advantages of active RFID and passive RFID. In access control management, personnel can be accurately positioned. , Regional positioning management, perimeter management, electronic fences and security alarms have great advantages.
2.2 Introduction to semi-active RFID technology
Semi-active RFID products, combined with the advantages of active RFID products and passive RFID products, under the trigger of the low frequency 125KHZ frequency, let the microwave 2.45G play its advantage. Semi-active RFID technology, which can also be called low-frequency activation triggering technology, uses low-frequency short-distance precise positioning, microwave long-distance identification and data upload to solve the functions that pure active RFID and passive RFID cannot achieve. Simply put, it is to activate positioning at a short distance, identify and upload data at a long distance. Really achieve the demeanor of a general of “strategic strategy, decisive victory thousands of miles away”.
2.3 Features and advantages of semi-active RFID technology
Semi-active RFID is a flexible application technology that is easy to control, simple and practical, and especially suitable for automatic control. The identification work does not require manual intervention. It can support both read-only working mode and read-write working mode without contact Or aiming; can work freely in various harsh environments, short-distance radio frequency products are not afraid of oil stains, dust pollution and other harsh environments, and can replace barcodes, such as tracking objects on the assembly line of a factory; long-distance radio frequency products are mostly used in traffic, The recognition distance can reach tens of meters, such as automatic toll collection or vehicle identification. Its unique advantages are beyond the reach of other identification technologies, mainly in the following aspects:
Easy and quick to read:
Data reading does not require a light source, and can even be carried out through the outer packaging. The effective recognition distance is larger, and the effective recognition distance can reach more than 30 meters;
Fast recognition speed:
Once the terminal enters the magnetic field, the reader can read the information in it instantly, and can process multiple terminals at the same time to realize batch recognition;
Large data capacity:
The two-dimensional barcode (PDF417) with the largest data capacity can only store up to 2725 numbers; if it contains letters, the storage capacity will be less; RFID terminals can be expanded to dozens of K according to the needs of users;
Long service life and wide application range:
Its radio communication method makes it possible to work in highly polluted environments such as dust and oil pollution and radioactive environments without being in them. The closed packaging of the terminal makes the service life much longer than the printed bar code;
The label data can be changed dynamically:
The programmer can be used to write data, which gives the RFID tag the function of interactive portable data file, and the writing time is less than that of printing a bar code;
Better security:
Not only can it be embedded or attached to products of different shapes and types, but also password protection can be set for the reading and writing of terminal data, thus having higher security;
Dynamic real-time communication:
The terminal communicates with the reader at a frequency of 50-100 times per second, so as long as the object attached to the RFID terminal appears within the effective recognition range of the reader, its position can be dynamically tracked and monitored.
{$page$}
3.General introduction of semi-active RFID system
3.1 System principle
The APS real-time positioning and tracking system uses RFID (electronic tag) as the most advanced identification code at present. It has the characteristics of not easy to break, reliable data, long service life, and long effective communication distance. It is an alternative to barcode and infrared identification. The best choice. Install it on the controlled target to be the unique identification of the target for tracking and positioning.
At work, managers use networked wireless identification base stations to track and locate targets.
3.1.1 Semi-active RFID electronic tags
The semi-active RFID electronic tag integrates the advantages of the active RFID electronic tag and the passive RFID electronic tag as a special marker. In normal conditions, it is in a dormant state and does not work, and does not send RFID signals to the outside world. Only when it enters the activation signal range of the low-frequency activator, the tag starts to work.
3.1.2 Working principle of semi-active RFID automatic identification
Combined with a low-frequency activator, a semi-active RFID tag works normally after being activated. The activation distance of the low-frequency activator is limited. It can only be accurately activated at a small distance and a small range. In this way, the low-frequency activator is used as the base point for positioning, and different base points are installed in different positions, and then used for a long distance in a large area. The reader recognizes and reads the signal, and then uploads the signal to the management center in different uploading methods. In this way, the entire process of signal collection, transmission, processing, and application is completed.
3.1.3 Principles of regional positioning
Schematic diagram:

Figure 3-1 Schematic diagram of system area positioning
As shown in the figure above, we use RFID semi-active technology for personnel area positioning management. In each monitored area, such as each room, a semi-active positioning base station, which is our company’s low-frequency activator, is installed, and each low-frequency activation The device has 4 or 6 activating antennas. 4 or 6 adjacent rooms can share a low-frequency activator. In our positioning system, the positioning base station is the smallest base point, which is the nearest base of the positioning point. The base point, the distance of the activation tag is 3-3.5 meters, that is, each tag is activated within the range of 3-3.5 meters from the activator, and its positioning accuracy can be described as 3-3.5 meters. The activators in different areas have their own unique address codes. When a person enters the positioning base station with a semi-active low-frequency activation tag and is activated, the tag works normally and sends the ID number of the tag to the outside world and also sends out the activation tag. The address code of the activator, in this way, through the address code of the activator, we can locate the location of the label. When the tag is taken from one activator to another location, the uploaded activator address code will also change accordingly, thus forming a complete positioning system. The data uploaded by the tag is received by a large-scale positioning base station gateway, and the information is uploaded to the management center for processing, completing the entire positioning system.
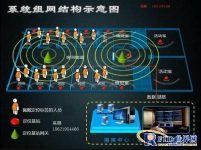
3.2 The overall structure of the system
3.2.1 System composition and architecture
The personnel area location management system based on semi-active RFID technology is composed of semi-active RFID electronic tags, semi-active low-frequency activators, readers (receivers, electronic monitoring base stations), network equipment, computers, servers and system software. The following figure shows the system architecture of a simple personnel area positioning management system:

3.2.2 Schematic diagram of system area positioning

Figure 3-3 Schematic diagram of area positioning
As shown in the above figure: through the address codes of the activators uploaded by different activated tags, the situation of the people near the different activators can be judged, including the number of people, names, positions and other information. In this way, no matter where people go, there will be a local activator lock them to determine their specific location, and timely upload the information to the management center, the management center through a series of transformation processing, and get relevant results. At the same time, we also easily accomplished our established goal, which is to manage the regional positioning of personnel.
3.2.3 Access control management system

Figure 3-4 Schematic diagram of access control management
As shown in the figure above, we install a low-frequency activator for each access control that needs to be managed. Each activator leads to 2 low-frequency activation antennas, namely No. 1 antenna and No. 2 antenna, which are arranged on the outside and inside of the door. A 2.45G long-distance reader/writer independently developed and produced by our company is installed next to the access control as a signal receiver. When a person wearing a semi-active RFID low-frequency activation tag enters the door, they are activated by the activation antenna No. 1 and the activation antenna No. 2, so that the system judges that the person has entered the door. On the contrary, the system recognizes that it is going out. This completes the management of the entire access control system personnel entry and exit judgment.
3.2.4 Concealed installation of equipment
When installing the equipment, we can make full use of the basic conditions of the installation site and flexibly grasp the installation method. Generally, our active antenna is installed on the ceiling and installed secretly to form a beautiful and concise style.

Figure 3-5 Installation diagram
3.3 System functions
Real-time control area target dynamic display function:
1) Query and display the number, distribution and identity of targets in the controlled area at any time;
2) Query the current actual position of one or more controlled targets;
3) Multi-point sharing of information can be realized for multiple departments and leaders to view at different locations at the same time;
Rich map functions:
It has the functions of zooming in, zooming out, moving, ruler distance measurement, field of view control, center movement, soil layer control, map printing, etc.
Forbidden zone alarm function:
For the designated restricted area, if there is unauthorized entry, a real-time alarm will be issued, and the target and identity of the restricted area will be displayed.
Target track query:
You can find the path that a target has gone through in a certain period of time, and draw the line trajectory in the graph.
Abundant control target attendance ability:
It can perform statistics on the goals in and out of the deployment control area, achieve the goal attendance records, and establish various information reports of the goals (such as: time report, attendance monthly report, overtime report, absence report, etc.).
Emergency control:
Once there is an emergency, the host computer can immediately display the target number, information, location and historical situation of the site and other information, which greatly improves the efficiency and effectiveness of the safety management work.
3.4 System performance characteristics
Powerful system processing capabilities:
1) Highly automated;
2) Geographical information display and query system based on GIS technology;
3) Complete data analysis capabilities;
Excellent recognition performance:
1) High recognition reliability, 100% front-end recognition rate;
2) Long recognition distance (recognition distance up to 2-100 meters adjustable);
3) Very high anti-collision performance (each identifying base station can simultaneously identify hundreds of moving targets at most);
4) High recognition stability (bit error rate is less than 1/100,000);
5) Fast recognition speed (up to 200 km/h recognition speed).
On-site advantages:
1) Environmental adaptability: high anti-interference, no special requirements for interference sources and perimeter environment;
2) Installation convenience: integrated structure design, no need for external antenna;
3) Operational reliability: The internal circuit is highly integrated, and the device failure rate is minimized.
Electrical characteristics:
1) Ultra-low power consumption: nanowatt-level ultra-low power consumption design, RFID tags can work continuously for more than 3 years without changing the battery;
2) Convenience and safety, the label does not need an external power supply, no need to charge, no need to replace the battery;
3) No radiation, no impact on human body and environment, safer and healthier.
System hardware design:
1. Industrial frequency band
The use of 2.4G industrial control frequency band wireless communication does not require the approval of the Radio Regulatory Commission, and does not need to pay spectrum occupancy fees.
2. Ultra-low power consumption
The RFID tag uses a unique nanowatt ultra-low power design to ensure that it can continue to work for about 3 to 5 years with battery support. At the same time, the low-power design of the overall structure not only ensures the effective operation of the equipment, but also reduces the complexity and cost of application implementation.
3. Large network capacity
A regional positioning network can accommodate more than 60,000 RFID identification targets and a large number of access points. The large capacity guarantees the powerful data collection capability of the network. At the same time, the high redundancy of the network ensures that the entire network can still operate normally even when individual nodes stop working.
4. High reliability
The core technology of the APS real-time positioning system currently uses a unique positioning algorithm to realize network self-awakening, self-fault tolerance, and self-healing.
5. Low operating and maintenance costs
All hardware equipment of APS adopts maintenance-free design, and the labor cost required for construction and maintenance is very low. Any authorized RFID tag can be automatically added to the network as long as it is placed within the wireless signal coverage of the network without any installation. Configuration. The high degree of intelligence reduces the manpower and time required for network maintenance to the greatest extent, and the low price of the network node itself makes the maintenance cost of the system extremely low.
{$page$}
4.Semi-active RFID system software introduction
4.1 Front desk login interface

Figure 4-1 System login at the front desk
4.2 Software interface navigation diagram

Figure 4-2 Software interface navigation diagram
4.3 The overall process of tracking and positioning monitoring

Figure 4-3 The overall process diagram of the software application
4.4 Backstage management login interface

Figure 4-4 System background login
4.5 Personnel File Module
Establish a digital file of each person, record various information of each person in detail, and establish a multi-dimensional query system, which can query various information simply and quickly. The original personnel information system can be integrated to realize information sharing. Recording the daily behavior of the managed personnel can comprehensively analyze their behavior patterns.
Administrator information: including tag ID, personnel number, name, gender, certificate name, certificate number, certificate address, postal code, contact phone number, personnel level, personnel category, status, remarks, photos, resumes, characteristics;
Add, modify, delete, and query personnel data.
Personnel information includes: personnel unique system ID, electronic tag ID number, personnel number, name, gender, certificate name, certificate number, certificate address, certificate address postal code, contact address, contact address postal code, contact phone number, identity level, Authorization group ID, actual authorization string, and controlled object status.
For example, the personnel ID or name can be entered in the management terminal to quickly locate the personnel.
It includes five parts: personnel information management, administrator information management, monitoring equipment management, electronic map management, and monitoring area management.

4.6 Real-time location monitoring of personnel
You can view the information of people in a certain area on the map

Figure 4-6 Real-time location monitoring of personnel
4.7 Accurate and quick search of personnel

Figure 4-7 Accurate and quick search of personnel
It is also possible to accurately search for a certain person’s situation, such as the current location, the route passed during a certain period of time, and so on.
4.8 Emergency call

4.9 Remote monitoring and inspection

You can remotely check on-site conditions through the network.
4.10 Device management
Equipment information: including equipment ID, equipment number, equipment name, equipment IP, category, location, status, remarks;

Figure 4-10 Device management
4.11 Label data management
Maintain and manage wristband tags, add, delete and modify. The activation and termination of the wristband tag can be set.
4.12 Electronic drawing management
Maintain and manage the electronic map, add, delete and modify, and refine it to specific floor rooms.
Note: The electronic map part needs to be discussed separately.
4.13 Area Management
Management strategies can be set to maintain, manage, add, delete and modify specific areas. An area has independent locator ID, receiver ID and repeater ID, and has a maximum capacity.
4.14 Alarm Policy Setting
It can realize overall on-site monitoring and partial on-site monitoring, and realize the alarm linkage interface function, which can realize the linkage function.
The alarm strategy has the following 5 methods:
When the authorized person goes out for more than the scheduled time and does not return;
Exceeding volume alarm: When the total number of people in the designated area is greater than the maximum capacity of the area, the system will alarm after acceptance;

Tag damage alarm: When the wristband tag worn by the person is damaged, the receiver will continuously send disconnection information, and the system will alarm immediately after receiving it
Boundary alarm: When the wristband tag breaks into an unauthorized area, the receiver will continuously send illegal intrusion information, and the system will alarm after receiving it.

4-12 Perimeter alarm
Disappearance alarm: When the wristband tag is on the designated receiver, there is no signal reception after the time limit, and the system will alarm after it is accepted
4.15 Statistics query report

The historical access records can be queried by personnel, by region, and by time period;
The alarm log can be queried by personnel, by region, and by time period;
The access records can be inquired by personnel, area, and time period.

Figure 4-14 Track playback
[ad_2]