File RFID intelligent management information system
[ad_1]
1. The status quo and problems of file management
In recent years, my country’s archives industry has made great progress. The scale of archives industry has expanded and the number has increased day by day. The types of archives have become increasingly diversified, and the amount of information has expanded rapidly. However, the problems caused by traditional file management methods and technologies have become increasingly prominent:
(1) The file cataloging process is cumbersome and inefficient, and the organization time is long
In the traditional way, the archives need to be classified, sorted, and stapled after entering the library, and then the relevant information of the archive box is manually written, and finally the archive directory is manually copied, and the directory and the files are packaged in the archive box.
(2) The order of file storage is easier to be disrupted
Although files are generally stored in categories, in the process of file access, due to the randomness of manual operations and some inevitable errors, the order of file storage will inevitably be disrupted, resulting in disorderly file storage and difficulty in searching.
(3) Long time-consuming file review
With the increasing size and variety of files, when searching for a certain file, the administrator first finds the file shelf where the file of that type is stored, and then searches each grid of the file shelf according to the cataloging information of the file.
(4) The inventory operation of files is unscientific
Due to the large number of files and the file materials are all enclosed in file boxes, generally only the number of file boxes is counted when counting files.
(5) The management of invalid files is lagging behind
The validity period is one of the important signs of the value of archives. Therefore, archives exceeding the validity period are of no value and need to be destroyed frequently to reduce the occupation of archive inventory resources. As a new generation of material tracking and information identification, the rapid development of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Technology) technology has brought the possibility of automation and intelligence in file management, and has unparalleled advantages in other methods.
2. Scheme design of RFID technology applied to file management
(1) Introduction to RFID technology
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), or radio frequency identification, is an automatic identification technology that emerged in the 1990s. A typical RFID system consists of three parts: a radio frequency electronic tag, a reader or reader, and an antenna. It integrates multiple technologies such as coding, carrier, identification and communication. The main principle is to use radio waves to read, write and identify a marked medium. Non-contact is its obvious feature.
(2) Applying RFID technology to file management has the following advantages:
1. Non-contact data collection. .
2. Fast scanning, and a large amount of one-time data processing.
3. The label information capacity is large, the service life is long, and it can be reused.
4. High security. The data access of the label is protected by a password, and the identification code is unique and cannot be forged. This high-security protection measure makes the data on the label not easy to be forged and tampered with.
5. Strong anti-pollution performance and durability. The carrier of traditional bar codes is paper, so it is easy to be contaminated, but RFID has strong resistance to water, oil, chemicals and other substances.
6. The volume is miniaturized and the shape is diversified. RFID is not limited by size and shape in reading, and does not need to match the fixed size and printing quality of the paper for reading accuracy.
7. It can be reused. Nowadays, the bar code cannot be changed after it is printed. The RFID tag can repeatedly add, modify, and delete the data stored in the RFID tag to facilitate the update of information.
8. Penetrability and non-barrier reading. When covered, RFID can penetrate non-metal or non-transparent materials such as paper, wood, and plastic, and can perform penetrating communication.
9. The tag has the EAS anti-theft function, and cooperates with the door-shaped channel antenna, which can prevent the loss of files and realize the alarm function of illegal removal
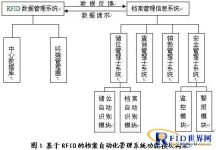
(3) The functional module design of RFID-based archive automation management system
As shown in Figure 1.

1. RFID data management system
The system consists of a central database and a terminal manager, which is the data access center and information input and output terminals of the system.
2. File management information system
The system consists of a storage location management subsystem, a query management subsystem, a destruction management subsystem, and a safety management subsystem.
3. The specific functions of the system are as follows:
(1) Storage location management subsystem: This subsystem can automatically match the file box number stored in the automatic file identification module with the storage location number stored in the storage location automatic identification module, so that it is better when the files are in and out of the library. Realize the positioning of archive storage. .
(2) Inquiry management subsystem: When files need to be consulted, this subsystem provides file cataloging inquiries, secret level inquiries, etc., and issues outbound instructions. The instructions transmit the inquiry signal to the file rack through the computer bus, so that the file rack is placed on the file rack. The indicator light is on, and the management personnel perform library operations according to the indicator light.
(3) Destruction management subsystem: Before the archives are put into storage, the storage period of each file is set in the destruction management subsystem. When the storage period is reached, the destruction management subsystem automatically reminds the management personnel of the relevant information of the invalid file. Personnel for further processing. Managers can also view the archive information that is about to expire or has expired from the subsystem.
(4) Security management subsystem: This subsystem is responsible for file anti-theft and on-site supervision, and implements the security mechanism of file management.
(4) Application scheme of hardware equipment
Generally speaking, the area of the archives warehouse is small, and readers and passive electronic tags in the high frequency or ultra-high frequency (HF/UHF) frequency band can be selected. RFID tags can be divided into file tags and storage tags according to different uses.
1. Setting of label information items
The information items stored on the file label include: file category, file name, file number, file secret level, storage time, preservation period, summary of file content, etc.
The information items stored on the storage location label include: storage location type, storage location number, stored file number interval and quantity.
2. Label installation
² In the file label, seal the electronic label into a card or self-adhesive paper and stick it on each file box or file. ² The storage tag generally only needs to be installed once when the storage location does not need to be adjusted or the tag is not damaged.
3. Electronic label
4. Reader installation
Install the reader on the wall or ceiling of the file room. The normal operation of the device requires an external 110-240 WAC power adapter and a local area network or wireless local area network coverage for data transmission.Connect the RJ45 port of the RFID tag reader to the computer network port to connect the RFID tagReaderThe read data is transmitted back to the server via the network or wireless network.
5. Antenna installation
In order to ensure the reading of the file label data, the antenna layout needs to be determined according to the actual situation of the file room, including the size and style of the file cabinet and the file storage rack, to ensure the best read and write effect, and the antenna needs to be customized.
6. Multi-antenna splitter
WX-23 UHF RFID antenna splitter is the latest generation product developed by Wenrui Intelligent. The splitter is an UHF antenna splitter with 1-8 interfaces, which can be used for networking and distribution of RFID antennas in real-time file asset tracking and smart shelves. The WX-3 antenna splitter is composed of a main antenna splitter and a slave antenna splitter.
Up to 32 RFID antennas can be connected to each RF output port (ANT1~ANT8) of the main antenna splitter. That is, each main antenna splitter can support 4 slave antenna splitters. Note: Considering the actual application occasions, the actual number of antennas may not reach 256 antennas. Please plan reasonably to maximize the performance. Flexible antenna arrangement, expand the read and write control radius, and greatly save system cost.
(5) The process design of RFID technology applied to archives management
(1) Admission
Before the new archives are put into storage, the new archives must be cataloged according to the relevant information such as archives category, year and secret level, and written into the RFID tags through the terminal manager, and the generated electronic tag data is sent to the central database for system preparation. Called by other modules.
The process of file admission is shown in Figure 2:

When entering the library, the storage location management subsystem of the archive management information system issues an entry instruction, and then reads the file box information to be entered, and then the storage location automatic identification module matches the file box information with the archive automatic identification module. The storage location automatic identification module allocates the storage location of the archive box. After confirming that it is correct, the administrator sends an admission confirmation message, which is transmitted to the archive rack through the computer bus, the storage location indicator lights up, and the administrator puts the file box in To the storage position indicated by the indication point, press the confirmation button on the storage position, the indicator light will go out, and the confirmation signal will be fed back to the management system, and admission is over. After all the archives have been stored in the library, the archive information that has been in the library can be inquired in the query management subsystem, so as to realize the visualization and dynamic management of the archives.
(2) Inventory
becauseRFIDInventory of archives becomes a simple and fast task: the query subsystem of the archives management information system issues an inventory instruction, and the RFID reader immediately completes the collection of relevant information of the archives and the corresponding storage information, and automatically returns to the office. The collected information is checked against the data in the central database. For the information that cannot be matched, the management personnel shall use a handheld reader to conduct on-site verification, modify the system information or on-site information, and complete the file inventory.
(3) Consult
The review process of the archives is shown in Figure 3:

When querying related archives, the administrator first consults the catalog number of the archives through the query management subsystem. The system will extract the data information stored in the central database according to the catalog number, and issue an outbound instruction after verification. The automatic file identification module will map its storage location number according to the catalog number to find the physical location where the file is stored. The manager issues an outbound instruction, and the storage indicator lights up. When the file passes through the warehouse, the RFID reader at the warehouse will feed back the read file information to the management system, and the management staff will confirm that the checked file is consistent with the exported file before confirming the warehouse. At this time, the system will record the time information of the archive’s delivery time. If the feedback information is inconsistent with the query information, the monitoring module will send an abnormal alarm to the alarm module.
(4) Safety management
The security management subsystem can realize real-time monitoring and abnormal alarm functions on the archives site to prevent archives from being destroyed and stolen.
(5) Anti-destroy management
When each file enters the library, its weight, page number and other physical characteristics are accurately measured and stored in the RFID data management system. The monitoring module monitors this information. When the file is returned after being consulted, the administrator checks the physical characteristics of the file again and checks it with the data before the file is lent, so that it can find out whether the file is torn, missing, etc. in time.
(6) Anti-theft management
All collection files are in the reading range of the reader. When the file is taken out, the RFID reader at the exit port captures the file information and checks it with the outgoing instruction information. If the file leaves the warehouse abnormally without the outgoing instruction issued by the archive management information system, the monitoring module will be activated The alarm module issues an alarm for abnormal conditions.
(7) Destroy
The value of archives has a time effect. The archives that have lost their archived value need to be destroyed to reduce the occupation of archive management resources. When the archives are in the library, the storage period is written into the RFID tag and stored in the central database. During the storage process, when a file reaches the storage period, the destruction management subsystem will automatically pop up the file failure prompt, and the administrator will destroy it or continue the storage process. At the same time, managers can also send wireless instructions through the archive destruction management subsystem, and the RFID tags on each archive box will feed back the storage period information, so as to realize the effective period management of the archives.
[ad_2]