Application Design of RFID Technology in Automated Warehouse
[ad_1]
According to the management of automated three-dimensional warehouses in modern logistics systems, the basic principles of radio frequency identification technology and radio frequency identification technology have the characteristics of wireless information transmission, large amount of information transmission, and convenient and accurate information dissemination. Combining the working conditions of automated three-dimensional warehouses, the radio frequency identification technology Applied to the automated three-dimensional warehouse, an automated three-dimensional warehouse based on radio frequency identification technology is constructed. Through practical tests, the system can process information more than 10 times faster than traditional methods, and can process data information in real time, which meets the needs of modern logistics systems.
With the gradual maturity of the production technology of automated warehouse system equipment and the gradual popularization of its application, the traditional manual recording-based management method can no longer meet the current needs of enterprises, while the magnetic card, bar code and other technologies are no longer available due to their own defects. It is suitable for the development of logistics industry in the future. These models have exposed many shortcomings in the development process of modern enterprises, which have greatly affected the process of enterprise information automation.
RFID technology is a new and advanced automatic identification technology. Its broad development prospects in various industries have attracted the attention of various countries and enterprises in the world. RFID technology has waterproof, antimagnetic, high temperature resistance, long service life, long reading distance, convenient and fast reading, data on the label can be encrypted, storage data capacity larger, storage information change freely, and various shapes that other identification technologies do not have. The advantages of chemistry. The emergence of RFID technology has solved the problem of automatic data identification, processing information more quickly and accurately, reducing manual intervention, avoiding cumbersome manual input and other processes, thereby reducing production costs. Therefore, this paper proposes a design that applies RFID technology to a three-dimensional warehouse system, which can not only realize the normal operation of an automated warehouse with 80 storage locations with higher accuracy and speed, but also adapt to the production management of modern factories and enterprises.
1 Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology
1.1 Introduction to Radio Frequency Identification Technology
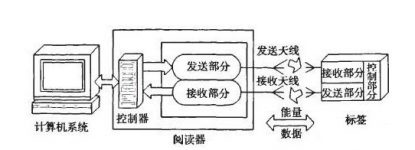
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio frequency signals through spatial coupling (alternating magnetic or electromagnetic fields) to achieve contactless information transmission and achieve identification through the transmitted information. The basic RFID system is generally composed of electronic tags, antennas, readers and so on.
(1) Electronic tags (Tag). Composed of coupling components and chips, each electronic tag has a global identification number (ID), which cannot be modified or imitated, providing security. Electronic tags must be attached to objects to mark the target object. The electronic label generally saves electronic data in an agreed format, such as the type, production batch, quantity, and location number of the shelf where the object to be identified is stored.
(2) Antenna. The radio frequency signal is transmitted between the tag and the reader, that is, the data information of the tag and the command information issued by the reader.
(3) Reader. Devices that read or write electronic tag information, including handheld and fixed types. The reader can read and identify the electronic data stored in the electronic tag without contact, so as to achieve the purpose of automatically identifying the object. And it is connected with the computer to process the read label information. The composition of the RFID system is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 RFID system composition
Compared with traditional identification technology, RFID has the following advantages: fast processing speed; small size and diversified shapes; strong anti-pollution ability and durable; reusable; strong penetrability, which can realize barrier-free reading; data memory capacity Large; high security.
1.2 The working principle of RFID technology
The reader uses its antenna to emit energy in a certain area to form an electromagnetic field. The size of the area depends on the transmission power, operating frequency and antenna size. When the tag enters this area, it receives the radio frequency pulse of the reader, charges the capacitor after bridge rectification, and uses it as the working voltage after being stabilized. At the same time, the data demodulation part demodulates the commands and data from the received radio frequency pulses and sends them to the control logic. The control logic receives the instructions and sends out the product information (Passive Tag, passive tag or passive tag) stored in the tag. Or the tag actively sends a signal of a certain frequency (Active Tag, active tag or active tag). After the reader receives the returned data, it decodes and performs error checking to determine the validity of the data, and then sends it to the central information system for relevant data processing.
2 The overall design of an automated three-dimensional warehouse based on RFID technology
2.1 The composition of automated warehouse system
The main body of the automated three-dimensional warehouse system is the automated three-dimensional warehouse. In order to realize the automatic storage and retrieval of materials, a corresponding management and monitoring system is also required. Therefore, the composition of the system is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 The composition of an automated warehouse system
2.2 Main components of automated warehouse system
(1) The main controller. The main controller used in this design adopts Siemens’ small PLC, which has the processing capacity of 40 digital I/O points, and has two-channel communication/programming ports, which can realize the network control of multiple stations in the system Features.
(2) Detection device. The detection of the system includes location detection, status judgment of the system’s various actuators, etc. The detection devices used include contact position sensors, photoelectric sensors (Omron CX-24), rotary encoders (Omron E6A2-CW5C), etc.
(3) Stacker. The main actuator in the automated warehouse system is a stacker, whose function is to automatically deposit and withdraw goods from the shelves. The stacker designed in this system is mainly composed of a three-axis motion mechanism composed of stepping motors. The selected motor adopts HS series high-torque square hybrid stepping motors, which are relatively small in size and high in accuracy. The stacker and the PLC controller can meet the requirements of accurate positioning.
(4) Conveying system. Its role is to transport the goods to the stacker or remove the goods from the stacker. Common conveyors include chain conveyors and belt conveyors.
(5) RFID system. The system uses the V600 series produced by Japan’s Omron Company as the RFID system. The device is electromagnetically coupled and the oscillation frequency is 530kHz. It mainly includes read-write heads, ID controllers, and passive electronic tags.
①The read-write head, model V600.H11, is a bridge between the electronic tag and the ID controller to exchange information, and it belongs to the built-in amplifier. Through the read-write head, the command of the host can be sent to the electronic tag within a certain range through the ID controller, and the response information of the electronic tag can be transmitted to the ID controller at the same time. ②ID controller, model V600-CA5D02, is used to connect with the read-write head of the V600-H series, execute the command of the host to read and write the electronic label, and return the response signal of the electronic label to the host at the same time. ③The electronic label, model V600.D23P66N, is the battery-free data carrier in the Omron V600 series and belongs to the passive electronic label.
2.3 System process analysis
According to the flow of goods, the main process of the system is divided into the inbound operation process and the outbound operation process, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
(1) Warehousing operation process
① Preparation for storage. The storage preparation of the system includes initialization of the system state and data initialization. At this time, the stacker is in the initial state, and the ID controller is ready to detect the goods. ②Release the warehousing order. The warehousing order can be sent to the main controller manually or electronically. The main controller can identify the type of goods according to the information on the warehousing order. At the same time, it also needs to process the ID information of the detected goods fed back by the read-write head. Compare the two information, when the goods information is consistent with the warehousing list, the system automatically assigns a location number to the warehousing goods, which is written into the electronic label by the read-write head. ③Receive in the warehouse. Inbound entry means that the stacker is transferred from the inbound port to the pickup platform. The system assigns a space coordinate point to the stacker according to the warehouse number assigned by the goods. At this time, the stacker runs from the initial state to the warehouse entrance, and transfers the goods from the loading platform to the stacker’s pickup platform. Prepare for the next release. ④ Put into storage and put on shelves. Inbound and shelf-in is the last operation step of warehouse inbound. The stacker will put the goods on the pick-up table into the designated storage location. The stacker automatically finds an optimal trajectory according to the space coordinate points allocated by the system, and delivers the goods from the warehouse entrance to the warehouse. ⑤The storage is over. After the goods are put on the shelves, the stacker returns to the standby state, and the system updates the location data and completes the corresponding records.

(2) Outbound operation process
① Preparation for delivery. The preparation of the system is similar to the preparation of the warehouse. ②Release the outbound order. The outbound order can be sent to the main controller manually or electronically. The main controller recognizes the type of goods according to the information on the outbound order. At the same time, it also needs to process the ID information of the detected goods fed back by the read-write head. The two information is compared, and when the goods information is consistent with the outbound order, the system is ready to be outbound. ③Exit and enter. After the system confirms the outbound operation, the stacker will obtain a certain spatial coordinate point according to the location information determined by the outbound order. Under the operation of the main controller, the stacker will follow the optimal path from the current position to the designated position. ④Release from the warehouse. In the warehouse area, the stacker removes the goods from the designated position, and at the same time the read-write head reads the goods ID information and feeds it back to the main controller. The main controller judges whether the outgoing goods information is consistent with the outgoing order information. When the information is confirmed, it performs the pick-up operation and transports the goods to the outbound port. At the same time, the electronic label system writes out the outgoing information into the electronic label. Update storage data. ⑤Exit is over. The stacker returns to the standby state, the system data is updated, and the corresponding records are completed.
3 program design
During the operation of the entire system, the core control technology includes two aspects: on the one hand, the automatic tracking and spatial positioning of the stacker in the automated warehouse; on the other hand, the RFID system automatically detects and updates data information.
It can be seen from the system flow chart (see Figure 3 and Figure 4) that the RFID system is mainly divided into two functions in the application, namely, read information operation and write information operation. For the read and write operations of electronic tags, there is a corresponding fixed communication format in the corresponding system, and the user can complete the corresponding control only according to the communication format.
By changing the command code in the communication format, commands such as read and write operations can be realized. The following takes the main controller to control the reader to complete the read operation as an example to illustrate the design of the program.
In order to complete the PLC control of the ID controller, the PLC controller needs to send the correct commands to the ID controller, so the controller’s free VI instructions XMT (data sending instructions) and RCV (data receiving instructions) are used to complete the purpose of operating the ID controller .
When the goods arrive at the storage port, the switch signal of the photoelectric sensor is triggered. At this time, the PLC executes the port sending command XMT, and the port sends an automatic read command (AUTO READ), and then the PLC receives the command RCV through the port to receive the read Cargo information is judged by the system. When the goods in the warehouse are consistent with the information in the warehousing list, the warehousing instruction is issued according to the warehousing process, the warehousing subroutine is started, and the warehousing is completed.
4 Conclusion
Practice has proved that the application of RFID system achieves the goal of high efficiency and speed, can replace some sensors and other detection equipment on the original production line, save space and I/O ports of related controllers, reduce the complexity of programming, and speed up materials The turnover improves the production efficiency, accuracy and safety of the device.
[ad_2]