Container RFID logistics management system design scheme
[ad_1]
1. Background and significance
With the further acceleration of economic globalization and the rapid development of international trade, container transportation has become an important form of transportation modernization due to its high efficiency, convenience and safety. Since the “9.11” terrorist incident, in order to prevent terrorist organizations from using ships to carry weapons of mass destruction or terrorists from entering the United States, the US government has continuously strengthened its port and shipping security measures. The United States implemented excellent inspections of containers from corresponding ports of the CSI (Container Security Agreement), which strongly stimulated the rapid development of electronic seal technology.
How to efficiently manage the containers parked at Shanghai Port and ensure the safety of the entire container during the transportation process has become a problem that plagues Shanghai Port Group.
Traditional container management mainly relies on manual management, which is in a manual and semi-manual state, and the efficiency is very low. Modern container management urgently needs an electronic tag that can record box, cargo and flow information in real time, record the time of opening and closing boxes and geographic information, so as to improve the overall level of container logistics. The application environment of container electronic tags is very complicated, and the technical difficulty is very high. The technical indicators, functional requirements, and process requirements proposed are far greater than those of ordinary electronic tags. Container electronic tags have very strict requirements on the safety and reliability of the tags.
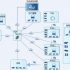
RFID electronic seals perfectly solve this problem, and incorporate a new generation of reusable electronic tags with GPRS technology. Electronic tags enter container, cargo and other data, and transmit them to the data center through wireless LAN, and implement real-time online monitoring of the container. All nodes of the container logistics chain can check logistics information on the system website at any time, and the time and location of legal and illegal unpacking All can be accurately recorded and displayed on the website in real time. Including container information, loading/unloading information, container transportation information, inspection information, opening/closing time, geographic location, status, and logistics information can all be queried in real time, and can be transmitted in real time to thousands of miles away The background management system can log in to the system platform to query the status of a certain container from anywhere in the world.
2. Process flow introduction
In view of the characteristics of cross-border container transportation, the project team determined the process flow of applying container electronic tags from container packing point, arrival, loading, unloading, departure to unpacking point. According to the operation process, it can be divided into two major processes: “door-to-door” and “port-to-port”.
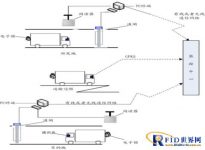
(1) “Door to door” process
A. Packing point:
Use the handheld reading and writing device to initialize the tag first, enter the tag number, container number, cargo name, etc. on the tag, and select the GPS geographic location. Close the door of the loaded container, hang an electronic label and report the dynamic information to the server.
B. Entry/exit crossings in the port area:
a. When a container truck with an electronic tag enters the entrance/exit crossing channel, the fixed reader/writer installed at the entrance crossing automatically reads the electronic tag, uploads all security and logistics dynamic information to the server, and displays the logistics information on the On the web. Confirm the security status of the electronic tag (whether the door is opened and closed illegally, the system will send out an alarm message, which is convenient for the sender/receiver to track down).
b. According to the container number, obtain the EDI electronic packing list data from the server, and record part of the EDI data in the label, and upload dynamic information such as security and logistics to the server.
C. Customs inspection:
a. At the inspection point, after the customs confirms the security status of the container, it is authorized to open the label, pull out the steel bolt opening door on the label, and automatically record the time and geographic location information of the opening door in the label, and upload the dynamic information to Server, logistics information is displayed on the web page.
b. After the customs inspection, close the door of the box, and insert the steel bolt into the label under the authorization status to complete the labeling. At this time, the label automatically records the time of closing the box and the geographic location information is automatically recorded in the label, and the dynamic information is uploaded to the server at the same time.
D. Loading/unloading:
When a container equipped with an electronic tag is loaded/unloaded, the fixed reader/writer installed on the crane automatically reads the information of the electronic tag, and uploads dynamic information such as the security status and logistics of the container to the server.
E. Unpacking point:
At the unpacking point of receiving the goods, use a mobile read-write device to manually read the electronic tags, upload the full dynamic information of the container logistics to the server for archiving, and authorize to open and remove the electronic tags.
The dynamic information of the whole process safety, container, cargo, logistics and other dynamic information of the container with the electronic label through 6 controlled points is displayed on the web page.
(2) “Port-to-port” process
Export process:
As the shipping containers are distributed all over the country, the packing has been completed at each packing point. Therefore, the research team arranges the operation of attaching electronic tags in this process before the container enters the port crossing.
The handheld reader/writer device is used to initialize the tag first, enter the tag number, container number, cargo name and other information on the tag, select the GPS geographic location and report the dynamic information to the server.
The operation process of approach, inspection, and shipment refers to the “door-to-door” process.
Import process:
The operation of unloading refers to the “door to door” process.
The operation of exiting and untagging is completed at the exit crossing.
When a container truck equipped with electronic tags enters and exits the crossing channel, the fixed reader installed at the crossing automatically reads the electronic tags, and uploads the dynamic information of the container logistics to the server for archiving, and removes the electronic tags and logistics information Display on the web page. The container truck drove out of the crossing.


product photo:


3. Research and test of container electronic tags
The container management project has gone through a variety of RFID technology solutions, and many foreign and domestic manufacturers have participated in the selection before and after. Many international shipping companies have carried out research on the container electronic label system, but the container logistics is monitored online in real time. The system has been fully put into operation on international container routes. The “Shanghai Port of China-Savannah Port of the United States” demonstration route is the first internationally, indicating that my country is leading the world in terms of technology in this field.
[ad_2]