Intelligent warehouse management system based on RFID and barcode
[ad_1]
This solution is mainly aimed at the current status and existing shortcomings of SME warehouse management, using radio frequency and bar code technology to optimize the design of SME warehouse management. After analyzing the value of radio frequency and bar code technology in SME warehouse management, A solution of warehouse management system for small and medium-sized enterprises based on radio frequency and bar code technology is proposed. The plan described in detail the three processes of warehouse-in, warehouse-out, and inventory based on RFID and barcode technology. On this basis, a system model based on RFID and barcode technology is constructed.
Modern inventory management involves a large number of complex products. If you want to gain an advantage in fierce competition, you must put forward higher requirements for inventory management: improve the accuracy of product query, improve the quality of inventory operations, and reduce costs; once it is lower than the safety inventory system, the system can automatically Warning; improve the efficiency of goods in and out of the warehouse to provide managers and decision makers with timely and accurate inventory information. For small and medium-sized enterprises, their own characteristics determine that the financial and human resources invested in warehouse management are subject to greater restrictions, so they need a warehouse management system solution that fits their own reality.
1. Analysis of the status quo of warehouse management in SMEs
The number of small and medium-sized enterprises in my country has reached more than 42 million, accounting for 9,918% of the total number of enterprises in the country. The degree of information automation of these enterprises directly affects and reflects my country’s productivity and overall national strength. With the development of information technology, enterprise inventory management technology presents a series of new development trends, but there are still some problems, especially the sharing and integration of information. Based on the analysis of existing inventory management, the following deficiencies are summarized:
(1) The methods of information collection are backward. Most companies use manual collection methods that are relatively inefficient. Even if the barcode technology is adopted, it is impossible to completely break away from the artificial function, so it is difficult to avoid some errors and the efficiency is extremely low.
(2) Information cannot be integrated and shared. The informatization construction of some enterprises has not realized the integration and sharing in the true sense, cannot realize the automatic transmission of business information and financial information, and cannot implement real-time control of the enterprise. Even more enterprises still rely on manual operation to a certain extent, and it is difficult to improve the efficiency of the enterprise, and it is impossible to fundamentally reduce the cost of the enterprise. In addition, due to the inability to realize the integration of information, some valuable information of the enterprise may not be available and the application loses the effectiveness of the information.
2. The value of RFID and barcode technology in the warehouse management of small and medium-sized enterprises
At present, there are two main methods for the existing warehouse management of small and medium-sized enterprises: one is a method of combining artificial memory and cards, which is mainly used in enterprises with relatively few raw materials. This method is not only time-consuming and labor-intensive, but also prone to errors, which makes goods storage The link efficiency is low, which brings greater losses to the enterprise; the other is through the implementation of a warehouse management system, using barcode scanning technology as a method of synchronizing the flow of goods and information in the warehouse management. The barcode has low cost and can effectively classify , Can convey the advantages of many items information, but with the continuous improvement of the informationization requirements of enterprises, the shortcomings of bar code technology such as the inability to change the information, the small storage capacity, and the inconvenience to read the information have caused the information system to appear when the original data is collected. The lack of completeness makes it more difficult for companies to analyze and predict these data later. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-contact data collection and automatic identification technology with its large capacity, long life, anti-fouling, non-contact, automation and other characteristics has gradually become a major object identification technology.
For the breakthrough technology of RFID, the chief scientist of Accenture Labs Ferguson commented this way: First, it can identify a single very specific object, instead of only identifying one type of object like a barcode; second, it uses radio frequency , The data can be read through external materials, and the barcode must be read by laser; third, multiple objects can be read at the same time, and the barcode can only be read one by one. However, due to the high cost of electronic tags, lack of industry standards, security issues, etc., RFID will not completely replace barcodes. From the current maturity of barcode technology in various industries, the status quo of RFID technology R&D and application, and the development of these two technologies Judging by characteristics, the application of RFID technology and barcode technology will coexist for a long time. The introduction of RFID and barcode technology into the warehouse management system can meet the requirements of small and medium-sized enterprises for the informatization, automation and modernization of warehouse management, realize the visualization of the real-time status of the warehouse, make warehouse management more quickly respond to environmental changes, and improve the interior of the warehouse. Resource utilization.
3. Design of warehouse system scheme for small and medium-sized enterprises based on RFID and barcode
The same type of items on the receipt share an electronic label, and each item’s packaging is affixed with a bar code. At the same time, the corresponding relationship between the electronic label and the bar code is stored in the database. Information automatically completes the warehousing operation. A position label is placed on each position in the warehouse, and the position label is updated with the information on the item label. Finally, the electronic label of the item is recovered to make it recyclable. By embedding RFID technology in the original bar code mode, the solution effectively improves the automation of information collection, realizes real-time monitoring of inbound and outbound operations, facilitates the location and query of inventory goods, and avoids the complete replacement of electronic tags. The high cost of bar codes greatly improves the efficiency of warehouse operations.

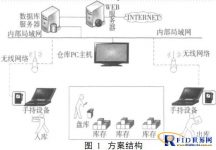
This system is mainly composed of five parts: database management system, handheld electronic label barcode reader, article label and location label, article barcode, and host management system. The structure of the scheme is shown in Figure 1. The entire system is mainly based on handheld readers, assisting desktop fixed devices for card issuance; tags are divided into cargo tags and cargo location tags, and wireless routers are connected to the local area network for wireless handheld terminals to access the network; handheld The users of the reader-writer general warehouse connect to the system through the local area network, and the database server connects to the local area network to provide data storage functions; the host management system is implemented on the background application server, which mainly expands the traditional warehouse management software, using RFID and barcode technology Complete the functions of goods storage, storage, reloading and so on.
1. Analysis of warehousing process
When goods are put in storage, multiple operations such as input of goods information, generation of receipts, inspection and placement of goods, and generation of warehousing orders are required. The main process is shown in Figure 2:

(1) The goods are received and inspected. The warehouse receiver judges whether the batch of items are purchased by the company based on the order number or supplier name on the delivery note, conducts a preliminary acceptance check on the quantity and appearance of the items, and generates a receipt. The same type of items on the receipt An electronic label is printed on the article, and a bar code is printed on the packaging of each article; the quality inspector samples the raw materials, inspects various indicators of the raw materials, and enters the acceptance sheet to give the final conclusion of the material. The receipt form corresponds to the acceptance form through the bar code.
(2) In the warehousing operation module of the inventory management system, select the information of the goods to be warehousing, and generate a new warehousing list.
(3) The goods are put into storage. The warehouse manager puts the accepted items on the trailer, and scans the electronic tags on the items with the handheld electronic tag barcode reader to obtain the items to be stored in the warehouse. The system displays the inventory location of the items according to the inventory management.
(4) Update the cargo location label.The warehouse clerk places the items according to the position of the items on the handheld electronic tag barcode reader
Update the location label according to the information of the item label; for new items and new locations, the warehouse manager puts the item on the shelf according to the principle of location management, and changes the item label to the shelf label, and updates the electronic label bar code table and material inventory through the handheld device Bit table.
(5) The label of the recovered goods has been put into the warehouse. After the goods are put on the shelf, remove the label of the article, initialize the label of the article with the handheld device, and update the electronic label bar code table to prepare for the next use. Compared with the traditional warehousing business, because the warehousing acceptance work is mainly completed by the RFID system automatic warehousing, the warehouse manager only needs to put the accepted goods on the warehousing trolley in the normal way, and the system will automatically read and write. RFID tags are used to complete the warehousing work of goods, which reduces the time and manpower for the delivery of goods, and greatly improves the efficiency of the warehousing work.
2. Analysis of the outbound process
The operation of goods delivery is the inverse process of the warehousing operation, which requires operations such as generating the delivery list, extracting items, updating the label, and confirming the delivery. The operation is shown in Figure 3.

(1) In the outgoing operation module of the inventory management system, select the information of the goods to be out of the warehouse according to the sales order number or the production task order number, and generate a new outgoing order. The system lists the location of each item through the inventory management.
(2) The goods are shipped out of the warehouse. The warehouse clerk goes to the designated place to remove the corresponding goods according to the outbound order, scans the bar code on the packing box of the goods, and puts the goods on the trailer. Follow the above steps after the batch of goods out of the warehouse is taken and placed. The operator makes the final confirmation of the outbound operation on the handheld device, and then the handheld device will automatically batch process all the information to generate the outbound backup information.
(3) Update the cargo location label. The warehouse manager reads the inventory information of the current shelf label through the handheld device. The handheld device recalculates the new inventory information based on the spare information, writes it into the designated information block on the location label, and updates the electronic label bar code table at the same time to generate the operation Log.
(4) Complete the delivery.
3. Analysis of the inventory process
RFID-based automatic inventory The traditional inventory inventory time is short, and the data can be automatically entered. It is different from the traditional inventory operation in the operation process. The operation process includes: inventory data preparation, barcode data scanning, tag data update, error data verification, The operations of inventory report generation, inventory profit and loss processing, etc. are shown in Figure 4.

(1) Inventory data preparation. Organize the book data of the inventory in the inventory management system, but in addition to summarizing the total amount of materials when printing the inventory, you also need to get the information recorded on the RFID tag on the book, such as the corresponding barcode material code, material name, quantity, Location etc.
(2) Update label data. Inventory personnel enter the area that needs to be counted with an activated handheld device, and count each label as a unit. Set the handheld device in the inventory counting state, and use the handheld device to scan the barcodes of all the goods on the shelf. After scanning all the barcodes of a single raw material, the operator confirms the raw material inventory operation on the handheld device. The handheld device calculates the obtained barcode information to generate the raw material inventory information, and then the operator writes the inventory information on the handheld device Enter the raw material label.
(3) Error data verification. With the above two types of data, the inventory data of the raw material warehouse can be proofread, according to whether the barcode, material name, quantity, location and other parameters corresponding to the code in the RFID tag are consistent with the system data. For inconsistent data, manually confirm whether the book data or the deviation of the RFID data and make corrections.
(4) Inventory report generation. For the above detailed inventory data classification, an inventory report is formed and stored to summarize the detailed inventory data to obtain an inventory report similar to the traditional inventory of enterprises. The introduction of RFID technology only changes the inventory process and improves inventory efficiency. There is not much change in the form of upper-level application reports. This also makes inventory management personnel not resistant to the introduction of RFID technological innovation by enterprises.
(5) Handling of inventory gains and losses. Compare the physical data with the book data, and divide the results into inventory balance (book data=physical data), inventory profit (book data
Four, system software design
The system software design includes the design of card reader and tag receiving and dispatching program, back-end server equipment management software and back-end database. The transceiver program of the card reader and the tag mainly completes the program initialization, defines the physical address of the RF sending/receiving, the length of the sending/receiving address, the sending/receiving frequency band and speed and other parameters; the server-side software adopts VisualStdio.netC# to design and realize the background The database adopts SQL Server 2000, and the system framework is shown in Figure 5.

Five, application examples
A certain food company in Tianjin has about 250 employees, most of the products are customized for customers, and the raw materials involved in different orders are not the same. The variety of complex materials and products with a wide range of names make the warehouse management labor a huge amount. Prior to the application of RFID, inventory management relied on manual operations, and the receipt or delivery receipts were manually processed every day; although computers were used for inventory management, warehouse clerks still used paper warehouse cards to manage physical objects. When encountering people in peak seasons and high frequency of outgoing, operators need to frequently perform manual documents and computer operations, and there are delays in the entry and exit of the book and the actual operation of the warehouse, which makes the sales staff unable to grasp the exact product inventory And the inventory of raw materials, resulting in decision-making errors and failure to deliver on time.
The system includes basic data management, equipment and label management, storage management, storage management, inventory management, statistical analysis and other functional modules. Some functional modules are described as follows:
The warehousing operation management automatically displays the detailed information of the goods in and out of the warehouse by selecting the order number or the name of the supplier, and automatically generates the warehousing order number according to the date and time, and generates the internal label code and barcode after filling in the quantity and unit price of the goods in the warehouse. To identify the goods after storage.
Outbound operation management Select sales order or production task list to automatically display the detailed information of outbound goods, and automatically generate the inbound order number according to the date and time, and the operator performs outbound operations based on the outbound order details on the shelf information and barcode .
Inventory management can query the inventory of the goods in the warehouse and the total inventory of the goods by selecting the type and name of the goods. At the same time, when the inventory of the warehouse is surplus or deficit, the inventory of goods can be fine-tuned through this module.
Statistical analysis has always been an important method in inventory management. This module is similar to a small statistical software, which counts the above information according to classification items, and displays the statistical results with various charts. It mainly includes the details of warehouse entry and exit, summary of warehouse entry and exit, inventory ledger, inventory product inspection information, etc.
6. Benefits to the company after the successful implementation of the RFID warehouse management system
(1) Realize real-time monitoring of inventory status and operation process;
(2) Realize the automatic input of warehousing and exit vouchers, which greatly reduces the labor intensity of storage system operators;
(3) Improve the quality of inventory operations;
(4) Provide timely and accurate inventory information to managers and decision makers.
[ad_2]