RFID intelligent warehouse management system solution
[ad_1]
1. Goal
1. Standardize warehouse management, standardize basic data, and standardize warehouse operations;
2. Strengthen the synchronization and refinement of logistics and information flow, and improve the timeliness and visibility of logistics information.
In terms of specific warehouses, the goals are:
1. In this solution, speed, efficiency, accuracy, and information integration are the key goals pursued. Mainly to improve the accuracy of warehouse management, management accuracy and convenience of operation, and reduce data errors and delays;
2. Use two electronic tags of cargo packaging and cargo location in the RFID system to assist in warehouse management and improve efficiency;
3. According to the packaging unit management, that is, the storage packaging unit (board, piece, box) has a unique label, which provides support for the fine management of inventory, and the inventory is real-time visible and traceable; (the packaging unit is in accordance with the packaging granularity that needs to be managed)
4. Record goods receipt, packaging, warehousing and storage, picking, and shipping bundles in and out quantity, location and other information; record goods change information (type, quantity, etc.) through the warehouse label association to track warehouse goods and improve entry, The correct rate of export, storage and transfer, reduce dependence on people in daily work, and reduce human errors;
5. Goods in and out correspond to the label of the cargo space, and accurately record the inventory of each specification product corresponding to the corresponding cargo space, reduce warehousing and picking errors, and improve shelf utilization; it can flexibly use the cargo space;
6. In the inventory check, separate the documents to improve the inventory efficiency, not only count the inventory quantity but also check the position and ensure the correct rate of the goods and the position (location), and can carry out the regional inventory at any time in normal times to ensure the inventory in the daily warehouse work. Correct, especially when the entry and exit are normal, the inventory work can be carried out;
7. Effectively distinguish physical inventory and listed inventory, effectively manage the time difference between invoices and objects, and facilitate warehouse and financial reconciliation.
2. Business needs
(1) Scope of implementation
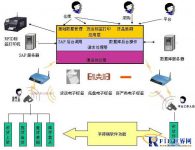
With PetroChina warehouse as the implementation target, the inventory management system uses RFID as the information carrier, and the Rfid warehouse management system realizes data interaction with the back-end logistics system.
Solution diagram

(2) Process
1. Warehousing process
1) After the arrival of the goods and before entering the warehouse: After the goods arrive in the warehouse, the operator can query the relevant information of the goods (such as product name, quantity, supplier code, etc.) according to the delivery document number in the management terminal, and then scan the code on the warehouse goods , At the same time, it checks whether the packaging of the goods is damaged, and the system then checks whether the items in the delivery document are consistent with the actual arrival. If there is any data that does not conform to the delivery document, the system will directly alert and the warehouse operator will refuse to receive the goods; if it matches the warehousing document, the system will give corresponding information. At the same time, the relevant information after acceptance needs to be automatically identified and transmitted to the WCS system by the RFID reading and writing equipment, and the storage confirmation is completed in the SCM management system, and the storage receipt is printed at the same time.
2) After the goods are put into the warehouse: the warehoused goods are stacked by the staff according to the storage location of the warehouse. The stacking type can be stacked by point, batch by batch, sorted by different manufacturers, and supporting stacking, etc. The operator holds the terminal, scans the cargo label, scans the location label, records the location (associated with the cargo information), confirms the storage, and synchronizes the required inventory information to the WCS and SCM management system.
2. Shipping process
1) Before the goods out of the warehouse: After the RFID system is adopted, the operator enters relevant information in the RFID system according to the outbound voucher, the system queries the goods that meet the outbound voucher, and generates a picking list that meets the requirements, including the picking list number, Picking location, code, box number, destination, total package quantity, location picking is automatically instructed to generate graphical interface prompts according to pre-set rules, allowing operators to manually specify in the system.
2) Outbound picking: For outbound picking steps, you can refer to the process of the RFID system. It should be noted here that different goods may be packaged separately, or packaged by product, or several products are combined. The former does not need to be unpacked or sorted, and can be shipped out of the warehouse directly; in the latter two cases, it is necessary to disassemble and sort and then ship out the warehouse. Zero splitting and sorting cannot be completely avoided. This requires the RFID system to effectively control the flow of the zero splitting and sorting units and other information (including authorized personnel, operators, time, reasons, etc.).
3) Outbound confirmation: When the transport vehicle arrives to pick up the goods, the operator conducts outbound inspection to confirm whether the picked goods are consistent with the picking list or delivery notice, and complete the outbound confirmation work; here it is required that the required goods be finally out The library information is synchronized to the WCS system, and the warehouse out confirmation is completed in the SCM system, and the warehouse list is printed.
3. Process of moving warehouses
When the delivery of a batch of goods is nearing completion, and the inventory is low, or when the next batch of bulk goods is notified, the warehouse needs to be moved to free up the storage space to welcome the arrival of new goods.
The actual implementation of the transfer of warehouses to confirm the correctness of the operation of the transfer can also refer to the relevant procedures in the RFID system. What needs to be done by the RFID system is to save the data of each transfer of the warehouse, and it is required to be able to call these easily. data.
4. Inventory process
Warehouse inventory is to carry out periodic warehouse acquisition and inventory work in accordance with conventional requirements, so as to grasp the status of inventory goods in time. Therefore, when inventory, you can refer to the process of RFID system operation. It is only required to generate a variety of different items according to the instructions of the operator. Inventory result report, including inventory profit and loss, inventory, position report, etc.
In addition, there is also an inventory check for each engineering project, requiring timely reporting of the incoming, outgoing, inventory, and backlog time of each batch of engineering goods.
Three, functional design
1 Storage
1.1 Process of warehousing according to plan

1.2 Unplanned warehousing process

1.3 Process description
1. Obtain the receipt data from the SCM system or directly enter the receipt data in the WCS;
2. Warehousing acceptance and data collection: When the goods arrive, the warehousing data that needs to be checked and accepted are called from the management terminal handheld according to the order number. Because the method of using a label for each pallet, the goods can be assigned to Pallet, and associate the pallet label with the cargo information (single number, box number, etc.); in this way, you can scan and install the label before palletizing; in other words, the unloading worker can place the goods on the pallet after the inspection and loading and unloading. Complete the data collection work for acceptance at the same time, thus replacing manual information entry.
Non-conformance reminder: As the pallets are allocated and the pallets are scanned to establish an association after each goods are checked and accepted at the time of acceptance, the number of final scanned goods may not match the delivery documents. At this time, the operator needs to be reminded, and the operator can do the following according to the reminder judge:
1) The actual quantity is inconsistent with the plan due to the partial arrival of the goods, the operator can consider the acceptance to be correct and continue to the next step
2) When the operator finds that the label scan does not reflect during the scan, then rescan or replace the label; if the number of scans is found to be inconsistent with the visual inspection, rescan or manually enter the quantity of goods;
3) In the case other than the above, you can check this batch of incoming goods; obtain the pallet labels of this batch of incoming goods from the system, and check them one by one to eliminate the quantity error caused by the operation error.
In the future, you can consider installing tags before delivery and storage, and transfer the tag code data of each arrival to the WCS system in advance, and quickly read the data through the door reader. When the scanned tag code data is compared with the transmitted When the data is not the same, the alarm will be sent directly.
3. Generation of the shelf list: the operator is equipped with a handheld terminal or a vehicle-mounted terminal, and presses the corresponding button on the system terminal to generate and enter the warehouse according to the acceptance data according to certain rules (such as a certain location can only store certain goods, or determine whether the maximum storage capacity is exceeded, etc.) The instruction sheet indicates the location where the current goods should be stored (manual adjustment is allowed). When the location is found, the forklift driver is instructed to put the goods into the warehouse, and then confirm the storage on the terminal. The shelf list is a record for a location, so a record on the warehousing document may generate multiple shelf location records corresponding to the box number, quantity, customer, supplier, etc. of the goods in each location. .
4. Execution of the shelf: Considering the warehouse layout and the specific conditions of the staff, if the forklift driver confirms the storage, the mobile terminal (handheld or on-board) will indicate the specific location and route of the batch number when it is put on the shelf; if If the operator confirms the shelf placement, he can first scan the storage location through the handheld terminal to confirm and then instruct the forklift driver to put it in. Whether to store according to the product category or the delivery destination when storing, at the system level, it only allows one storage location to store the same product from different suppliers or different products from the same supplier or even different products from different suppliers, which has little to do with RFID.
5. Warehousing receipt confirmation: After the receipt of the batch of goods has been put on the shelf and warehousing, press the “Confirm” button, and the WCS and SCM inventory data will be updated; if the receipt of all goods is completed, press the “Close” button Close the document.
2 Delivery
2.1 Process of outgoing warehouse according to plan

2.2 Unplanned delivery process

2.3 Process description
1. Obtain the receipt data from SCM or directly enter the receipt data in WCS.
2. Outgoing picking generation: The picking order number is automatically generated on the terminal according to the outgoing order number according to the set rules, allowing the operator to specify the outgoing location.
3. Outbound picking: The operator selects the goods according to the designated location of the terminal, first confirms the location by scanning the location label, and then scans the pallet label to confirm the pallet label. If the pallet is a package of goods, and the label represents the package For goods, the quantity does not need to be changed. If there are unpacked goods on the pallet, you need to enter the actual picked quantity. When the unpacked goods are put into a new box and put on the shelf, the label on the new or pallet needs to be scanned and associated with the picking list, and the quantity associated with the original label is deducted. In order to be automatically scanned when leaving the warehouse, the sorting and stacking needs to be stacked in two rows; as for the number of layers, the number of layers is standardized according to the type of goods. If the scanned location and cargo label are inconsistent with the instructions, an alarm will prompt, and another location or cargo will be selected for sorting until it is consistent with the instructions.
4. Picking confirmation: If the picking of goods in a certain location is completed, the record will no longer appear in the picking instruction sheet; the picking instruction sheet will display the next picking location, pallet number, goods and quantity.
5. Outbound inspection:
The fixed scanning device at the door is temporarily used for outbound inspection.
1) Automatically complete the collection of outbound data through the read-write equipment and electronic tags installed at the door of the outbound warehouse, and the discrepancy prompt:
A. If the label of the goods that should not be shipped is detected during the shipment process, the alarm equipment installed at the door of each warehouse will give an alarm and deal with it accordingly;
B. If the number of tags scanned is inconsistent with the standardized data or the number of sorted tags for this kind of goods out of the warehouse, the alarm will be handled in the same way, and the re-reading method or the handheld scanning method or the manual confirmation method will be adopted for processing.
2) The quantity and variety of each order must be completely matched with the picking list. If there is a picking list that cannot be matched at the end, it will be indicated in red, which can be easily searched and prompted.
6. Outgoing confirmation: the outgoing variety, box number and quantity are consistent with the picking list, then the outgoing list will be automatically closed (manual closing is allowed).
[ad_2]



