Shanghai Ditong Industry-RFID Logistics Management and Distribution Center Design
[ad_1]
1 Problems existing in traditional logistics distribution centers
Consumers need high-level services and competitive prices, so it is necessary to set up distribution centers for centralized distribution, which can organize logistics activities more effectively and control logistics costs; centrally store materials and maintain reasonable inventory; improve service quality, Expand sales; prevent unreasonable transportation. In order to accomplish these goals, traditional distribution centers face the following problems:
(1) Inaccuracy of inventory statistics
Because some barcodes are unreadable or there are some human errors, inventory statistics are often not very accurate, which affects the distribution center to make the right decision.
(2) Irregular order filling
Many orders are not filled in correctly, so it is difficult to ensure that the distribution center can send the correct quantity of the required goods to the correct location every time.
(3) Loss of cargo
The loss of goods during transportation is always a problem that plagues the distribution center. Loss is caused by goods stored in the wrong location, goods are lost due to theft, and errors are caused by packaging or shipping. According to a survey in the United States, the loss of goods in the retail industry can reach 1.71% of sales.
(4) Counting goods
The traditional method is very inefficient when cleaning up the goods, and in order to know the inventory status of the goods in time, it needs to count at any time, which requires a lot of manpower and material resources.
(5) Labor cost
Labor cost has become a more serious problem. Statistics show that in the entire supply chain cost, labor cost has risen to about 30%.
2 Introduction to the logistics distribution center model
The establishment of the distribution center is mainly to complete the distribution operations in logistics. The distribution center is located at the logistics node and specializes in cargo distribution activities. The significance of the distribution center is to improve service levels and turnover, reduce costs and increase benefits. In order to achieve this goal, it is necessary to study the delivery time of the distribution center, whether there is out of stock, error rate, information on delayed-selling products, information on new products, and samples.
A modern logistics distribution center needs to be equipped with automated and labor-saving logistics equipment and technology, as well as a modern logistics management information system and modern management methods. The following will briefly introduce the application of RFID in the warehouse management of the distribution center with a specific example model.
Taking a distribution center of a certain computer accessories as a model, the application of RFID in the distribution center is studied. The distribution center deals in various computer accessories, such as CPUs, hard drives, memory, motherboards, monitors, etc. The customers of the distribution center are relatively stable and large-scale distributors. In the logistics operation process of the distribution center, the data collection technology adopts RFID technology.
The process of the distribution center is the basis for planning the distribution center. Different distribution centers have different characteristics and scales due to different distribution products and distribution requirements.
The main activities of the computer parts distribution center are divided into two parts: information flow and logistics. The level of information flow is divided into: the upper level is strategy information, the middle level is management information, and the lower level is logistics operation information. The middle-level business management information is mainly divided into three management information such as purchase, inventory, and sales; the lower-level logistics operation management is divided into warehouse management, warehouse (inventory) management and warehouse management.
Due to the characteristics of the customer base of the distribution center, the distribution center adopts the method of picking according to the order. After picking, there is no need to classify the goods according to the customer, and they can be loaded directly for delivery. The main operations and their relationships are shown in Figure 12.1.
620)this.style.width=620;” border=0>
3 RFID logistics management distribution center design
3.1 Process design of the entire supply chain
Because the chip on the RFID tag provides a unique identification of the physical object, the product can be tracked throughout the entire supply chain. Only by considering the logistics and RFID information flow throughout the entire supply chain, can we better reflect the role of RFID technology in the distribution center and even the various nodes of the entire supply chain, and reflect the true value of RFID. The management process of RFID distribution center is as follows:
1.Add RFID tags to products
The supplier adds a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag to each box of goods supplied. With this label, companies can identify, count and track goods in a fully automated and cost-effective manner.
2.Leave factory
When the goods leave the factory, the radio frequency waves emitted by the RFID reader on the lintel of the outgoing port are directed to the electronic tags, which activate these tags and supply their power at the same time. The tag is “awakened” to start data transmission or ID communication with the reader. The reader reads the tag information and records until all the information in the tag is read.
3.Internal Operations of Distribution Center
Inbound operations. Since there is an RFID reader in the unloading area, it can be directly checked into the warehouse without opening the package to check the contents. By checking with the corresponding purchase order, this batch of goods can be quickly stored on the shelf.
Outbound operations. Similar to warehousing. Since there is an RFID reader at the exit of the warehouse, it can be directly checked and accepted without opening the box to check the goods inside.
4.Retailer
The delivery van arrives at the retailer. Retailers are also equipped with terminal readers. When the goods are delivered, the retailer’s retail system will be automatically updated immediately, and each box of goods delivered will be recorded. In this way, the retailer can automatically confirm its inventory of this kind of goods, which is accurate and reliable, and there is no cost.
In addition, retailers’ retail shelves are equipped with integrated readers. When goods are purchased, the shelf can “recognize” the newly added goods. At this time, if a certain customer purchases a certain amount of the product, the shelf will send a replenishment message to the retailer’s automatic replenishment system.
RFID can also facilitate customer settlement. Customers don’t need to wait in line for a long time for payment, customers only need to push the selected items out. The reader-writer installed on the door can identify the goods in the shopping cart through the information of the goods, and the customer can leave by swiping the payment card or credit card.
From the perspective of the entire supply chain, commodities flow through the entire supply chain, and the most frequent operations are the outbound/inbound operations. The application of RFID in the process of in/out of the distribution center has very good promotion value.
3.2 Overall functional design
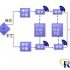
The overall functional modules of the system are shown in Figure 12.2, which are mainly divided into: system management, outbound/inbound management, order management, delivery planning, report management, query, abnormal logistics, data maintenance, and help.
620)this.style.width=620;” border=0>
3.3 Main process module design
1. Storage (as shown in Figure 12.3)
620)this.style.width=620;” border=0>
In terms of the tasks that need to be completed, the warehousing operation is not much different from the traditional warehousing operation, and it is mainly composed of two parts, the receiving inspection and the warehousing. However, in warehouse management that uses bar code and other identification technologies, when entering the warehouse, the goods are generally transported to the receiving area, the type and quantity of the products are manually inspected, and then the operators use the bar code scanner to scan the goods in turn. As a warehousing record.
In a distribution center using RFID technology, from receiving the goods to putting them on the shelves, it can be completed in one step. After the goods arrive at the distribution center, they are directly transported by a forklift. At the entrance, inspection, storage records, and cargo space allocation are completed in one go, which greatly reduces the workload in the warehouse and saves time.
2. Out of the library (as shown in Figure 12.4)
The outbound operation process is the same as the traditional operation procedure, which requires the completion of inspection and outbound operations. Similar to the warehousing operation, after RFID is applied, the check and the record of the warehousing are also completed in one step. When the reader reads the goods out of the library, the detailed information of the goods (such as number, name, quantity, etc.) is displayed on the interface, and the operator selects the corresponding customer order number to read the detailed information of the order from the system for verification. It can be shipped out without error.
620)this.style.width=620;” border=0>
3. Order processing flow (as shown in Figure 12.5)
Order processing is not only the beginning of the logistics operation of the distribution center, but also the starting point of the entire information flow operation. In the overall operation of the distribution center, order management usually plays an important role. In essence, the entire logistics process takes place in order to complete the order. Generally speaking, the client accepts the order data, processes and outputs it, and then warehouse personnel start a series of logistics operations such as picking, inspection, and delivery based on the processed order data. In order to increase the accuracy of the system and realize the tracking management of orders, the system sets the order status for the order. For each step of the order, the order status will change, and the system will give a certain degree of operability.
[ad_2]