Solution based on RFID warehousing logistics management system
[ad_1]
1. Project background
Logistics refers to the effective flow of raw materials, finished products, and related information from starting point to ending point. Modern logistics uses a brand-new management concept, through the planning, implementation and control of multiple elements in the entire logistics process, organically integrates transportation, warehousing, loading and unloading, processing, sorting, distribution, information and other links to form a complete supply chain. Users provide high-efficiency, multi-functional and integrated comprehensive services. It plays a very important role in accelerating economic circulation, reducing costs, optimizing resource allocation, promoting enterprise structure adjustment, improving enterprise economic strength and enhancing enterprise competitiveness. At present, logistics is generally called “the last frontier of cost reduction” in the world, ranking it as the “third source of profit” after reducing raw material consumption and increasing labor productivity. With the continuous acceleration of economic globalization and informatization, the logistics industry, as an emerging service industry with broad prospects and value-added functions, is developing rapidly on a global scale, setting off a “modern logistics revolution”.
my country has joined the WTO. To integrate the Chinese economy into the world economy, it must accelerate the creation of a macro environment for the development of modern logistics. To participate in domestic and foreign market competition, Chinese enterprises must accelerate the adoption of advanced logistics management concepts, technologies and organizational methods, and continuously improve their core competitiveness.
Although the concept of modern logistics has been introduced into our country for several years, due to the influence of the long-term planned economic system and the restriction of the level of economic development, our understanding and practice of modern logistics still lag far behind that of developed countries. In recent years, with the continuous development of the national economy, modern logistics has been highly valued by governments and enterprises at all levels in our country. Some enterprises with higher management level regard modern logistics as a new profit growth point for enterprise development, improve internal organizational structure, optimize enterprise logistics resources, and transform and upgrade logistics systems.
2. Program objectives
Traditional warehouse management generally relies on a non-automated paper document-based system to record and track incoming and outgoing goods. The internal management of the warehouse is completely implemented manually. Therefore, the efficiency of warehouse management is extremely low, and the warehouse that can be managed The scale is also very small. With the popularization of computer applications, most of the enterprise warehouse management data materials have begun to use computer data systems for management, but the data is still collected and statistically organized by first recording on paper and then manually inputting it into the computer. This not only causes a lot of waste of human resources, but also due to human factors, the data entry speed is slow and the accuracy rate is low.
With the continuous development of the scale of the enterprise, the number of types of materials managed by the warehouse is increasing, the frequency of in and out of the warehouse has increased sharply, and the warehouse management operations have become very complex and diversified. The traditional manual warehouse operation mode and data collection method have been difficult to meet the warehouse management. The rapid and accurate requirements of the company have seriously affected the efficiency of the operation of the enterprise and become a major obstacle to the development of the enterprise.
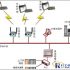
The warehouse management system based on Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) introduces RFID technology into existing warehouse management, and performs various operations such as warehouse arrival inspection, warehousing, outgoing, allocation, shifting, and inventory counting. Automated data collection is carried out on the data of each link to ensure the speed and accuracy of data input in each link of the warehouse management, to ensure that the enterprise grasps the real data of the inventory in a timely and accurate manner, and reasonably maintains and controls the enterprise inventory. Through scientific coding, it is also convenient to manage the batch and shelf life of items. Using the system’s location management function, you can also grasp the current location of all inventory materials in a timely manner, which is conducive to improving the efficiency of warehouse management.
After adopting RFID technology, it will bring the following benefits to enterprises:
(1) Save the cost of manual data collection;
(2) Automated warehouse management operations to improve work efficiency;
(3) Reduce management costs and human errors
(4) More precise control of import, sale and inventory;
(5) Enhancing partnerships;
(6) Quickly respond to customer needs and expand product sales.
Three, system architecture
a. System design principles
This program strictly follows the technical specifications involved in the project. Maximize the use of the most advanced technology of existing computers. Follow the principles of real-time, integrity, stability, advancement and scalability, and establish an economically reasonable and resource-optimized system design plan.
(1) Real-time: This system adopts the most advanced high-speed wireless network technology to make all the planning, operation, scheduling, control and management of the warehouse real-time, greatly improving the efficiency of existing equipment and personnel in the warehouse, and realizing logistics management The greatest benefit.
(2) Integrity: This system involves wireless handheld devices, wireless receiving devices, database front-end and back-end database servers. Although they are physically separated from each other, they all have their own system support. In order to enable the various parts to work in a unified and coordinated manner, the overall consistency between them must be ensured in the design.
(3) Stability: This system is a production information system for warehouse management and field operations. For this reason, when designing the system, an error analysis module is added to verify all possible errors. In addition, the efficiency and stability of the system are optimized in the design, so that the system can ensure the stability while ensuring the speed. Through the above measures, when the system is in operation, when there are human errors or some random errors in the system, it does not affect its operation.
(4) Advancement: This system is an intelligent system integrating computer software and hardware technology, wireless network technology, internet network technology, bar code automatic identification technology and database technology. The electronic commerce subsystem of the system adopts the most popular computer three-tier structure system in the industry, adopts Java language, and provides XML interface.
(5) Scalability and maintainability: According to the principles of software engineering, system maintenance occupies the largest proportion in the entire software life cycle. Therefore, improving the scalability and maintainability of the system is an indispensable means to improve the performance of this system. This system adopts a structured and modular structure, and a certain module can be modified and new functions can be added as needed to make it have good maintainability. The system also reserves interfaces with other subsystems, which makes the system have better scalability.
b. Main functions of the system
① Update various information automatically and accurately;
When the goods are in and out of the warehouse and need to be updated, you only need to fix the corresponding data through the handheld PDA to complete the update of the warehouse; or through the query database, find the corresponding model of the goods and update the data.
②Query and track cargo information;
Log in to the system software terminal, search for the specific information of the goods to be queried, and transfer the searched information to the PDA, so that the identification plate can be easily found and the goods can be tracked;
③Cargo position query, dynamic allocation of goods position, random storage, so as to maximize the use of storage space;
Log in to the system software terminal, query the cargo location information, and realize the dynamic allocation of goods according to the cargo location storage space information, so as to maximize the use of storage space
④Realize the dynamic and comprehensive allocation of human and material resources;
In the warehouse management process, not only the support of the system terminal database is required, but also the manual operation with a PDA is required to realize the dynamic and comprehensive allocation of human and material resources.
⑤Comprehensive inventory function of warehouse system;
When the warehouse system inventory is carried out, the passive tags on the identification plates can be read through the handheld PDA, the statistics of the goods, and the data are returned to the system terminal for processing and inventory
⑥ Random inspection and inventory within the warehouse;
Log in to the system terminal, then search for a certain type of goods, obtain relevant information about the goods, and transfer the data to the handheld PDA. The staff can find the corresponding cargo location according to the transmitted data, and complete the random inspection and inventory work within the warehouse;
⑦Real-time statistical reports, summarizing all kinds of information.
The warehouse identification plate is read through the handheld PDA, the information is obtained, and the information is transmitted to the system terminal, which can realize the system summary of the warehouse and make statistical reports.
C. System design ideas
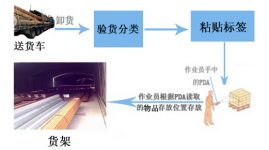
When the items are put into the warehouse, they are classified according to the specifications, put into the corresponding storage area, and an identification plate is installed for each storage area, and each identification plate is affixed with an electronic label, which is called an identification label . And give each identification plate number, the label stores the id number that can uniquely identify the shelf, and the staff can hold the PDA to read the id number on the label, and then call the back-end system database to obtain the stored information. The information includes: items Type, name, model, unit, unit price, production date, shelf life, performance, etc.;
When goods need to be moved to the warehouse, log in to the system software terminal, and the system sends the warehouse instruction to the PDA. The warehouse staff finds the designated goods location, takes out the designated quantity of goods from the warehouse, and transports the goods to the destination warehouse, and the goods are sent in Warehouse location, modify the shelf label content; send back to the on-site system the operation information of the warehouse.
The PDA in the operator’s hand scans the inventory identification board, and sends the scanned data to the terminal computer in real time, and the monitoring personnel perform inventory statistics and make statistical reports.
When performing warehouse management operations, read the tag number to determine whether the current job location is correct. In addition, as long as the id number of a certain shelf is entered, the relevant information of the id can be retrieved from the online database, so as to realize the material storage function and realize the online browsing and query.
d. System composition
The warehouse management information system consists of three parts:
(1) Warehouse management center subsystem: Responsible for the centralized management and maintenance of the warehouse management database, responsible for the formulation of purchase plans, outbound plans and ordering; printing and generating various management reports.
(2) Warehouse management on-site subsystem: issue warehousing tags, perform real-time inventory management (location management), and issue warehouse management instructions through the wireless network.
(3) Warehouse management execution subsystem: complete specific operations such as storage, storage, transfer, and inventory, and return to the actual status of execution.
Fourth, the program operation process
1 Production and installation of location labels
Unless the location is adjusted or the label is damaged, generally the location label only needs to be made and installed once.
2 Warehousing operation process

3 Outbound operation process

4 Work process of moving the library

5 Disk library operation process

6 Data transmission method
No matter what kind of operations such as storage in, out of storage, inventory, transfer, etc., warehouse administrators need to transfer data between the handheld PDA and the system database backend. The transmission method is as follows:

Read the electronic tag data through a handheld PDA. After receiving the signal, the PDA sends the data to the data receiver through GPRS. The receiver is connected to the system terminal through the 485/232 interface, and the received signal is transmitted to the database to complete the corresponding update operation of the data .
Five, hardware equipment selection
Fuen M8E Handheld Terminal
Self-adhesive electronic label
[ad_2]