Jiangsu Dongji RFID logistics innovative solutions
[ad_1]
In today’s global market, competition is fierce. More and more companies use “make-to-order production”, “zero inventory management”, “multiple batches and less batches” to coordinate all links of the supply chain by integrating the supply chain of products. Ensure efficient, timely and minimal cost delivery of products to end users. In this process, the difficulty of logistics management also increases, inventory information is inaccurate, shipment error rate remains high, transportation and distribution are unreasonable, and no-load Many problems, such as high rates, plague enterprises. Therefore, it has become an urgent task to establish a logistics information system that can interact with customers, provide real-time query, browse, online cargo tracking of service information, realize distribution route planning, logistics resource scheduling, cargo inspection and other services. With the help of the logistics information system, it can not only reduce the cost of some enterprises, improve the efficiency of communication between enterprises and customers, but also increase the reaction speed of both parties’ transactions, so that customers can truly experience the value-added experience brought by value-added services.
There are many links in the logistics application process. In this case study, the two major links, warehouse management and distribution management, which are frequently used by RFID handheld terminals, are explained. The application methods and business processes are described in detail below.
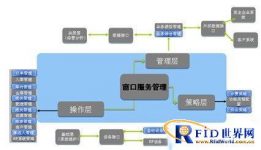
The overall framework of the system:

One warehouse management
Warehouse management is the core part of the enterprise information logistics system. In warehouse management, accurate and precise inventory of inbound and outbound data must be achieved. Jiangsu Dongji’s innovative logistics solutions can quickly and efficiently achieve precise and scientific management of warehouses. .
1.1 Block diagram of the deployment and implementation of the warehouse management system
The overall warehouse management system includes three major links: inbound management, inventory management, and outbound management. The overall structure is as follows:

1.2 Process of warehousing management system
Warehousing management specifically includes important links such as warehousing notification, quantity counting, confirmation of receipt, and handling of shelves. The handling of abnormal situations includes warehousing rejection, cross-docking and other links.

1.3 Outbound management system process
Picking out of the warehouse is a highly procedural operation, and it is one of the most important operational links in warehousing logistics operations. It has a very close relationship with other systems (distribution system, kanban distribution instruction system, etc.). Based on various outbound information (allocation, sorting, etc.), this system uses radio frequency technology to scan barcodes to confirm the accuracy of various outbound operations (manufacturer, product name, quantity, etc.). Important links in outbound management include acceptance Order, confirm picking wave, start picking, check out warehouse, etc.

1.4 Asset inventory
The system supports a variety of inventory methods: dynamic inventory, regular inventory and irregular sampling inventory, etc. According to the scope of inventory, the system can provide multiple functions such as full inventory, warehouse area inventory, cargo category inventory, and single product inventory. After entering the actual quantity, the system can automatically calculate the inventory difference. After the inventory difference is confirmed, it can be connected with the two functions of “Inventory Adjustment” and “Scrap” to complete the inventory result processing. If there is a inventory difference, the system supports re-inventory. . The designed system supports the working mode of using the RF data terminal for inventory.
The operation of the warehouse inventory system is shown in the figure below:

Two distribution management
The general distribution process includes three major steps: stock preparation, tally, and delivery. Here we focus on the application of handheld terminals in the delivery process.
Delivery operation is the end operation of the distribution center, and it is also an important link in the entire distribution process, including product loading and actual delivery. To complete these operations, you need to plan the division of the distribution area or the distribution line arrangement in advance, and the order of the distribution line selection To determine the order of product loading, and carry out product tracking, control and handling of unexpected situations during the delivery of the product.
The following is the overall distribution map.

2.1 Tracking on the way
The handheld terminal is combined with the GPS system, and the intelligent dispatching system can automatically update the transportation status with the information returned by the GPS, so as to realize the tracking and monitoring of the whole transportation task. The logistics monitoring subsystem is a combined application of GPS/GIS and electronic seals, which can monitor the real-time route, driving conditions, parking and opening times and places of the delivery vehicles.
The role, input and output of three handheld terminals
3.1 What problems are solved
1. Process informatization, real-time tracking of goods, improvement of data lag, and improvement of customer satisfaction, forming a fast and efficient logistics link;
2. Automatic collection, strong data reliability, reducing the error rate and also reducing the consumption of expensive paper operations;
3. Realize scientific storage and retrieval, precise inventory management, and improve the competitiveness of the enterprise;
4. Whether it is mail management or transportation operations, it saves a lot of operating time and improves work efficiency.;
5. Simple cargo plan, route arrangement and dispatch to avoid costly misloading;
6. Accurately monitor the conditions of drivers and vehicles and transmit dynamic routing decisions, which will help reduce transportation costs and some illegal behaviors.
[ad_2]



